Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleCreative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported Licence
Molecular dynamics simulation for the impact of an electrostatic field and impurity Mg2+ ions on hard water
Lin Zhu a,
Yong Han
a,
Yong Han *a,
Chuanxin Zhanga,
Ruikuan Zhaoa and
Shoufeng Tangb
*a,
Chuanxin Zhanga,
Ruikuan Zhaoa and
Shoufeng Tangb
aMeasurement Technology and Instrumentation Key Laboratory of Hebei Province, School of Electrical Engineering, Yanshan University, Qinhuangdao 066004, P. R. China. E-mail: hanyong@ysu.edu.cn
bSchool of Environmental and Chemical Engineering, Yanshan University, Qinhuangdao 066004, P. R. China
First published on 10th October 2017
Abstract
A detailed analysis of the structural parameters and dynamic parameters of hard water solutions under an external electrostatic field was performed by molecular dynamics (MD) simulations with the presence of impurity Mg2+ ions. The CaCl2 aqueous solution was chosen in the study as hard water because calcium carbonate is the main component of water scale. The effects on the CaCl2 aqueous solution caused by adding different numbers of Mg2+ ions and using an electrostatic field are examined in terms of the self-diffusion coefficient of Ca2+ ions and water molecules, the residence time of water molecules in the first water shell of Ca2+ ions, solution viscosity, characteristics of hydrogen bonds and some structural parameters, and how these effects influence the formation process of calcium carbonate when there are CO32− ions. The goal behind the study is to attain additional insights into the influence on the scale-inhibiting performance with the presence of impurity Mg2+ ions when electrostatic anti-fouling technology is used practically in hard water.
1 Introduction
The scale issue is a key problem in heat exchangers, such as cooling towers and boilers. Scaling causes at least two problems: degradation in the performance of heat exchangers and a decrease of flow rate or an increase in pressure drop across the heat exchanger. To solve the scale problem, electrostatic anti-fouling (EAF) systems are used. Many researchers have studied the anti-fouling mechanism of the EAF system. Calcium carbonate is the main component of water scale. Therefore, the vast majority of researchers who investigate the anti-fouling mechanism of EAF systems focus on the effect of electromagnetic fields on calcium carbonate. It mainly includes two aspects: the formation process of calcium carbonate crystallization and the change in the crystal structure of scale under an electromagnetic field. Qi et al.1 investigated the effect of an electric field (EF) on the crystallization of calcium carbonate. Their results showed that the lattice structure and crystalline morphology of CaCO3 can be tailored by the electric field applied to the solution during its crystallization. Liu et al.2 found that the content of aragonite increased in the scale sample formed in electrostatic water.However, although the composition of scale is mainly calcium carbonate, there is a small amount of precipitation formed by Mg2+ ions, such as magnesium carbonate and magnesium hydroxide, which are produced by Mg2+ and exist in natural water at high temperatures. Therefore some researchers have studied the effect of Mg2+ ions on the crystal structure of calcium carbonate. Mitsutaka Kitamura3 studied the crystallization and transformation mechanisms of calcium carbonate polymorphs under the effect of Mg2+. The experimental results showed that Mg2+ ions can inhibit the growth of calcite and suppress vaterite transformation to calcite. Gutjahr et al.4 studied the influence of the divalent cation Mg2+ on the growth and dissolution rates of calcite and aragonite. The results showed that ions of the transition metals exhibit stronger inhibition than earth alkaline ions, and Mg2+ has no influence on the growth and dissolution of aragonite. DeLeeuw5 found that the presence of magnesium and iron ions inhibits calcite growth using molecular dynamics simulations. However, the influence on the microcosmic particle structure in aqueous solutions containing impurity ions under an electrostatic field has received less attention.
There are almost no CO32− ions in hard water because of the very low solubility of calcium carbonate. But many HCO3− ions exist. Ca2+ ions exist in aqueous solution as hydrated ions. These hydrated ions are also combined with other water molecules by hydrogen bonding.6–8 The structural and dynamical properties of Ca2+ directly affect the formation, growth and crystal structure of calcium carbonate precipitation. Therefore, research to determine the influence of an electrostatic field and Mg2+ ions on the structure and dynamics of hydrated Ca2+ may help discern the anti-fouling mechanism of EAF technology.9–17 In the present study, a mixed solution of calcium chloride and magnesium chloride was chosen. The structure and dynamics performance of the CaCl2 aqueous solution (the viscosity of the CaCl2 aqueous solution, the location of the first water shell of Ca2+, the structure of the hydrated Ca2+ and the self-diffusion coefficient of Ca2+ and water molecules, and the hydrogen bonding in solution) under an external electrostatic field with different numbers of Mg2+ ions added were studied using MD simulations.
2 Model and simulation details
The MD simulation used in the present study was an equilibrium MD simulation process. All MD simulations in this work were performed using the Gromacs 5.0.2 software.18 The length of the simulation box is 4 nm × 4 nm × 3 nm. To study the effect of Mg2+ on the CaCl2 aqueous solution system under the electrostatic field, four sets of aqueous solution systems were built as shown in Table 1. The concentration of the CaCl2 aqueous solution was 4 mol kg−1, and the concentration uncertainties between simulations and experiments were below 0.5%.12 The SPCE model was adopted for water molecules in our work. The GROMOS force field19–21 was used in this simulation for ion–water interactions. For Lennard-Jones interactions, a cut-off was applied at 0.7 nm, while electrostatic interactions were treated with the particle mesh Ewald (PME)20 method and a real space cut-off of 0.7 nm. The value of Fourier spacing is 0.12 nm. Table 2 presents the Lennard-Jones potential parameters for particles used in the GROMOS force field. The time step used for all the simulations was 2.0 fs. The simulation time was 2.5 × 104 ps. Averages of parameters (except the data of the self-diffusion coefficient) were obtained from the last 1.5 × 104 ps of every simulation and the averages of parameters were obtained by calculating the average value of 1.5 × 104 ps, which was divided into ten segments. The type of integration algorithm for the equations of motion is the Leap frog algorithm. The temperature was set at 300 K. The pressure was set at 1.01 × 105 Pa. All simulations were carried out in NPT ensembles.| Sample | [H2O] | [Mg2+] | [Ca2+] | [Cl−] | [Total] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a Note: “0M” means no Mg2+ ions are added, “1M” means 10 Mg2+ ions are added, “2M” means 20 Mg2+ ions are added and “3M” means 30 Mg2+ ions are added. | |||||
| 0M | 1110 | 0 | 80 | 160 | 1350 |
| 1M | 1110 | 10 | 80 | 180 | 1380 |
| 2M | 1110 | 20 | 80 | 200 | 1410 |
| 3M | 1110 | 30 | 80 | 220 | 1440 |
| ε/(kJ mol−1) | σ/nm | |
|---|---|---|
| Ca2+ | 0.5069 | 0.2813 |
| Mg2+ | 0.3126 | 0.1933 |
| Cl− | 1.2889 | 0.3470 |
| O | 1.7250 | 0.2626 |
The study consists of two parts. In the first part, a different number of Mg2+ ions was added to the CaCl2 aqueous solution compared to the condition of no Mg2+ ions added. In the second part, an external electrostatic field was added compared to the condition of no electrostatic field. The electrostatic field had an intensity of 1 V μm−1. The electrostatic field was applied along a given direction (corresponding to the y-axis). The correctness of our MD simulations and error analysis has been verified in previous work.22
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Self-diffusion coefficients of Ca2+ ions and water molecules
In this section the self-diffusion coefficients of Ca2+ and water molecules were studied when there is an external electrostatic field and a small number of Mg2+ ions in the CaCl2 aqueous solution system. The self-diffusion coefficient of ions is an important parameter which can influence the chemical reaction process in aqueous solution systems. In addition, the self-diffusion coefficient can vary significantly when the structure of the cation or anion changes or when some other kind of ion gets involved.23In this paper, the self-diffusion coefficients of Ca2+ (DCa) and water molecules (Do) are calculated based on the “Einstein relation”:24
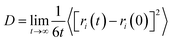 | (1) |
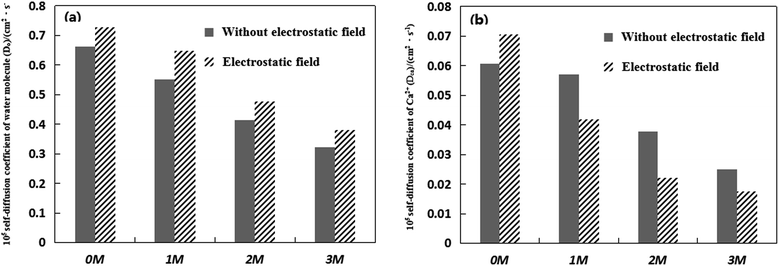
Fig. 1 shows the effect of Mg2+ on the self-diffusion coefficients of Ca2+ and water molecules under an electrostatic field and with no electrostatic field. The standard deviations of the simulation data presented in Fig. 1 are conservatively estimated to be in the range of 0.0046% × 10−5–0.0078% × 10−5 cm2 s−1 for self-diffusion coefficients. According to Fig. 1, the diffusion coefficients of Ca2+ and water molecules both decrease with the addition of Mg2+ whether there is an electrostatic field or not. Moreover, the more Mg2+ ions added, the lower the self-diffusion coefficients of Ca2+ and water molecules are. Under no electrostatic field, when ten Mg2+ ions are added, Do and DCa have maximum values of 0.5505 × 10−5 cm2 s−1 and 0.0570 × 10−5 cm2 s−1, respectively. When thirty Mg2+ ions are added, Do and DCa have a minimum value of 0.3223 × 10−5 cm2 s−1 and 0.0250 × 10−5 cm2 s−1, respectively. In addition, Fig. 1(a) shows that the external electrostatic field can make the self-diffusion coefficient of water molecules larger no matter how many Mg2+ ions are added to the CaCl2 aqueous solution in all simulations. According to Fig. 1(b), the external electrostatic field can make the self-diffusion coefficient of Ca2+ larger without Mg2+ addition, which is consistent with the results of our previous study.26 However, the electrostatic field can make the self-diffusion coefficient of Ca2+ smaller when Mg2+ ions are added to the CaCl2 aqueous solutions, which means that the combination of impurity Mg2+ and of an external electrostatic field can limit the activity of Ca2+ more strongly.
In the aqueous solution system, the valence state and structural order of cations can influence the diffusivity of water molecules.27 Mg2+ ions lose two electrons and, hence, have a strong binding ability towards water molecules. The first water shell of Mg2+, which consists of six water molecules, has octahedral symmetry. The stability of the nearest shell surrounding the Mg2+ ions justifies the assumption that the ion and its first shell can be considered as a solute.28,29 To sum up, when Mg2+ ions are added to the CaCl2 solution, the strong ability of Mg2+ to bind water molecules makes the activity of water molecules more limited.30 The self-diffusion coefficient of water molecules decreases. And the more Mg2+ ions added, the more limited the activity of the water molecules is. The reduction of the self-diffusion coefficient of Ca2+ can be attributed to the presence of Mg2+. The electrostatic interaction between Mg2+ and water molecules makes the CaCl2 aqueous solution more compact, which limits the activity of Ca2+, and hence reduces the self-diffusion coefficient of Ca2+.
When the electrostatic field is applied to the pure water solution, the order of the water molecules and the strength of the hydrogen bonds are enhanced, which decrease the self-diffusion coefficient of the water molecules.31 It means that the electrostatic field strengthens the correlation ability of the water molecules and the hydrogen bond network in a pure water solution. However, the results in Fig. 1(a) show that the electrostatic field can make the self-diffusion coefficient of water molecules larger for the four representative CaCl2 aqueous solutions. Therefore, the increase of the diffusion coefficient of water molecules in the CaCl2 aqueous solution should be due to the activity of existing metal ions. The increase of the self-diffusion coefficient of water molecules illustrates that the electrostatic field increases the ionic motion and influences the relatively stable water molecules’ hydrogen bond network.
The electrostatic field can not only reduce the diffusion coefficient of Ca2+ but also increase the diffusion coefficient of water molecules in the CaCl2 aqueous solution when the Mg2+ ions are added. The less active the Ca2+ ions, the smaller the chance of the chemical reaction produced by the combination of Ca2+ and CO32− is. As the self-diffusion coefficients of Ca2+ ions decrease, less CaCO3 precipitate is generated in solution. Therefore, the application of an electrostatic field with the addition of Mg2+ ions is beneficial to scale inhibition, which is consistent with some researchers’ work, who have pointed out the inhibition effect of Mg2+ on calcium carbonate under an electrostatic field.5 Then the scale problem is alleviated.
3.2 Dynamical residence time
The residence time is another important parameter related to the dynamic structure of the solution.32 The residence time describes the stability of the water molecules, and is related to the strength of hydration.33 Dynamical residence time γres is defined as how long an atom or ion stays in a certain shell of another atom or ion.12 In the present paper the dynamical residence time of water molecules in the first hydration shell of Ca2+ was studied to investigate the translational dynamics of the water molecule. The dynamical residence time was calculated using eqn (2):34
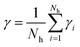 | (2) |
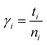 | (3) |
Table 3 shows the mean dynamical residence time of water around Ca2+ in four representative CaCl2 aqueous solutions under the electrostatic field. The values of γres under no electrostatic field have been presented for comparison. The standard deviation of γres is between 0.0086 ps and 0.0095 ps. According to Table 3, under the electrostatic field the mean dynamical residence time of water molecules around Ca2+ decreased. In addition, it can be found that the mean dynamical residence time of water around Ca2+ rises with the increase in the number of Mg2+ ions added in CaCl2 systems whether the electrostatic field is applied or not.
| Without an electrostatic field | Under an electrostatic field | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0M | 1M | 2M | 3M | 0M | 1M | 2M | 3M | |
| γres (ps) | 3.7123 | 3.7503 | 4.4396 | 5.9746 | 3.5893 | 3.6639 | 4.1182 | 5.2266 |
Naor et al.35 studied Ca2+ in liquid water using the Car–Parrinello molecular dynamics simulation finding that the γres is 10 ps. Schwenk et al.36 studied the dynamics of the solvation process of Ca2+ in water based on DFT/MM and QM/MM-HF simulations and the results showed that γres is 1.2 ps and 2 ps, respectively. According to Table 3, the values of γres are distributed in the range of 3 to 5 ps, which are similar to the results given in the literature. The increase in the mean dynamical residence time of water molecules around Ca2+ is because of the change in the diffusion coefficient of water molecules. When Mg2+ ions are added to the calcium chloride solution, the electrostatic interaction between Mg2+ and water molecules makes the diffusion coefficient of water molecules decrease, which causes the water molecules around Ca2+ to move in and out of the first shell less frequently.37 According to Table 3, the electrostatic field can make the mean dynamical residence time of water molecules around Ca2+ in the four representative CaCl2 aqueous solutions decrease. This is because the activity of water molecules is enhanced by the electrostatic field, which makes the water molecules around Ca2+ move in and out of the first shell much more frequently. Therefore the mean dynamical residence time of water around Ca2+ decreased.
3.3 Viscosity of the CaCl2 aqueous solution
The dynamic viscosity of a liquid is a kinetic property that influences the rates of conformational changes of solutes in the liquid. It can be influenced by an electrostatic field.38 The viscosity (η) can be calculated using the following equation:
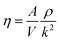 | (4) |
ax = A![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) cos(kz), k = 2π/lz cos(kz), k = 2π/lz
| (5) |
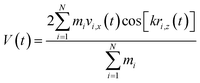 | (6) |
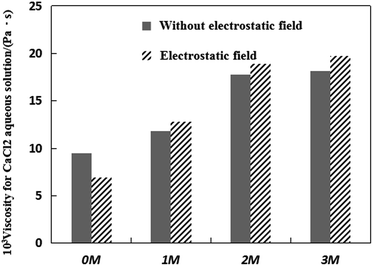
Fig. 2 shows the viscosity of four representative CaCl2 aqueous solutions under an electrostatic field. The values under no electrostatic field are presented for comparison. From Fig. 2, it can be found that the viscosity of the four representative CaCl2 aqueous solutions increases under the action of Mg2+, and there is a positive correlation between the viscosity value and the number of Mg2+ ions added in the CaCl2 systems. In addition, the electrostatic field can make the viscosity of CaCl2 aqueous solutions smaller without the addition of Mg2+ ions. But the electrostatic field can make the viscosity of CaCl2 aqueous solutions increase when a certain amount of Mg2+ ions is added to the CaCl2 aqueous solutions.
The dynamic viscosity can be described as a type of friction caused by the fluid’s motion inside the solution system. Its value is proportional to the number of carbon–hydrogen bonds and the particles’ molecular weight in the solution system. It should be realized that the viscosity is a macroscopic property that represents the average behaviour of a large number of water molecules in aqueous solution.32 Therefore, the change in dynamic viscosity can be attributed to the changes in the structural and dynamics parameters of water molecules. Bakker32 found that the large influence of some ions on the viscosity of water is due to the long lifetime of their first hydration shells using molecular dynamics simulations. The longer residence times of the water molecules in ion hydration shells strongly increases the viscosity. Since CaCl2 is an inorganic salt in an aqueous solution, there is no carbon–hydrogen bond in it. Therefore, the decrease in the viscosity of the CaCl2 solution should only be attributed to the changes in the structural change and dynamics parameters of water molecules. Combined with Fig. 2, the addition of Mg2+ forms a water shell which can result in a long residence time of water molecules in the Mg2+ hydration shells. Moreover, the addition of Mg2+ makes the mean dynamical residence time of water around Ca2+ increase as discussed earlier, which can also increase the viscosity of the CaCl2 aqueous solutions. This result can also match with the data in Fig. 1. The activity of water molecules is related to the viscosity of the solution. According to Fig. 1, the activity of water molecules is more limited when more Mg2+ ions are added, and this can make the viscosity of the solution increase. The results in Fig. 2, show that the electrostatic field can make the viscosity of CaCl2 aqueous solutions decrease without the addition of Mg2+ ions. The electrostatic field increases the activity of water molecules and decreases the mean dynamical residence time of water around Ca2+, which causes a decrease in the dynamic viscosity. In the case of the CaCl2 solution containing Mg2+, although the electrostatic field increases the activity of water molecules that can result in the viscosity decrease, the Mg2+ has a stronger binding ability with water molecules than Ca2+ due to the smaller effective radius37 and the longer lifetime of water molecules around Mg2+.32 This means that Mg2+ has a stronger ability to increase the viscosity of the solution than Ca2+. The electrostatic interaction between Mg2+ ions and water molecules can make the viscosity of the solution increase. This ability is stronger than the ability of the electrostatic field to decrease the viscosity of the solution, which causes an increase in the dynamic viscosity of the CaCl2 solution. To sum up, a certain amount of Mg2+ can increase the viscosity of the CaCl2 aqueous solution, and when the electrostatic field is applied to the CaCl2 solution containing Mg2+, the viscosity of the CaCl2 aqueous solution can also be increased.
3.4 Effects of Mg2+ ions and electrostatic fields on hydrogen bonds
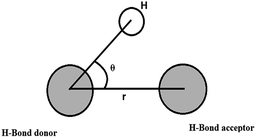
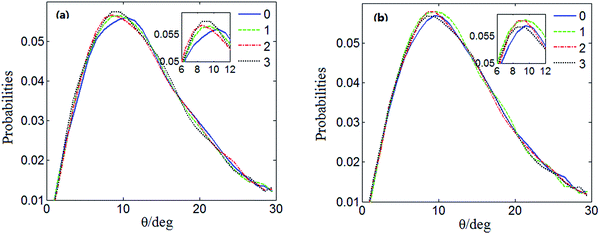
Fig. 4 shows the distribution of the hydrogen bond angle θ under the electrostatic field and the value under no electrostatic field is presented for comparison. Fig. 5 shows the distributions of the hydrogen bond angle θ under no electrostatic field and under the electrostatic field with different numbers of Mg2+ ions added, respectively. For clarification, the peaks are enlarged in the small figures. The distributions of the hydrogen bond angle θ shown in Fig. 4 and Fig. 5 are Poisson distributions, which are similar to those obtained from other simulations.42,43
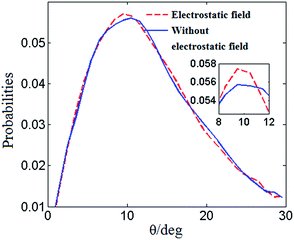 | ||
| Fig. 4 Distribution of the hydrogen bond angle θ without an electrostatic field (solid line) and with an electrostatic field (dashed line). | ||
It can be seen in Fig. 5(a) that under no electrostatic field the peak coordinates of the distribution of the hydrogen bond angle θ are (11.5, 0.0560083), (9.5, 0.0569745), (8.5, 0.0562455) and (9.5, 0.0588264) when 0 Mg2+ ions, ten Mg2+ ions, twenty Mg2+ ions, and thirty Mg2+ ions are added, respectively. According to Fig. 5(b), when 0 Mg2+ ions, ten Mg2+ ions, twenty Mg2+ ions, and thirty Mg2+ ions are added, respectively, under an electrostatic field, the peak coordinates of the distribution of the hydrogen bond angle θ are (9.5, 0.0585088), (8.5, 0.0585088), (8.5, 0.0592885) and (7.5, 0.0558013). It is shown in Fig. 5(a) and (b) that the positions of the statistical curve peaks all shift to smaller angles. The heights of the peaks all rise with the increase in the number of added Mg2+ ions and the application of an electrostatic field. Both the electrostatic field and Mg2+ ions can change the distribution of the hydrogen bond angle and make the average hydrogen bond angle smaller. It means that the Mg2+ and the electrostatic field can enhance the hydrogen bonding between water molecules to a certain extent.
In the present study the number of hydrogen bonds (nHB) and the percentage of water molecules with n hydrogen bonds (fn) are also investigated. The fn and nHB in CaCl2 aqueous solutions without Mg2+ ions added (0M), with ten Mg2+ ions added (1M), with twenty Mg2+ ions added (2M) and with thirty Mg2+ ions added (3M) are listed in Table 4. In addition, the influence of the electrostatic field is also presented.
| Without an electrostatic field | Under an electrostatic field | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0M | 1M | 2M | 3M | 0M | 1M | 2M | 3M | |
| f0 (%) | 58.09 | 60.85 | 62.41 | 64.49 | 57.99 | 60.12 | 62.10 | 64.00 |
| f1 (%) | 31.17 | 29.36 | 28.25 | 28.19 | 31.08 | 29.44 | 28.52 | 28.39 |
| f2 (%) | 8.230 | 7.520 | 7.140 | 6.260 | 8.340 | 7.560 | 7.170 | 6.570 |
| f3 (%) | 1.560 | 1.330 | 1.260 | 1.010 | 1.630 | 1.340 | 1.270 | 1.140 |
| nHB | 580.67 | 537.14 | 514.11 | 485.63 | 584.43 | 545.16 | 518.18 | 495.33 |
According to Table 4, the electrostatic field can decrease the fraction of molecules having no hydrogen bonds, while it can increase the fraction of molecules having one to three hydrogen bonds and the average number of hydrogen bonds per water molecule whether Mg2+ is added or not. The reduction of f0 and the increase of nHB, f1, f2, and f3 show that the activity of water molecules is restrained and more water molecules shift from a free state to a hydrogen-bonded state, which means that the hydrogen bonding of water molecules was enhanced by the electrostatic field. The results in Table 4 also show that the Mg2+ ions can increase f0 and decrease nHB, f1, f2, and f3 whether the electrostatic field is applied or not. Furthermore, f0 increases with the increase in the number of Mg2+ ions added, and nHB, f1, f2, and f3 decrease with the increase in the number of Mg2+ ions added to the CaCl2 systems.
The electrostatic field of ions can influence the hydrogen bond structure when water molecules are in the vicinity of cations that do not form any hydrogen bonds. The water molecules in the cation hydration shells are also held through ion–dipole interactions.44 When the cation is present, more non hydrogen-bonded water molecules stay in the ion hydration shell due to attractive ion–dipole interactions. The number of water molecules bound by hydrogen bonding decreases. Then a smaller number of hydrogen bonds are formed, the fraction of molecules having no hydrogen bonds increases, and the fraction of molecules having one to three hydrogen bonds and the average number of hydrogen bonds per water molecule decrease.
The lifetime of hydrogen bonds (τHB) can be calculated using eqn (7):21
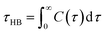 | (7) |
| C(τ) = 〈hi(t)hi(t + τ)〉 | (8) |
According to Table 5, the electrostatic field increases the average lifetime of the hydrogen bond whether Mg2+ is added or not. The increase of τ due to the hydrogen bonding of water molecules is enhanced by the electrostatic field as discussed earlier. In addition, the results in Table 5 show that the Mg2+ ions can increase the average lifetime of the hydrogen bond. The hydrogen bond formed in the cationic water shell is relatively strong.46 Therefore, the addition of Mg2+ can cause more water shells to form with water molecules which increases the average lifetime of the hydrogen bond.
| Without an electrostatic field | Under an electrostatic field | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0M | 1M | 2M | 3M | 0M | 1M | 2M | 3M | |
| τ (ps) | 52.06 | 53.18 | 54.27 | 55.99 | 52.21 | 53.23 | 54.54 | 56.37 |
3.5 Structure parameters
In this section, the average radii of the first water shell of Ca2+ ions (RCa–O), the first coordination numbers of Ca2+ (nCa–O) and the RDF (radial distribution function) of Ca2+ and water molecules are discussed under the addition of Mg2+ ions, the external electrostatic field and no electrostatic field, respectively. RCa–O can be obtained from the radial distribution function [g(r)]. The form of [g(r)]47 is shown in eqn (9):
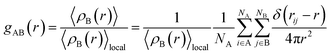 | (9) |
The value of nCa–O is calculated using eqn (10)19
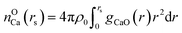 | (10) |
For nCa–O, rs is the location of the first local minimum of gCaO(r).
Table 6 presents the effect of Mg2+ ions on the average radii of the first water shell for Ca2+ and the first water coordination number of Ca2+. The standard deviation of RCa–O is between 0.0014 nm and 0.0016 nm, and the standard deviation of nCa–O is between 0.024 and 0.030. The results in Table 5 show that the electrostatic field can make the radii of the first water shell of Ca2+ smaller.
| Without an electrostatic field | Under an electrostatic field | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0M | 1M | 2M | 3M | 0M | 1M | 2M | 3M | |
| RCa–O (nm) | 0.282 | 0.282 | 0.280 | 0.282 | 0.278 | 0.280 | 0.276 | 0.280 |
| nCa–O | 5.62 | 5.30 | 5.07 | 5.00 | 5.70 | 5.41 | 5.22 | 4.90 |
According to Table 6, the addition of Mg2+ had no significant effect on RCa–O. Meanwhile, Table 5 shows that nCa–O decreases with the increase in the number of Mg2+ ions added. The hydration between Mg2+ ions and water molecules is stronger than the hydration between Ca2+ and water molecules, which means the existence of Mg2+ ions can make fewer water molecule stay in the water shell of Ca2+. The addition of Mg2+ ions has no obvious effect on RCa–O, but decreases nCa–O.
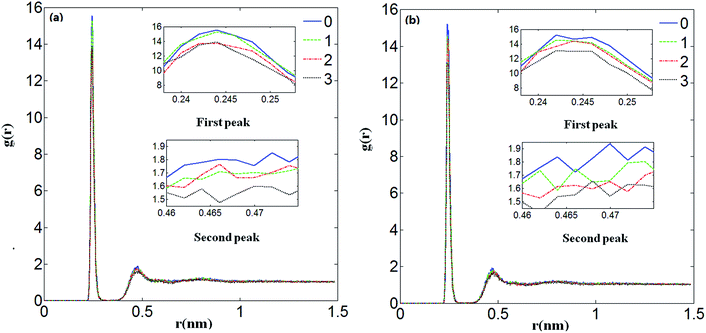
The RDFs of Ca2+ and water molecules with different numbers of Mg2+ ions added under no electrostatic field (a) and under the electrostatic field (b) are presented in Fig. 6. It shows the effects of Mg2+ ions on gCa–water(r). It can be seen that the first and second peaks decrease with the increase in the number of Mg2+ ions added, which means the addition of Mg2+ ions weakens the interaction between Ca2+ and water molecules. It matches the previous conclusion that Mg2+ weakens the interaction between Ca2+ and water molecules due to the Mg2+ ions binding more strongly than Ca2+ to water molecules.
According to Table 6, compared with the structure parameters under no electrostatic field, the values of RCa–O are smaller and the values of nCa–O are larger under the electrostatic field, which means that an electrostatic field can not only make the Ca2+ ions and water molecules gather more compactly but it can also increase the number of coordinated water molecules when no, ten or twenty Mg2+ ions are added in it. Therefore when there is an electrostatic field, the decrease of RCa–O and the increase of nCa–O all can be attributed to the enhanced hydration between Ca2+ ions and water molecules. The enhanced electrostatic interaction not only causes the hydrated water molecules to be closer to Ca2+ but also attracts more water molecules as coordinated water molecules. The increase of the first water coordination number of Ca2+ ions enhances their inhibition to carbonate ions, which shows that the electrostatic field decreases the formation probability of the calcium carbonate precipitate.
4 Conclusions
The influences of Mg2+ ions and the electrostatic field on CaCl2 aqueous solutions were studied. The effects of different numbers of Mg2+ ions were compared and the anti-fouling performance under the influence of an electrostatic field and under no electrostatic field was compared, and the structural changes and dynamic properties of CaCl2 aqueous solutions under the electrostatic field were researched by a systematic long-time, equilibrium molecular dynamics simulation. Some important conclusions were obtained.The electrostatic field decreases the mobility of the Ca2+ ions when Mg2+ ions are added. The impurity Mg2+ ions can effectively increase the viscosity of the CaCl2 aqueous solution and decrease the self-diffusion coefficient of particles by the electrostatic interaction between Mg2+ ions and water molecules. The more Mg2+ ions are added, the bigger the viscosity of the CaCl2 aqueous solution is, and the lower the diffusion coefficient of the particles is. Therefore, the presence of Mg2+ ions can decrease the rate of the chemical reaction between Ca2+ and CO32− ions by decreasing the activity of ions.
The addition of Mg2+ ions can make the average hydrogen bond angle smaller and increase the average lifetime of hydrogen bonds. The addition of Mg2+ ions can also increase the mean dynamical residence time of water around Ca2+ ions. The more Mg2+ ions are added, the bigger the average lifetime of hydrogen bonds is, and the bigger the mean dynamical residence time of water around Ca2+ ions is. The electrostatic field enhances the hydrogen bonding between water molecules which reflects in the decrease of the average hydrogen bond angles, the increase in the number of hydrogen bonds, and the average lifetime of hydrogen bonds.
Electrostatic fields can decrease the radii of the first water shell of hydrated Ca2+ ions. Under the action of an electrostatic field, regardless of whether or not Mg2+ ions exist, the ratio of free water molecules in the calcium chloride solution decreased and the binding force of the hydrated calcium ions to the surrounding water molecule is enhanced.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest to declare.Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51408525 and 51608468).References
- J. Q. Qi, R. Guo and Y. Wang, Nanoscale Res. Lett., 2016, 11, 120 CrossRef PubMed.
- L. I. Haihua, Z. F. Liu and Y. H. Gao, CIESC J., 2013, 64, 1736 Search PubMed.
- M. Kitamura, J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2001, 236, 318–327 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Gutjahr, H. Dabringhaus and R. Lacmann, J. Cryst. Growth, 1996, 158, 310–315 CrossRef CAS.
- N. H. DeLeeuw, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2002, 106, 5241–5249 CrossRef CAS.
- G. J. Zhao, J. Y. Liu and L. C. Zhou, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2007, 111, 8940–8945 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- G. J. Zhao and K. L. Han, Acc. Chem. Res., 2012, 45, 404 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. S. Chen, M. H. Yuan and J. P. Wang, J. Phys. Chem. A, 2014, 118, 8986 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. L. De and M. L. Chávez, Langmuir, 2005, 21, 10874–10884 CrossRef PubMed.
- Y. I. Cho and R. Liu, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer, 1999, 42, 3037–3046 CrossRef.
- X. Xiaokai, M. Chongfang and C. Yongchang, Chem. Eng. Technol., 2010, 28, 1540–1545 CrossRef.
- J. Wang, X. Feng and W. Du, Mol. Phys., 2008, 106, 2685–2697 CrossRef.
- X. K. Xing, C. F. Ma and Y. C. Chen, Chem. Eng. Technol., 2010, 28, 1540 Search PubMed.
- N. A. Hewish, G. W. Neilson and J. E. Enderby, Nature, 1982, 297, 138–139 CrossRef CAS.
- J. L. Fulton, Y. Chen and S. M. Heald, J. Phys. Chem. A, 2006, 125, 431 Search PubMed.
- G. Licheri, G. Piccaluga and G. Pinna, J. Phys. Chem., 1976, 64, 2437 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Zhang, C. Li and M. Benjamin, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2003, 37(8), 1663–1669 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Nedyalkova, S. Madurga and S. Pisov, J. Chem. Phys., 2012, 137, 1 CrossRef PubMed.
- A. A. Chialvo and J. M. Simonson, J. Chem. Phys., 2003, 119, 8052–8061 CrossRef CAS.
- R. E. IseleHolder, W. Mitchell and A. E. Ismail, J. Chem. Phys., 2012, 137, 1133 Search PubMed.
- W. F. V. Gunsteren, Biomolecular Simulation: the GROMOS96 Manual and User Guide, Zürich, Groningen, 1996 Search PubMed.
- Y. Han and Y. Zhao, Int. J. Electrochem. Sci., 2012, 7, 10008–10026 CAS.
- S. Tsuzuki, W. Shinoda and H. Saito, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2009, 113, 10641–10649 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. Henritzi, A. Bormuth and F. Klameth, J. Chem. Phys., 2015, 143, 164502 CrossRef PubMed.
- M. A. Fischler and R. C. Bolles, Commun. ACM, 1981, 24, 381 CrossRef.
- Y. Han, L. Zhu and Y. Zhang, Chem. Res. Chin. Univ., 2016, 32, 1–6 CrossRef.
- B. Guo, H. B. Han and F. Chai, Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China, 2011, 21, s494–s498 CrossRef.
- F. C. Lightstone, E. Schwegler and R. Q. Hood, Chem. Phys. Lett., 2001, 343, 549–555 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Rybicki and E. Hawlicka, Chem. Phys., 2012, 400, 79–85 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Dian, K. Christopher and G. Alan, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2006, 110, 18553 CrossRef PubMed.
- S. Wei, C. Zhong and H. SuYi, Mol. Simul., 2005, 31, 555–559 CrossRef CAS.
- H. J. Bakker, Chem. Rev., 2008, 108, 1456 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Zhu, L. Xiaohua and D. Hao, Mol. Simul., 2003, 29, 767–772 CrossRef CAS.
- M. J. Wei, L. Zhang and L. Lu, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2012, 14, 16536–16543 RSC.
- M. M. Naor, K. V. Nostrand and C. Dellago, Chem. Phys. Lett., 2003, 369, 159–164 CrossRef CAS.
- C. F. Schwenk, H. H. Loeffler and B. M. Rode, Chem. Phys. Lett., 2001, 349, 99–103 CrossRef CAS.
- D. Jiao, C. King and A. Grossfield, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2006, 110, 18553 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- B. Hess, J. Chem. Phys., 2002, 116, 209–217 CrossRef CAS.
- W. J. Lee, J. G. Chang and S. P. Ju, Langmuir, 2010, 26, 12640–12647 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Z. Pan, J. Chen and L. Gang, J. Chem. Phys., 2012, 136, 164313 CrossRef PubMed.
- X. Zhang, Q. Zhang and D. X. Zhao, Acta Phys.-Chim. Sin., 2011, 27, 2547 CAS.
- H. S. Lee and M. E. Tuckerman, J. Chem. Phys., 2006, 125, 154507 CrossRef PubMed.
- K. Modig, B. G. Pfrommer and B. Halle, Phys. Rev. Lett., 2003, 90, 075502 CrossRef PubMed.
- A. Karmakar, J. R. Choudhuri and V. K. Yadav, Chem. Phys., 2013, 412, 13–21 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Luzar and D. Chandler, Nature, 1996, 379, 55–57 CrossRef CAS.
- E. Guàrdia, J. Martí and L. García-Tarrés, J. Mol. Liq., 2005, 117, 63–67 CrossRef.
- D. M. York, T. A. Darden and L. G. Pedersen, J. Chem. Phys., 1993, 32, 1443–1453 CAS.
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 |