Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleNew N-phenylacetamide-incorporated 1,2,3-triazoles: [Et3NH][OAc]-mediated efficient synthesis and biological evaluation†
Satish V. Akolkar a,
Amol A. Nagargojea,
Vagolu S. Krishnab,
Dharmarajan Sriramb,
Jaiprakash N. Sangshetti
a,
Amol A. Nagargojea,
Vagolu S. Krishnab,
Dharmarajan Sriramb,
Jaiprakash N. Sangshetti c,
Manoj Damaled and
Bapurao B. Shingate*a
c,
Manoj Damaled and
Bapurao B. Shingate*a
aDepartment of Chemistry, Dr. Babasaheb Ambedkar Marathwada University, Aurangabad 431 004, India. E-mail: bapushingate@gmail.com; Fax: +91-240-2403113; Tel: +91-240-2403313
bDepartment of Pharmacy, Birla Institute of Technology & Science-Hyderabad Campus, Jawahar Nagar, Hyderabad 500 078, India
cDepartment of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, Y. B. Chavan College of Pharmacy, Dr. Rafiq Zakaria Campus, Aurangabad 431 001, India
dDepartment of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, Srinath College of Pharmacy, Aurangabad 431136, MS, India
First published on 18th July 2019
Abstract
A facile, highly efficient, and greener method for the synthesis of new 1,4-disubstituted-1,2,3-triazoles was conducted using [Et3NH][OAc] as a medium by the implementation of ultrasound irradiation via click chemistry, affording excellent yields. The present synthetic method exhibited numerous advantages such as mild reaction conditions, excellent product yields, minimal chemical waste, operational simplicity, shorter reaction time, and a wide range of substrate scope. The synthesized compounds were further evaluated for in vitro antifungal activity against five fungal strains, and some of the compounds displayed equivalent or greater potency than the standard drug. A molecular docking study against the modelled three-dimensional structure of cytochrome P450 lanosterol 14α-demethylase was also performed to understand the binding affinity and binding interactions of the enzyme. Furthermore, the synthesized compounds were evaluated for DPPH radical scavenging activity and antitubercular activity against Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv strain.
1. Introduction
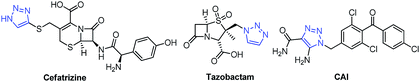
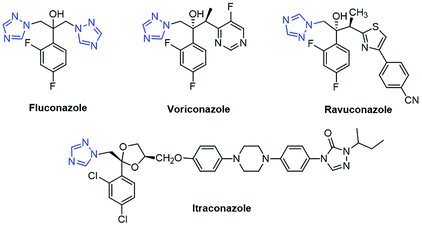
1,2,3-Triazole, a five-membered heterocyclic ring system, is a very well-known biologically active pharmacophore constructed by the copper-catalyzed azide–alkyne cycloaddition (CuAAC) reaction, which is popular as a click chemistry reaction.1 Over the last decade, 1,2,3-triazole has become one of the key structural motifs and is used in numerous fields including polymer chemistry,2 material science,3 and drug discovery.4 1,2,3-triazole-based molecules display various biological activities such as anti-fungal,5,6 anti-bacterial,6 anti-tubercular,7 anti-inflammatory,8 anti-allergic,9 anti-HIV,10 anti-cancer,11 and anti-phytopathogenic.12 Some marketed drugs have the 1,2,3-triazole unit in their structure, and these include Cefatrizine (a broad-spectrum antibiotic), Tazobactam (an antibiotic), and Carboxyamidotriazole (CAI) (a calcium channel blocker) (Fig. 1).Azole drugs have broad-spectrum activities against most yeasts and filamentous fungi and are mostly used in antifungal chemotherapy.13 Some well-known antifungal agents including fluconazole, voriconazole, ravuconazole, and itraconazole contain a 1,2,4-triazole ring in their structure, as shown in Fig. 2. However, their clinical uses have been restricted by their relatively high risk of toxicity, pharmacokinetic deficiencies, emergence of drug resistance, and undesirable side effects. These antifungal drugs inhibit CYP51, a key enzyme in the biosynthesis of ergosterol, through a mechanism in which the antifungal agent having a triazole scaffold is positioned perpendicular to the porphyrin plane with a ring nitrogen atom (N-4 of triazole) coordinated with a heme iron atom.14 Over a couple of decades, the incidence of systemic fungal infections has increased due to cancer chemotherapy, organ transplantation, tuberculosis, and immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection.15 However, the extensive use of antifungal drugs has led to an increase in the resistance to these drugs.16 Hence, there is an urgent need for developing new antifungal agents with effective activities, low toxicity, and minimum side effects.
Ionic liquids (ILs) are environment-friendly solvents because of their interesting properties and they can be used as alternatives to harmful organic solvents. Furthermore, they are useful in catalytic reactions17 and organic synthesis18 because of their unique properties, making them superior media for increasing selectivity, reactivity, and recyclability. Various ionic liquids have been significantly used in heterocyclic synthesis as solvents or catalysts.19 The copper-catalyzed 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition of organic azides and terminal alkynes has been reported by using ionic liquids such as [bmim][BF4],20a,b [Bmim]OH,20c (SNIL-Cu(II)),20d ([Hmim]TFA),20e and [C8dabco][N(CN)2],20f and DBU-based ionic liquids.20g The ionic liquid [Et3NH][OAc] has been used extensively in various organic transformations.21
Considering the importance of ionic liquids in organic synthesis and in continuation of our work7d,22 as well as for the development of new synthetic methodologies using ionic liquids,23 herein, we reported the efficient synthesis of new 1,4-disubstituted-1,2,3-triazoles via the click chemistry approach using [Et3NH][OAc] as the medium under ultrasonic irradiation. Furthermore, the newly synthesized compounds were investigated for their antifungal, antioxidant, and antitubercular activities.
2. Results and discussion
2.1 Chemistry
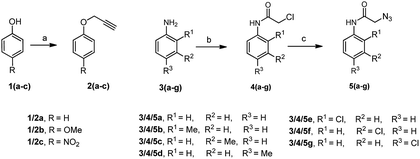
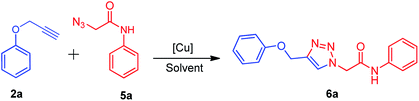
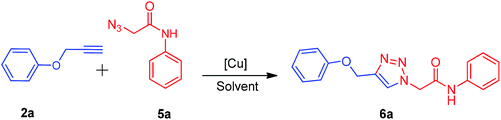
There are several reports on the synthesis of 1,4-disubstituted-1,2,3-triazoles bearing amide functionality and displaying various biological activities;24 recently, Ferroni et al. developed triazoles as non-steroidal anti-androgens for prostate cancer treatment.25 On the basis of these findings, we designed small 1,2,3-triazoles with amide linkage in their structures. Initially, the starting materials, i.e., (prop-2-yn-1-yloxy)benzenes 2a–c were prepared by a previously reported method.7d 2-Azido-N-phenylacetamides 5a–g were synthesized from their corresponding anilines via chloroacetylation using chloroacetyl chloride, followed by nucleophilic substitution with sodium azide in excellent yields (Scheme 1).After the synthesis of alkynes 2a–c and azides 5a–g, we considered the model substrates (prop-2-yn-1-yloxy)benzenes 2a (1.0 mmol) and 2-azido-N-phenylacetamide 5a (1.0 mmol) for the click reaction (Scheme 2).
The literature survey reveals the use of t-BuOH–H2O, THF–H2O, and DMF–H2O as solvents in combination with copper salts for the click reaction. Accordingly, we performed the model reactions of 2a and 5a by using CuSO4·5H2O, Cu(OAc)2·H2O, CuI, and CuCl with or without sodium ascorbate as a reducing agent in solvents such as t-BuOH and THF (Table 1). In our initial attempt, the model reaction was carried out by using the conventional method, i.e., the reaction mixture was stirred at room temperature for 10 h using various copper salts in t-BuOH or THF as a solvent (Table 1, entries 2–7). The product 2-(4-(phenoxymethyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-1-yl)-N-phenylacetamide 6a was obtained in 28–72% yield. Furthermore, the model reaction was carried out using copper salts and t-BuOH/THF as a solvent under ultrasound irradiation (40 kHz, 30 °C) for 7 h, which resulted in the product 6a in 32–83% yield (Table 1, entries 2–7). These results indicate a longer reaction time with a lower yield of the product 6a.
| Entry | Copper salt | Solvent/medium | Conventional method | US method | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Timea | Yieldb (%) | Timea | Yieldb (%) | |||
| a Reaction conditions: 2a (1 mmol), 5a (1 mmol), and 10 mol% [Cu], 1 mL solvent, 30 °C; reaction progress monitored by TLC.b Isolated yield, US: ultrasonication. | ||||||
| 1 | — | t-BuOH![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) H2O H2O |
10 h | 0 | 6 h | 0 |
| 2 | CuSO4·5H2O | t-BuOH![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) H2O H2O |
10 h | 28 | 6 h | 32 |
| 3 | CuSO4·5H2O + Na ascorbate | t-BuOH![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) H2O H2O |
10 h | 70 | 6 h | 78 |
| 4 | Cu(OAc)2·H2O | t-BuOH![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) H2O H2O |
10 h | 72 | 6 h | 82 |
| 5 | Cu(OAc)2·H2O + Na ascorbate | t-BuOH![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) : :![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) H2O H2O |
10 h | 72 | 6 h | 83 |
| 6 | CuI | THF | 10 h | 70 | 6 h | 80 |
| 7 | CuCl | THF | 10 h | 60 | 6 h | 65 |
| 8 | — | [Et3NH][OAc] | 10 h | 0 | 6 h | 0 |
| 9 | Cu(OAc)2·H2O | [Et3NH][OAc] | 7 h | 90 | 35 min | 95 |
| 10 | Cu(OAc)2·H2O + Na ascorbate | [Et3NH][OAc] | 7 h | 90 | 35 min | 95 |
| 11 | CuSO4·5H2O + Na ascorbate | [Et3NH][OAc] | 7 h | 81 | 35 min | 84 |
| 12 | Cu(OAc)2·H2O | [Et3NH][Cl] | 7 h | Trace | 35 min | 10 |
| 13 | Cu(OAc)2·H2O | [Et3NH][HSO4] | 7 h | Trace | 35 min | 12 |
| 14 | Cu(OAc)2·H2O | [HDBU][OAc] | 7 h | 84 | 45 min | 88 |
| 15 | CuSO4·5H2O + Na ascorbate | [HDBU][OAc] | 7 h | 81 | 45 min | 84 |
| 16 | Cu(OAc)2·H2O | [HDBU][HSO4] | 7 h | 10 | 45 min | 14 |
Ionic liquids have unique properties as solvents and as media; herein, we attempted to use various ionic liquids for the synthesis of new amide-linked 1,4-disubstituted-1,2,3-triazole 6a via the click chemistry approach. Freshly synthesized appropriate ionic liquids such as [Et3NH][OAc], [Et3NH][Cl], [Et3NH][HSO4], [HDBU][OAc], and [HDBU][HSO4] in combination with copper salts such as CuSO4·5H2O and Cu(OAc)2·H2O were used along with sodium ascorbate as a reducing agent to carry out the model reaction (Table 1, entries 9–16) at room temperature for 7 h. The maximum yield (90%) of the product 6a was obtained by using Cu(OAc)2·H2O as the catalyst and [Et3NH][OAc] as the solvent (Table 1, entries 9 and 10). In our further attempt, the model reaction was carried out under ultrasound irradiation for appropriate times (35 and 45 min) (Table 1, entries 9–16). The product 6a was obtained in 95% yield under ultrasound irradiation using Cu(OAc)2·H2O as the catalyst and [Et3NH][OAc] as the solvent (Table 1, entries 9 and 10). In short, it was observed from the optimization of the best reaction conditions that the Cu(OAc)2·H2O-catalyzed click reaction in [Et3NH][OAc] ionic liquid under ultrasound irradiation at 30 °C efficiently gives the desired 1,4-disubstituted-1,2,3-triazole derivative 6a as compared to the conventional method with respect to the reaction time and yield (Table 1, entry 9).
In order to evaluate the amount of the Cu(OAc)2·H2O catalyst for the model reaction for different concentrations such as 5, 10, 15, and 20 mol% (Table 2, entries 1–4), the reaction was carried out in the presence of 1 mL of [Et3NH][OAc] as a solvent at 30 °C under ultrasound irradiation. It was observed that 10 mol% of Cu(OAc)2·H2O was sufficient to achieve an excellent yield of the product 6a in the shortest reaction time (Table 2, entry 2), while an excess amount of the catalyst (up to 20 mol%) did not increase the yield of the product. The above results reveal that 10 mol% of Cu(OAc)2·H2O in [Et3NH][OAc] is the sufficient catalyst amount in terms of an excellent yield and short reaction time (Table 2, entry 2).
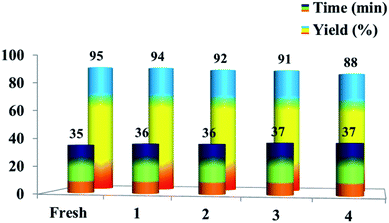
The recyclability of the [Et3NH][OAc] solvent was also explored for the model reaction. The reaction was conducted for four successive cycles on the same recycled solvent. After completion of the first reaction with 95% yield, the reaction mass was poured into ice cold water to get the solid product, which was isolated by filtration. The filtrate was subjected to evaporation of water to get a viscous liquid, which on cooling gave the ionic liquid. Then, the recovered [Et3NH][OAc] was reused for four more successive cycles without significant loss in the yield of the product 6a. The yields achieved were 94%, 92%, 91%, and 88% after the successful runs (Fig. 3). The result demonstrates the high stability of the ionic liquid [Et3NH][OAc] under the reaction conditions, which could be recycled and reused without a significant loss in the product yield.
In a further attempt, we also examined a one-pot reaction for the selected model reaction with 2a (1.0 mmol), 4a (1.0 mmol), and sodium azide (1.5 mmol) for the synthesis of 6a, which was optimized for different copper sources (Table 3) for the one-pot, three-component click reaction in [Et3NH][OAc] as the solvent, thus producing 2-(4-(phenoxymethyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-1-yl)-N-phenylacetamide 6a (Scheme 3). The optimization result of this one-pot model reaction revealed that 15 mol% of Cu(OAc)2·H2O in [Et3NH][OAc] as the solvent was a sufficient catalyst loading amount to obtain an excellent yield. However, it required a longer reaction time and higher concentration of the Cu catalyst (Table 3, entry 2) than the two-component reaction, as discussed earlier.
| Entry | Catalyst | mol% | Time (h) | Isolated yield (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Cu(OAc)2·H2O | 10 | 17 | 90 |
| 2 | Cu(OAc)2·H2O | 15 | 16 | 95 |
| 3 | Cu(OAc)2·H2O | 20 | 16 | 95 |
| 4 | CuSO4·5H2O + Na ascorbate | 10 | 18 | 81 |
| 5 | CuSO4·5H2O + Na ascorbate | 15 | 17 | 87 |
| 6 | CuI | 10 | 18 | 50 |
| 7 | CuI | 15 | 17 | 61 |
| 8 | CuCl | 10 | 17 | 40 |
| 9 | CuCl | 15 | 17 | 45 |
 | ||
| Scheme 3 Synthesis of 1,4-disubstituted-1,2,3-triazole 6a via the one-pot three-component click reaction. | ||
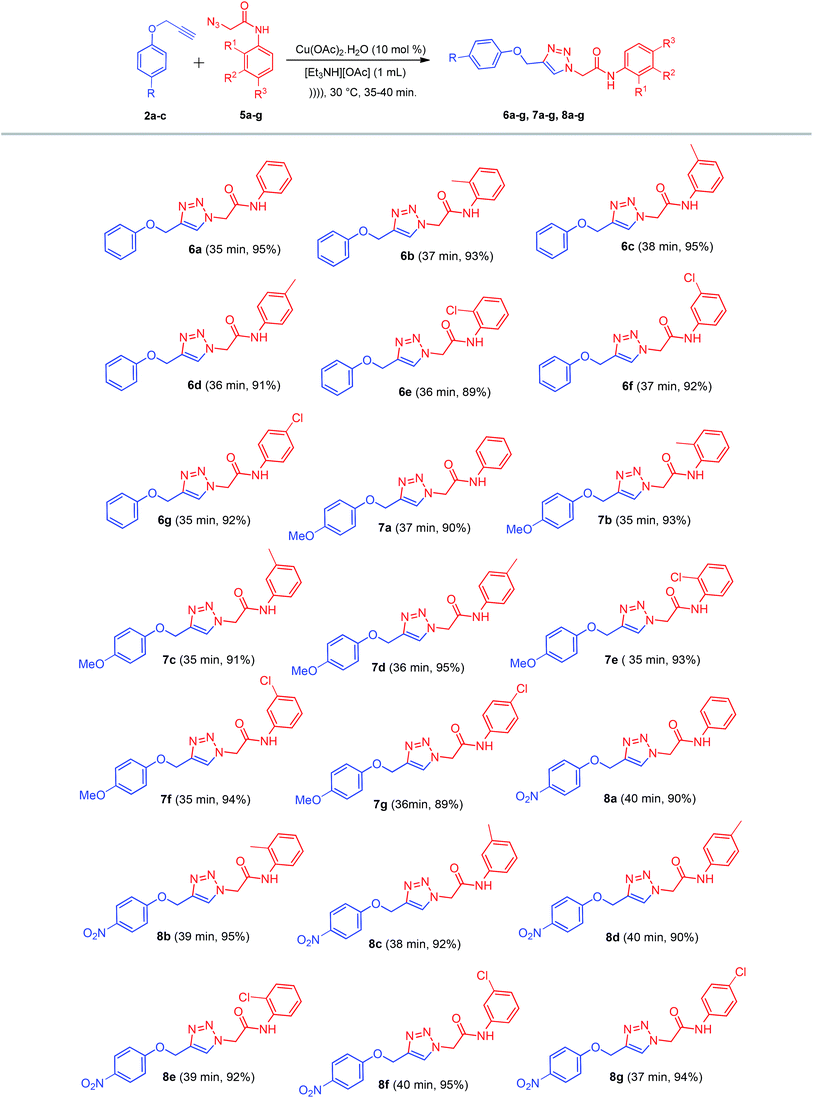
After optimization of the reaction parameters and to define the present methodology, as discussed earlier, the reaction was assessed with a variety of substituted alkynes 2a–c and azides 5a–g in the presence of Cu(OAc)2·H2O in [Et3NH][OAc] under ultrasound irradiation. The reaction conditions were favorable for the electron-donating and electron-withdrawing groups on alkynes 2a–c and azides 5a–g, resulting in the corresponding 1,4-disubstituted-1,2,3-triazole derivatives 6a–g, 7a–g, and 8a–g in excellent yields (Scheme 4).
All the synthesized compounds, namely, 6a–g, 7a–g, and 8a–g were confirmed by physical data and spectral analysis.
2.2 Biological activity
| Entry | Antifungal activity | Anti TB MTB H37Rv | DPPH IC50 (μg mL−1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CA | FO | AF | AN | CN | |||
| a CA: Candida albicans; FO: Fusarium oxysporum; AF: Aspergillus flavus; AN: Aspergillus niger and CN: Cryptococcus neoformans. MA: Miconazole, DPPH: 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl; INH: Isoniazid; RIF: Rifampicin; EMB: Ethambutol; CIP: Ciprofloxacin; BHT: butylated hydroxytoluene; *no activity was observed, NA: not applicable. | |||||||
| 6a | 87.5 | 100 | 175 | 125 | 187.5 | 25 | 55.37 |
| 6b | 150 | 125 | 150 | 150 | * | >25 | 26.64 |
| 6c | 175 | 200 | 150 | 175 | 200 | 25 | 20.54 |
| 6d | 187.5 | 162.5 | 187.5 | 200 | * | >25 | * |
| 6e | 200 | * | * | 187.5 | 175 | >25 | 29.64 |
| 6f | 150 | 175 | 162.5 | 200 | * | 25 | 74.28 |
| 6g | 162.5 | 175 | 175 | 187.5 | 150 | >25 | 74.41 |
| 7a | 137.5 | 125 | 100 | 137.5 | 125 | >25 | 11.44 |
| 7b | 175 | 200 | 100 | 175 | 200 | >25 | 16.79 |
| 7c | * | * | 200 | * | 175 | >25 | 12.30 |
| 7d | 200 | 175 | 150 | 150 | 200 | >25 | 19.46 |
| 7e | 175 | 175 | 200 | * | * | >25 | 70.33 |
| 7f | 100 | 150 | 100 | 100 | 75 | >25 | * |
| 7g | 75 | 100 | 87.5 | 100 | 200 | >25 | 49.60 |
| 8a | 25 | 37.5 | 25 | 75 | 75 | >25 | 97.29 |
| 8b | 12.5 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 37.5 | >25 | * |
| 8c | 12.5 | 25 | 25 | 50 | 25 | >25 | 48.02 |
| 8d | 25 | 25 | 37.5 | 25 | 50 | >25 | 22.17 |
| 8e | 50 | 25 | 12.5 | 25 | 12.5 | >25 | 62.01 |
| 8f | 12.5 | 12.5 | 25 | 12.5 | 12.5 | >25 | * |
| 8g | 25 | 25 | 12.5 | 25 | 12.5 | >25 | 16.99 |
| MA | 25 | 25 | 12.5 | 25 | 25 | NA | NA |
| INH | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 0.1 | NA |
| RIF | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 0.2 | NA |
| EMB | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1.56 | NA |
| CIP | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1.56 | NA |
| BHT | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 16.47 |
The remaining compounds displayed moderate to low antifungal activities against all the tested fungal strains. The antifungal activity depends on the various substituents present on phenyl rings. Among the series, the compounds with nitro groups (8a–g) were the most active against all the tested fungal strains. Compounds 8f and 8g were the most active in the series as they possessed a nitro group at R and chloro groups at R2 and R3; the chloro group at the R1 position for 8e resulted in less activity against one fungal strain. The methyl group at the R1/R2/R3 position and the nitro group at the R position in 8b, 8c, and 8d resulted in good activity than that of the others in the series.
| Molecular docking score | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Entry | Total score (−log![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) Ki) Ki) |
Crash score | Polar score | Entry | Total score (−log![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) Ki) Ki) |
Crash score | Polar score |
| 6a | 7.0377 | −0.6933 | 1.9115 | 7e | 6.4127 | −1.2494 | 1.4225 |
| 6b | 6.4564 | −2.9621 | 0.0004 | 7f | 7.2492 | −1.4724 | 2.5093 |
| 6c | 6.8229 | −0.7726 | 2.0682 | 7g | 7.2394 | −1.4033 | 3.0192 |
| 6d | 6.0468 | −1.4517 | 1.3586 | 8a | 7.0868 | −1.1801 | 3.6314 |
| 6e | 6.5873 | −0.9241 | 2.8329 | 8b | 7.5441 | −2.8665 | 0.9019 |
| 6f | 6.7343 | −0.8582 | 3.0543 | 8c | 7.4658 | −1.0993 | 0.7391 |
| 6g | 7.0332 | −1.0463 | 1.6968 | 8d | 7.3945 | −1.5222 | 1.9024 |
| 7a | 6.0045 | −0.7865 | 2.8105 | 8e | 7.3314 | −0.9292 | 0.7808 |
| 7b | 6.6907 | −0.9183 | 4.5244 | 8f | 7.9971 | −1.9946 | 0.0031 |
| 7c | 6.5748 | −2.7834 | 0.0090 | 8g | 7.5972 | −1.3842 | 3.0509 |
| 7d | 7.0239 | −1.2982 | 3.2802 | MA | 6.4895 | −1.4009 | 1.0311 |
The docking results indicated that the triazole scaffold of the synthesized derivatives 6a–g, 7a–g, and 8a–g was incorporated appropriately in the active site of CYP450 and through various kinds of non-bonded interactions such as H-bond interactions and π bond interactions with the active sites of the amino acid residues. Among all the synthesized derivatives, 8f (7.9971), 8g (7.597), and 8b (7.544) were the most active triazole derivatives when compared with the standard Miconazole drug (6.4895). The most active triazole derivative 8f (7.9971) contained hydrophilic as well as hydrophobic amino acids in the active sites such as isoleucine, valine, methionine, cysteine, leucine, and phenylalanine. The hydrophobic amino acids Cys506 and Ile507 formed conventional hydrogen bonds with the oxygen (–O) of the nitro group on the phenyl ring with the distances of 1.95 and 2.02 Å, respectively. Met336 contains non-polar side chain forms conventional hydrogen bond interaction with a hydrogen atom (–H) attached to the nitrogen atom and methylene group with distance 2.41 and 2.45 Å, respectively. The hydrophobic amino acids such as Val166, Ile167, Ala182, Leu186, Leu240, Leu316, and Ala185 interacted with the π electron cloud to form weak π-interactions such as π-alkyl and alkyl interactions with the chloro-phenyl (–Cl) ring; the π electron cloud with the phenyl ring and the π electron cloud of the triazole ring are shown in Fig. 4a. The second most active triazole derivative 8g (7.597) interacted with the active site of amino acids by forming non-covalent bonded interactions such as H-bond interaction and π bond interaction. The hydrophobic amino acid Ala501 contains a non-polar side chain that interacts with the oxygen (–O) atom of the nitro group to form a conventional hydrogen bond interaction with distance of 2.02 Å. The polar aromatic amino acid Tyr168 forms hydrogen bond interactions with the nitrogen atom of the triazole ring with a distance of 1.84 Å.
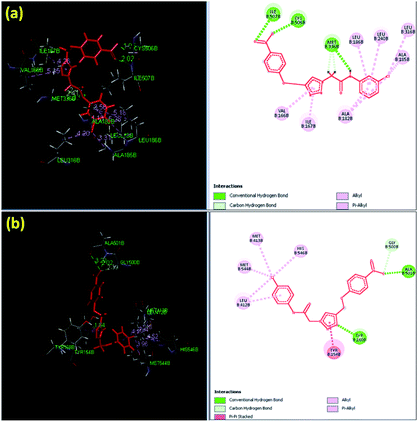 | ||
| Fig. 4 Binding pose and molecular interactions in the active sites of C. albicans lanosterol 14α-demethylase: (a) 8f and (b) 8g. | ||
The amino acid Gly500 formed a carbon–hydrogen bond with the oxygen (–O) of the nitro group on the phenyl ring with a distance of 2.39 Å. The hydrophobic amino acid Try154 with an aromatic ring interacted with the triazole π cloud to form π–π stacked interactions, while the amino acids Leu412, Met544, Met413, and His546 interacted with the π cloud of the chloro group on the phenyl ring (–Cl) and the phenyl ring to form weak π-alkyl and alkyl interactions, as shown in Fig. 4b.
3. Conclusion
In conclusion, we demonstrated [Et3NH][OAc]- and ultrasound-mediated synthesis of new N-phenylacetamide-incorporated 1,2,3-triazole derivatives 6(a–g), 7(a–g), and 8(a–g) in excellent yields via the click chemistry approach for the first time. This safer method reduced the use of harmful solvents and reaction time. We also studied the recovery and reusability of [Et3NH][OAc] as a medium. The synthesized triazole derivatives were evaluated for their antifungal, antioxidant, and antitubercular activities. Among the series, the compounds 8a, 8b, 8c, 8d, 8e, 8f, and 8g displayed excellent antifungal activities as compared to the standard drug Miconazole with lower MIC values.The in silico molecular docking study supported the experimental results and demonstrated that the 1,2,3-triazole derivatives 8f and 8g are the most active and have the potential to inhibit the survival of fungal species. The predictions of the pharmacokinetic parameters suggest that the synthesized derivatives have the potential to have high oral drug bioavailability.
4. Experimental
4.1 General methods
All the solvents and reagents were purchased from commercial suppliers, namely, Spectrochem Pvt. Ltd., Avra, Sigma Aldrich, and Alfa Aesar and were used without further purification. The progress of each reaction was monitored by thin layer chromatography (TLC) using silica gel F254 precoated TLC aluminium sheets (Merck, Germany) and by locating the spots using a UV light as the visualizing agent or iodine vapours. The melting points were obtained by the open capillary method and were uncorrected. The IR spectra were recorded on a Bruker FT-IR spectrometer. The 1H NMR spectra were recorded on Bruker AC-200 MHz and Bruker Advance III 500 MHz NMR spectrometers. The 13C NMR spectra were recorded on Bruker AC-50 MHz and Bruker Advance III 125 MHz NMR in DMSO-d6, CDCl3 + DMSO-d6, and CDCl3 + CD3OD using tetramethylsilane (TMS) as the internal standard; the chemical shifts (δ) were recorded in parts per million (ppm). The splitting pattern abbreviations are designed as singlet (s), doublet (d), double doublet (dd), triplet (t), quartet (q), and multiplet (m). High-resolution mass spectra (HRMS) were recorded on an Agilent 6520 (QTOF) ESI-HRMS instrument and Agilent Technologies 1200 series electron spray ionization (ESI) was used for the LC-MS data.4.2 General experimental procedure for the synthesis of N-phenylacetamide-incorporated 1,2,3-triazole derivatives (6a–g, 7a–g, and 8a–g)
The mixture of appropriate (prop-2-yn-1-yloxy) benzenes 2a–c (1 mmol), substituted 2-azido-N-phenylacetamide 5a–g (1 mmol) and Cu(OAc)2·H2O (10 mol%) in [NEt3H][OAc] (1 mL) was placed in a round bottom flask. The mixture was sonicated (40 kHz) at 30 °C for an appropriate time until the completion of the reaction. The progress of the reaction was monitored by TLC. After the completion of the reaction, the mixture was quenched with crushed ice. The obtained solid was filtered and washed with water. The crude solid was crystallized in ethanol to afford the corresponding pure product. The synthesized compounds 6a–g, 7a–g, and 8a–g were characterized by IR, 1H NMR, 13C NMR, and mass spectroscopy.![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O stretching); 1H NMR (200 MHz, DMSO-d6, δ ppm): 5.17 (s, 2H, –NCH2CO–), 5.36 (s, 2H, –OCH2), 6.96 (t, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H, Ar–H), 7.08 (t, J = 8.0 Hz, 3H, Ar), 7.28–7.38 (m, 4H, Ar–H), 7.59 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H, Ar–H), 8.26 (s, 1H, triazole), and 10.49 (s, 1H, NH); 13C NMR (50 MHz, DMSO-d6, δ ppm): 51.8, 60.5, 114.3, 118.9, 120.5, 123.5, 125.9, 128.6, 129.2, 138.0, 142.2, 157.7, and 163.8; HRMS calcd for C17H17N4O2 [M + H]+: 309.1346 and found 309.1340.
O stretching); 1H NMR (200 MHz, DMSO-d6, δ ppm): 5.17 (s, 2H, –NCH2CO–), 5.36 (s, 2H, –OCH2), 6.96 (t, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H, Ar–H), 7.08 (t, J = 8.0 Hz, 3H, Ar), 7.28–7.38 (m, 4H, Ar–H), 7.59 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H, Ar–H), 8.26 (s, 1H, triazole), and 10.49 (s, 1H, NH); 13C NMR (50 MHz, DMSO-d6, δ ppm): 51.8, 60.5, 114.3, 118.9, 120.5, 123.5, 125.9, 128.6, 129.2, 138.0, 142.2, 157.7, and 163.8; HRMS calcd for C17H17N4O2 [M + H]+: 309.1346 and found 309.1340.![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O stretching); 1H NMR (200 MHz, DMSO-d6, δ ppm): 2.24 (s, 3H, –CH3), 5.17 (s, 2H, –NCH2CO–), 5.41 (s, 2H, –OCH2), 6.95 (t, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H, Ar–H), 7.05 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H, Ar–H), 7.10–7.35 (m, 5H, Ar–H), 7.43 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H, Ar–H), 8.26 (s, 1H, triazole), and 9.84 (s, 1H, NH); 13C NMR (50 MHz, DMSO-d6, δ ppm): 17.5, 51.3, 60.5, 114.3, 120.4, 124.8, 125.8, 129.1, 130.1, 131.2, 135.1, 142.2, 157.7, and 164.0; HRMS calcd for C18H19N4O2 [M + H]+: 323.1508 and found 323.1510.
O stretching); 1H NMR (200 MHz, DMSO-d6, δ ppm): 2.24 (s, 3H, –CH3), 5.17 (s, 2H, –NCH2CO–), 5.41 (s, 2H, –OCH2), 6.95 (t, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H, Ar–H), 7.05 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H, Ar–H), 7.10–7.35 (m, 5H, Ar–H), 7.43 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H, Ar–H), 8.26 (s, 1H, triazole), and 9.84 (s, 1H, NH); 13C NMR (50 MHz, DMSO-d6, δ ppm): 17.5, 51.3, 60.5, 114.3, 120.4, 124.8, 125.8, 129.1, 130.1, 131.2, 135.1, 142.2, 157.7, and 164.0; HRMS calcd for C18H19N4O2 [M + H]+: 323.1508 and found 323.1510.![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O stretching); 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3 + DMSO-d6, δ ppm): 2.21 (s, 3H, –CH3), 5.10 (s, 2H, –NCH2CO–), 5.13 (s, 2H, –OCH2), 6.79–6.93 (m, 4H, Ar–H), 7.08 (d, J = 8.0 Hz 1H), 7.13–7.30 (m, 3H, Ar–H), 7.34 (s, 1H, Ar–H), 7.85 (s, 1H, triazole), and 9.70 (s, 1H, NH); 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3 + DMSO-d6, δ ppm): 21.1, 52.7, 61.4, 114.3, 116.7, 120.2, 124.8, 124.9, 128.3, 129.1, 137.3, 138.4, 143.7, 157.8, and 163.0; LC-MS for C18H18N4O2: [M]+ 323.1.
O stretching); 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3 + DMSO-d6, δ ppm): 2.21 (s, 3H, –CH3), 5.10 (s, 2H, –NCH2CO–), 5.13 (s, 2H, –OCH2), 6.79–6.93 (m, 4H, Ar–H), 7.08 (d, J = 8.0 Hz 1H), 7.13–7.30 (m, 3H, Ar–H), 7.34 (s, 1H, Ar–H), 7.85 (s, 1H, triazole), and 9.70 (s, 1H, NH); 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3 + DMSO-d6, δ ppm): 21.1, 52.7, 61.4, 114.3, 116.7, 120.2, 124.8, 124.9, 128.3, 129.1, 137.3, 138.4, 143.7, 157.8, and 163.0; LC-MS for C18H18N4O2: [M]+ 323.1.![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O stretching).
O stretching).![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O stretching); 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3 + DMSO-d6, δ ppm): 5.19 (s, 2H, –NCH2CO–), 5.31 (s, 2H, –OCH2), 6.94 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 3H, Ar–H), 7.05 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H, Ar–H), 7.16–7.34 (m, 4H, Ar–H), 7.89 (s, 1H, triazole), 8.02 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H, Ar–H), and 9.01 (s, 1H, NH); 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3 + DMSO-d6, δ ppm): 52.8, 61.3, 114.3, 120.8, 123.1, 124.3, 125.5, 127.1, 129.0, 133.7, 141.9, 157.7, and 162.6. LC-MS for C17H15ClN4O2: [M]+ 343.
O stretching); 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3 + DMSO-d6, δ ppm): 5.19 (s, 2H, –NCH2CO–), 5.31 (s, 2H, –OCH2), 6.94 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 3H, Ar–H), 7.05 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H, Ar–H), 7.16–7.34 (m, 4H, Ar–H), 7.89 (s, 1H, triazole), 8.02 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H, Ar–H), and 9.01 (s, 1H, NH); 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3 + DMSO-d6, δ ppm): 52.8, 61.3, 114.3, 120.8, 123.1, 124.3, 125.5, 127.1, 129.0, 133.7, 141.9, 157.7, and 162.6. LC-MS for C17H15ClN4O2: [M]+ 343.![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O stretching); 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3 + DMSO-d6, δ ppm): 5.45 (s, 2H, –NCH2CO–), 5.46 (s, 2H, –OCH2), 7.15–7.57 (m, 7H Ar–H), 7.67 (s, 1H, Ar–H), 7.92 (s, 1H, triazole), 8.15 (s, 1H, Ar–H), and 10.16 (s, 1H, NH). 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3 + DMSO-d6, δ ppm): 53.1, 61.7, 114.7, 117.9, 120.0, 121.2, 124.5, 129.5, 129.9, 134.4, 138.9, 158.1, and 163.5; LC-MS for C17H15ClN4O2: [M]+ 343.1.
O stretching); 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3 + DMSO-d6, δ ppm): 5.45 (s, 2H, –NCH2CO–), 5.46 (s, 2H, –OCH2), 7.15–7.57 (m, 7H Ar–H), 7.67 (s, 1H, Ar–H), 7.92 (s, 1H, triazole), 8.15 (s, 1H, Ar–H), and 10.16 (s, 1H, NH). 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3 + DMSO-d6, δ ppm): 53.1, 61.7, 114.7, 117.9, 120.0, 121.2, 124.5, 129.5, 129.9, 134.4, 138.9, 158.1, and 163.5; LC-MS for C17H15ClN4O2: [M]+ 343.1.![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O stretching); 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3, δ ppm): 3.76 (s, 3H, OCH3), 5.19 (s, 2H, –NCH2CO–), 5.20 (s, 2H, –OCH2), 6.83 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H, Ar–H), 6.92 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H, Ar–H), 7.14 (t, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H, Ar–H), 7.31 (t, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H, Ar–H), 7.43 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H, Ar–H), 7.81 (s, 1H, triazole), and 7.87 (s, 1H, NH); 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3, δ ppm): 53.9, 55.7, 62.5, 114.8, 115.9, 120.3, 125.4, 129.1, 137.0, 139.3, 152.1, and 162.3; LC-MS for C18H18N4O3: [M]+ 339.1.
O stretching); 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3, δ ppm): 3.76 (s, 3H, OCH3), 5.19 (s, 2H, –NCH2CO–), 5.20 (s, 2H, –OCH2), 6.83 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H, Ar–H), 6.92 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H, Ar–H), 7.14 (t, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H, Ar–H), 7.31 (t, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H, Ar–H), 7.43 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H, Ar–H), 7.81 (s, 1H, triazole), and 7.87 (s, 1H, NH); 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3, δ ppm): 53.9, 55.7, 62.5, 114.8, 115.9, 120.3, 125.4, 129.1, 137.0, 139.3, 152.1, and 162.3; LC-MS for C18H18N4O3: [M]+ 339.1.![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O stretching); 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3, δ ppm): 2.10 (s, 3H, CH3), 3.75 (s, 3H, –OCH3), 5.21 (s, 2H, –NCH2CO–), 5.22 (s, 2H, –OCH2), 6.82 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H, Ar–H), 6.91 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H, Ar–H), 7.08 (t, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H, Ar–H), 7.15 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H, Ar–H), 7.20 (t, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H, Ar–H), 7.80 (s, 1H, triazole), and 7.82 (s, 1H, NH); 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3, δ ppm): 17.4, 53.9, 55.7, 62.4, 114.8, 115.9, 122.3, 124.5, 125.9, 126.9, 127.9, 137.6, and 162.8; LC-MS for C19H20N4O3: [M]+ 353.1.
O stretching); 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3, δ ppm): 2.10 (s, 3H, CH3), 3.75 (s, 3H, –OCH3), 5.21 (s, 2H, –NCH2CO–), 5.22 (s, 2H, –OCH2), 6.82 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H, Ar–H), 6.91 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H, Ar–H), 7.08 (t, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H, Ar–H), 7.15 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H, Ar–H), 7.20 (t, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H, Ar–H), 7.80 (s, 1H, triazole), and 7.82 (s, 1H, NH); 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3, δ ppm): 17.4, 53.9, 55.7, 62.4, 114.8, 115.9, 122.3, 124.5, 125.9, 126.9, 127.9, 137.6, and 162.8; LC-MS for C19H20N4O3: [M]+ 353.1.![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O stretching); 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3 + DMSO-d6, δ ppm): 2.18 (s, 3H, CH3), 3.62 (s, 3H, OCH3), 5.01 (s, 2H, –NCH2CO–), 5.10 (s, 2H, –OCH2), 6.68 (d, J = 6 Hz, 2H, Ar–H), 6.79 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H, Ar–H), 7.04 (t, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H, Ar–H), 7.18 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H, Ar–H), 7.26 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H, Ar–H), 7.31 (s, 1H, Ar–H), 7.79 (s, 1H, triazole), and 9.73 (s, 1H, NH); 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3 + DMSO-d6, δ ppm): 21.3, 52.9, 55.5, 62.4, 114.5, 115.7, 116.8, 120.4, 124.4, 125.1, 128.5, 137.6, 138.5, 144.1, 152.2, 153.9, and 163.3. LC-MS for C19H20N4O3: [M]+ 353.1.
O stretching); 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3 + DMSO-d6, δ ppm): 2.18 (s, 3H, CH3), 3.62 (s, 3H, OCH3), 5.01 (s, 2H, –NCH2CO–), 5.10 (s, 2H, –OCH2), 6.68 (d, J = 6 Hz, 2H, Ar–H), 6.79 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H, Ar–H), 7.04 (t, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H, Ar–H), 7.18 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H, Ar–H), 7.26 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H, Ar–H), 7.31 (s, 1H, Ar–H), 7.79 (s, 1H, triazole), and 9.73 (s, 1H, NH); 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3 + DMSO-d6, δ ppm): 21.3, 52.9, 55.5, 62.4, 114.5, 115.7, 116.8, 120.4, 124.4, 125.1, 128.5, 137.6, 138.5, 144.1, 152.2, 153.9, and 163.3. LC-MS for C19H20N4O3: [M]+ 353.1.![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O stretching); 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3 + DMSO-d6, δ ppm): 2.10 (s, 3H, CH3), 3.55 (s, 3H, OCH3), 4.94 (s, 2H, –NCH2CO–), 5.02 (s, 2H, –OCH2), 6.62 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H, Ar–H), 6.72 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H, Ar–H), 6.89 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H, Ar–H), 7.24 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H, Ar–H), 7.73 (s, 1H, triazole), and 9.68 (s, 1H, NH); 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3 + DMSO-d6, δ ppm): 20.4, 52.6, 55.2, 62.1, 114.2, 115.4, 119.5, 124.2, 128.9, 133.5, 134.9, 151.9, 153.6, and 162.8; LC-MS for C19H20N4O3: [M]+ 353.1.
O stretching); 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3 + DMSO-d6, δ ppm): 2.10 (s, 3H, CH3), 3.55 (s, 3H, OCH3), 4.94 (s, 2H, –NCH2CO–), 5.02 (s, 2H, –OCH2), 6.62 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H, Ar–H), 6.72 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H, Ar–H), 6.89 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H, Ar–H), 7.24 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H, Ar–H), 7.73 (s, 1H, triazole), and 9.68 (s, 1H, NH); 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3 + DMSO-d6, δ ppm): 20.4, 52.6, 55.2, 62.1, 114.2, 115.4, 119.5, 124.2, 128.9, 133.5, 134.9, 151.9, 153.6, and 162.8; LC-MS for C19H20N4O3: [M]+ 353.1.![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O stretching); 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3 + DMSO-d6, δ ppm): 3.89 (s, 3H, OCH3), 5.32 (s, 2H, –NCH2CO–), 5.47 (s, –OCH2), 6.96 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H, Ar–H), 7.06 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H, Ar–H), 7.23 (t, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H, Ar–H), 7.39 (t, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H, Ar–H), 7.50 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H, Ar–H), 8.03 (s, 1H, triazole), 8.26 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H, Ar–H), and 8.98 (s, 1H, NH); 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3 + DMSO-d6, δ ppm): 53.0, 55.4, 62.3, 114.4, 115.6, 122.8, 124.3, 125.6, 127.3, 129.1, 133.4, 144.7, 152.0, 153.9, and 163.3; LC-MS for C18H17ClN4O3: [M]+ 373.
O stretching); 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3 + DMSO-d6, δ ppm): 3.89 (s, 3H, OCH3), 5.32 (s, 2H, –NCH2CO–), 5.47 (s, –OCH2), 6.96 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H, Ar–H), 7.06 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H, Ar–H), 7.23 (t, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H, Ar–H), 7.39 (t, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H, Ar–H), 7.50 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H, Ar–H), 8.03 (s, 1H, triazole), 8.26 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H, Ar–H), and 8.98 (s, 1H, NH); 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3 + DMSO-d6, δ ppm): 53.0, 55.4, 62.3, 114.4, 115.6, 122.8, 124.3, 125.6, 127.3, 129.1, 133.4, 144.7, 152.0, 153.9, and 163.3; LC-MS for C18H17ClN4O3: [M]+ 373.![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O stretching); 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3 + DMSO-d6, δ ppm): 3.57 (s, 3H, OCH3), 4.96 (s, 2H, –NCH2CO–), 5.05 (s, 2H, –OCH2), 6.63 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H, Ar–H), 6.73 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H, Ar–H), 6.87 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H, Ar–H), 7.03 (t, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H, Ar–H), 7.24 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H, Ar–H), 7.53 (s, 1H, Ar–H), 7.73 (s, 1H, triazole), and 10.04 (s, 1H, NH); 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3 + DMSO-d6, δ ppm): 52.4, 55.1, 62.0, 114.1, 115.27, 117.3, 119.3, 123.7, 124.1, 129.4, 133.8, 138.7, 151.8, 153.5, and 163.2; LC-MS for C18H17ClN4O3 [M + H]+ 373.
O stretching); 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3 + DMSO-d6, δ ppm): 3.57 (s, 3H, OCH3), 4.96 (s, 2H, –NCH2CO–), 5.05 (s, 2H, –OCH2), 6.63 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H, Ar–H), 6.73 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H, Ar–H), 6.87 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H, Ar–H), 7.03 (t, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H, Ar–H), 7.24 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H, Ar–H), 7.53 (s, 1H, Ar–H), 7.73 (s, 1H, triazole), and 10.04 (s, 1H, NH); 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3 + DMSO-d6, δ ppm): 52.4, 55.1, 62.0, 114.1, 115.27, 117.3, 119.3, 123.7, 124.1, 129.4, 133.8, 138.7, 151.8, 153.5, and 163.2; LC-MS for C18H17ClN4O3 [M + H]+ 373.![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O stretching).
O stretching).![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O stretching); 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3 + CD3OD, δ ppm): 5.18 (s, 2H, –NCH2CO–), 5.27 (s, 2H, –OCH2), 7.05 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 3H, Ar–H), 7.27 (t, J = 8.0 Hz, 3H, Ar–H), 7.49 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H, Ar–H), 7.98 (s, 1H, triazole), and 8.17 (d, J = 8 Hz, 2H, Ar–H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3 + CD3OD, δ ppm): 52.7, 61.9, 114.5, 125.1, 125.7, 128.8, 137.5, 141.7, and 162.8; LC-MS for C17H15N5O4: [M]+ 354.
O stretching); 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3 + CD3OD, δ ppm): 5.18 (s, 2H, –NCH2CO–), 5.27 (s, 2H, –OCH2), 7.05 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 3H, Ar–H), 7.27 (t, J = 8.0 Hz, 3H, Ar–H), 7.49 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H, Ar–H), 7.98 (s, 1H, triazole), and 8.17 (d, J = 8 Hz, 2H, Ar–H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3 + CD3OD, δ ppm): 52.7, 61.9, 114.5, 125.1, 125.7, 128.8, 137.5, 141.7, and 162.8; LC-MS for C17H15N5O4: [M]+ 354.![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O stretching); 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3 + CD3OD, δ ppm): 2.15 (s, 3H, CH3), 5.23 (s, 2H, –NCH2CO–), 5.25 (s, 2H, –OCH2), 7.03–7.13 (m, 6H, Ar–H), 7.47 (s, 1H, NH), 7.98 (s, 1H, triazole), and 8.14 (s, 2H, Ar–H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3 + CD3OD, δ ppm): 17.2, 52.6, 62.1, 114.9, 124.9, 125.4, 125.9, 126.4, 126.5, 127.4, 130.7, 131.2, and 163.7; LC-MS for C18H17N5O4 [M]+ 368.1.
O stretching); 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3 + CD3OD, δ ppm): 2.15 (s, 3H, CH3), 5.23 (s, 2H, –NCH2CO–), 5.25 (s, 2H, –OCH2), 7.03–7.13 (m, 6H, Ar–H), 7.47 (s, 1H, NH), 7.98 (s, 1H, triazole), and 8.14 (s, 2H, Ar–H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3 + CD3OD, δ ppm): 17.2, 52.6, 62.1, 114.9, 124.9, 125.4, 125.9, 126.4, 126.5, 127.4, 130.7, 131.2, and 163.7; LC-MS for C18H17N5O4 [M]+ 368.1.![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O stretching); 1H NMR (200 MHz, DMSO-d6, δ ppm): 2.28 (s, 3H, CH3), 5.36 (s, 4H, –NCH2CO, –OCH2), 6.91 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H, Ar–H), 7.19 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H, Ar–H), 7.27 (t, J = 8 Hz, 1H, Ar–H), 7.33 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H, Ar–H), 7.42 (s, 1H, Ar–H), 8.24 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H, Ar–H), 8.32 (s, 1H, triazole), and 10.42 (s, 1H, NH); 13C NMR (50 MHz, DMSO-d6, δ ppm): 21.1, 52.2, 61.9, 115.3, 116.4, 119.8, 124.5, 125.9, 126.7, 128.7, 138.1, 138.3, 141.0, 141.5, 163.3, and 164.0; HRMS calcd for C18H18N5O4 [M + H]+: 368.1359 and found 368.1364.
O stretching); 1H NMR (200 MHz, DMSO-d6, δ ppm): 2.28 (s, 3H, CH3), 5.36 (s, 4H, –NCH2CO, –OCH2), 6.91 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H, Ar–H), 7.19 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H, Ar–H), 7.27 (t, J = 8 Hz, 1H, Ar–H), 7.33 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H, Ar–H), 7.42 (s, 1H, Ar–H), 8.24 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H, Ar–H), 8.32 (s, 1H, triazole), and 10.42 (s, 1H, NH); 13C NMR (50 MHz, DMSO-d6, δ ppm): 21.1, 52.2, 61.9, 115.3, 116.4, 119.8, 124.5, 125.9, 126.7, 128.7, 138.1, 138.3, 141.0, 141.5, 163.3, and 164.0; HRMS calcd for C18H18N5O4 [M + H]+: 368.1359 and found 368.1364.![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O stretching); 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3 + CD3OD, δ ppm): 2.26 (s, 3H, CH3), 5.14 (s, 2H, –NCH2CO–), 5.26 (s, 2H, –OCH2), 7.0 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H, Ar–H), 7.07 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H, Ar–H), 7.35 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H, Ar–H), 7.96 (s, 1H, triazole), and 8.16 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H, Ar–H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3 + CD3OD, δ ppm): 17.7, 53.1, 62.6, 115.4, 124.8, 125.9, 126.5, 126.9, 131.2, 143.5, 152.0, and 164.2; LC-MS for C18H17N5O4: [M + H]+ 368.1.
O stretching); 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3 + CD3OD, δ ppm): 2.26 (s, 3H, CH3), 5.14 (s, 2H, –NCH2CO–), 5.26 (s, 2H, –OCH2), 7.0 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H, Ar–H), 7.07 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H, Ar–H), 7.35 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H, Ar–H), 7.96 (s, 1H, triazole), and 8.16 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H, Ar–H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3 + CD3OD, δ ppm): 17.7, 53.1, 62.6, 115.4, 124.8, 125.9, 126.5, 126.9, 131.2, 143.5, 152.0, and 164.2; LC-MS for C18H17N5O4: [M + H]+ 368.1.![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O stretching); 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3 + CD3OD, δ ppm): 5.31 (s, 2H, –NCH2CO–), 5.33 (s, 2H, –OCH2), 7.08 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 3H, Ar–H), 7.29 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H), 7.37 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H, Ar–H), 7.96 (s, 1H, triazole), 8.15 (s, 1H, NH), and 8.20 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H, Ar–H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3 + CD3OD, δ ppm): 53.2, 62.1, 114.8, 125.1, 126.0, 126.1, 127.7, 129.4, 133.5, 136.5, 146.4, 152.3, and 163.0; LC-MS for C17H14ClN5O4: [M]+ 388.
O stretching); 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3 + CD3OD, δ ppm): 5.31 (s, 2H, –NCH2CO–), 5.33 (s, 2H, –OCH2), 7.08 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 3H, Ar–H), 7.29 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H), 7.37 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H, Ar–H), 7.96 (s, 1H, triazole), 8.15 (s, 1H, NH), and 8.20 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H, Ar–H); 13C NMR (125 MHz, CDCl3 + CD3OD, δ ppm): 53.2, 62.1, 114.8, 125.1, 126.0, 126.1, 127.7, 129.4, 133.5, 136.5, 146.4, 152.3, and 163.0; LC-MS for C17H14ClN5O4: [M]+ 388.![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O stretching); 1H NMR (200 MHz, DMSO-d6, δ ppm): 5.36 (s, 2H, –NCH2CO–), 5.40 (s, 2H, –OCH2), 7.15 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H, Ar–H), 7.29 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H, Ar–H), 7.42 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H, Ar–H), 7.78 (s, 1H, Ar–H), 8.23 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H, Ar–H), 8.33 (s, 1H, triazole), and 10.81 (s, 1H, NH); 13C NMR (50 MHz, DMSO-d6, δ ppm): 52.3, 61.9, 115.4, 117.7, 118.9, 123.6, 125.9, 126.8, 130.7, 133.3, 139.9, 141.1, 141.7, 163.4, and 164.7; HRMS calcd for C17H15ClN5O4 [M + H]+: 388.0813 and found 388.0814.
O stretching); 1H NMR (200 MHz, DMSO-d6, δ ppm): 5.36 (s, 2H, –NCH2CO–), 5.40 (s, 2H, –OCH2), 7.15 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H, Ar–H), 7.29 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H, Ar–H), 7.42 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H, Ar–H), 7.78 (s, 1H, Ar–H), 8.23 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H, Ar–H), 8.33 (s, 1H, triazole), and 10.81 (s, 1H, NH); 13C NMR (50 MHz, DMSO-d6, δ ppm): 52.3, 61.9, 115.4, 117.7, 118.9, 123.6, 125.9, 126.8, 130.7, 133.3, 139.9, 141.1, 141.7, 163.4, and 164.7; HRMS calcd for C17H15ClN5O4 [M + H]+: 388.0813 and found 388.0814.![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O stretching); 1H NMR (200 MHz, DMSO-d6, δ ppm): 5.36 (s, 4H, –NCH2CO, –OCH2), 7.29 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H, Ar–H), 7.39 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H, Ar–H), 7.61 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H, Ar–H), 8.23 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H, Ar–H), 8.32 (s, 1H, triazole), and 10.64 (s, 1H, NH); 13C NMR (50 MHz, DMSO-d6, δ ppm): 52.2, 61.9, 115.3, 120.8, 125.8, 126.7, 127.4, 128.8, 137.3, 141.0, 141.6, 163.3, and 164.3; HRMS calcd for C17H15ClN5O4 [M + H]+: 388.0813 and found 388.0819.
O stretching); 1H NMR (200 MHz, DMSO-d6, δ ppm): 5.36 (s, 4H, –NCH2CO, –OCH2), 7.29 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H, Ar–H), 7.39 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H, Ar–H), 7.61 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H, Ar–H), 8.23 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H, Ar–H), 8.32 (s, 1H, triazole), and 10.64 (s, 1H, NH); 13C NMR (50 MHz, DMSO-d6, δ ppm): 52.2, 61.9, 115.3, 120.8, 125.8, 126.7, 127.4, 128.8, 137.3, 141.0, 141.6, 163.3, and 164.3; HRMS calcd for C17H15ClN5O4 [M + H]+: 388.0813 and found 388.0819.4.3 Experimental protocol for biological activity
Initially, the inoculum was prepared from a fresh LJ medium re-suspended in the 7H9-S medium (7H9 broth, 0.1% casitone, 0.5% glycerol, supplemented oleic acid, albumin, dextrose, and catalase [OADC]), adjusted to a McFarland tube no. 1, and diluted 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 20; 100 μL was used as the inoculum. Each drug stock solution was thawed and diluted in 7H9-S at four-fold the final highest concentration tested. Serial two-fold dilutions of each drug were prepared directly in a sterile 96-well microtiter plate using 100 μL 7H9-S. A growth control containing no antibiotic and a sterile control was also prepared on each plate. Sterile water was added to all perimeter wells to avoid evaporation during incubation. The plate was covered, sealed in plastic bags, and incubated at 37 °C in normal atmosphere. After 7 days incubation, 30 μL of alamar blue solution was added to each well, and the plate was re-incubated overnight. A change in the colour from blue (oxidised state) to pink (reduced) indicated the growth of bacteria, and the MIC was defined as the lowest concentration of the drug that prevented this change in colour.
20; 100 μL was used as the inoculum. Each drug stock solution was thawed and diluted in 7H9-S at four-fold the final highest concentration tested. Serial two-fold dilutions of each drug were prepared directly in a sterile 96-well microtiter plate using 100 μL 7H9-S. A growth control containing no antibiotic and a sterile control was also prepared on each plate. Sterile water was added to all perimeter wells to avoid evaporation during incubation. The plate was covered, sealed in plastic bags, and incubated at 37 °C in normal atmosphere. After 7 days incubation, 30 μL of alamar blue solution was added to each well, and the plate was re-incubated overnight. A change in the colour from blue (oxidised state) to pink (reduced) indicated the growth of bacteria, and the MIC was defined as the lowest concentration of the drug that prevented this change in colour.
| % of scavenging = [(Acontrol − Asample)/IJAsample × 100)], |
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.Acknowledgements
One of the authors, SVA, is very much grateful to the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), New Delhi for the award of research fellowship. Authors are also thankful to the Head, Department of Chemistry, Dr Babasaheb Ambedkar Marathwada University Aurangabad for providing laboratory facility.Notes and references
- (a) D. Dheer, V. Singh and R. Shankar, Bioorg. Chem., 2017, 71, 30 CrossRef CAS; (b) A. Massarotti, S. Aprile, V. Mercalli, E. D. Grosso, G. Grosa, G. Sorba and G. C. Tron, ChemMedChem, 2014, 9, 2497 CrossRef CAS; (c) S. G. Agalave, S. R. Maujan and V. S. Pore, Chem.–Asian J., 2011, 6, 2696 CrossRef CAS; (d) M. Whiting, J. Muldoon, Y. C. Lin, S. M. Silverman, W. Lindstrom, A. J. Olson, H. C. Kolb, M. G. Finn, K. B. Sharpless, J. H. Elder and V. V. Fokin, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2006, 45, 1435 CrossRef CAS; (e) V. V. Rostovtsev, L. G. Green, V. V. Fokin and K. B. Sharpless, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2002, 41, 2596 CrossRef CAS; (f) C. W. Tornoe, C. Christensen and M. Meldal, J. Org. Chem., 2002, 67, 3057 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) K. Kempe, A. Krieg, C. R Becer and U. S. Schubert, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2012, 41, 176 RSC; (b) N. Akeroyd and B. Klumperman, Eur. Polym. J., 2011, 47, 1207 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) J. J. Bryant and U. H. F. Bunz, Chem.–Asian J., 2013, 8, 1354 CrossRef CAS; (b) K. D. Hanni and D. A. Leigh, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2010, 39, 1240 RSC.
- (a) G. C. Tron, T. Pirali, R. A. Billington, P. L. Canonico, G. Sorba and A. A. Genazzani, Med. Res. Rev., 2008, 28, 278 CrossRef CAS; (b) A. D. Moorhouse and J. E. Moses, ChemMedChem, 2008, 3, 715 CrossRef CAS; (c) J. F. Lutz and Z. Zarafshani, Adv. Drug Delivery Rev., 2008, 60, 958 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) N. Fu, S. Wang, Y. Zhang, C. Zhang, D. Yang, L. Weng, B. Zhao and L. Wang, Eur. J. Med. Chem., 2017, 136, 596 CrossRef CAS; (b) H. J. Chen, Y. J. Jiang, Y. Q. Zhangc, Q. W. Jingb, N. L. Y. Wang, W. N. Zhangb and C. Q. Shenga, Chin. Chem. Lett., 2017, 28, 913 CrossRef CAS; (c) Z. C. Dai, Y. F. Chen, M. Zhang, S. K. Li, T. T. Yang, L. Shen, J. X. Wang, S. S. Qian, H. L. Zhu and Y. H. Ye, Org. Biomol. Chem., 2015, 13, 477 RSC; (d) Z. Jiang, J. Gu, C. Wang, S. Wang, N. Liu, Y. Jiang, G. Dong, Y. Wang, Y. Liu, J. Yao, Z. Miao, W. Zhang and C. Sheng, Eur. J. Med. Chem., 2014, 82, 490 CrossRef CAS; (e) N. G. Aher, V. S. Pore, N. N. Mishra, A. Kumar, P. K. Shukla, A. Sharma and M. K. Bhat, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 2009, 19, 759 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) B. Zhang, Eur. J. Med. Chem., 2019, 168, 357 CrossRef CAS; (b) X. L. Wang, K. Wan and C. H. Zhou, Eur. J. Med. Chem., 2010, 45, 4631 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) K. S. Raju, S. AnkiReddy, G. Sabitha, V. S. Krishna, D. Sriram, K. B. Reddy and S. R. Sagurthi, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 2019, 29, 284 CrossRef; (b) S. Zhan, Z. Xu, C. Gao, Q. C. Ren, L. Chang, Z. S. Lv and L. S. Feng, Eur. J. Med. Chem., 2017, 138, 501 CrossRef; (c) Z. Xu, X. F. Song, Y. Q. Hu, M. Qiang and Z. S. Lv, Eur. J. Med. Chem., 2017, 138, 66 CrossRef CAS; (d) M. H. Shaikh, D. D. Subhedar, L. Nawale, D. Sarkar, F. A. K. Khan, J. N. Sangshetti and B. B. Shingate, Med. Chem. Commun., 2015, 6, 1104 RSC; (e) S. R. Patpi, L. Pulipati, P. Yogeeswari, D. Sriram, N. Jain, B. Sridhar, R. Murthy, D. T. Anjana, S. V. Kalivendi and S. Kantevar, J. Med. Chem., 2012, 55, 3911 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) P. S. Rao, C. Kurumurthy, B. Veeraswamy, G. S. Kumar, Y. Poornachandra, C. G. Kumar, S. B. Vasamsetti, S. Kotamraju and B. Narsaiah, Eur. J. Med. Chem., 2014, 80, 184 CrossRef; (b) R. D. Simone, M. G. Chini, I. Bruno, R. Riccio, D. Mueller, O. Werz and G. Bifulco, J. Med. Chem., 2011, 54, 1565 CrossRef PubMed.
- D. R. Buckle, D. J. Outred, C. J. M. Rockell, H. Smith and B. A. Spicer, J. Med. Chem., 1983, 26, 251 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) Y. Tian, Z. Liu, J. Liu, B. Huang, D. Kang, H. Zhang, E. D. Clercq, D. D. mans, C. Pannecouque, K. H. Lee, C. H. Chen, P. Zhan and X. Liu, Eur. J. Med. Chem., 2018, 151, 339 CrossRef CAS; (b) G. Wu, W. A. Zalloum, M. E. Meuser, L. Jing, D. Kang, C. Chen, Y. Tian, F. Zhang, S. Cocklin, K. H. Lee, X. Liu and P. Zhan, Eur. J. Med. Chem., 2018, 158, 478 CrossRef CAS; (c) M. J. Giffin, H. Heaslet, A. Brik, Y. C. Lin, G. Cauvi, C. H. Wong, D. E. McRee, J. H. Elder, C. D. Stout and B. E. Torbett, J. Med. Chem., 2008, 51, 6263 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) M. Allam, A. K. D. Bhavani, A. Mudiraj, N. Ranjan, M. Thippana and P. P. Babu, Eur. J. Med. Chem., 2018, 156, 43 CrossRef CAS; (b) V. Prachayasittikul, R. Pingaew, N. Anuwongcharoen, A. Worachartcheewan, C. Nantasenamat, S. Prachayasittikul, S. Ruchirawat and V. Prachayasittikul, SpringerPlus, 2015, 4, 571 CrossRef; (c) Y. C. Duan, Y. C. Ma, E. Zhang, X. J. Shi, M. M. Wang, X. W. Ye and H. M. Liu, Eur. J. Med. Chem., 2013, 62, 11 CrossRef CAS; (d) Y. C. Zheng, Y. C. Duan, J. L. Ma, R. M. Xu, X. Zi, W. L. Lv, M. M. Wang, X. W. Ye, S. Zhu, D. Mobley, Y. Y. Zhu, J. W. Wang, J. F. Li, Z. R. Wang, W. Zhao and H. M. Liu, J. Med. Chem., 2013, 56, 8543 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Wang, Z. C. Dai, Y. F. Chen, L. L. Cao, W. Yan, S. K. Li, J. X. Wang, Z. G. Zhang and Y. H. Ye, Eur. J. Med. Chem., 2017, 126, 171 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. Cha and J. D. Sobel, Expert Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther., 2004, 2, 357 CrossRef CAS.
- N. H. Georgopapadakou and T. J. Walsh, Antimicrob. Agents Chemother., 1996, 40, 279 CrossRef CAS.
- D. A. Enoch, H. A. Ludlam and N. M. Brown, J. Med. Microbiol., 2006, 55, 809 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) G. I. Lepesheva, N. G. Zaitseva and W. D. Nes, et al., J. Biol. Chem., 2006, 281, 3577 CrossRef CAS; (b) L. Jeu, F. J. Piacenti, A. G. Lyakhovetskiy and H. B. Fung, Clin. Ther., 2003, 25, 1321 CrossRef CAS; (c) M. A. Pfaller, S. A. Messer, R. J. Hollis and R. N. Jones, Antimicrob. Agents Chemother., 2001, 45, 2862 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) T. L. Greaves and C. J. Drummond, Chem. Rev., 2008, 108, 206 CrossRef CAS; (b) R. Sheldon, Chem. Commun., 2001, 2399 RSC; (c) P. Wasserscheid and W. Keim, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2000, 39, 3772 CrossRef CAS; (d) T. Welton, Chem. Rev., 1999, 99, 2071 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) C. Rub and B. Konig, Green Chem., 2012, 14, 2969 RSC; (b) W. Miao and T. H. Chan, Org. Lett., 2003, 5, 5003 CrossRef CAS.
- M. A. P. Martins, C. P. Frizzo, A. Z. Tier, D. N. Moreira, N. Zanatta and H. G. Bonacorso, Chem. Rev., 2014, 114, PR1–PR70 CrossRef.
- (a) A. A. Ali, M. Konwar, M. Chetia and D. Sarma, Tetrahedron Lett., 2016, 57, 5661 CrossRef CAS; (b) M. Tavassoli, A. L. Isfahani, M. Moghadam, S. Tangestaninejad, V. Mirkhani and I. M. Baltork, ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng., 2016, 4, 1454 CrossRef CAS; (c) M. Dabiri, S. K. Movahed and D. I. MaGee, Res. Chem. Intermed., 2015, 41, 3335 CrossRef CAS; (d) H. Singh, J. Sindhu, J. M. Khurana, C. Sharma and K. R. Aneja, Eur. J. Med. Chem., 2014, 77, 145 CrossRef CAS; (e) A. Z. Ahmady, F. Heidarizadeh and M. Keshavarz, Synth. Commun., 2013, 43, 2100 CrossRef CAS; (f) A. Marra, A. Vecchi, C. Chiappe, B. Melai and A. Dondoni, J. Org. Chem., 2008, 73, 2458 CrossRef CAS; (g) Y. B. Zhao, Z. Y. Yan and Y. M. Liang, Tetrahedron Lett., 2006, 47, 1545 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) N. J. Parmar, H. A. Barad, B. R. Pansuriya and N. P. Talpada, RSC Adv., 2013, 3, 8064 RSC; (b) N. J. Parmar, B. R. Pansuriya, H. A. Barad, B. D. Parmar, R. Kant and V. K. Gupta, Monatsh. Chem., 2013, 144, 865 CrossRef CAS; (c) N. J. Parmar, R. A. Patel, B. D. Parmar and N. P. Talpada, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 2013, 23, 1656 CrossRef CAS; (d) P. Attri and M. Pal, Green Chem. Lett. Rev., 2010, 3, 249 CrossRef CAS; (e) T. R. Sutariya, B. M. Labana, N. J. Parmar, R. Kant, V. K. Gupta, G. B. Plata and J. M. Padroón, New J. Chem., 2015, 39, 2657 RSC; (f) A. K. Verma, P. Attri, V. Chopra, R. K. Tiwari and R. Chandra, Monatsh. Chem., 2008, 139, 1041 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) A. B. Danne, A. S. Choudhari, S. Chakraborty, D. Sarkar, V. M. Khedkar and B. B. Shingate, Med. Chem. Commun., 2018, 9, 1114 RSC; (b) S. P. Khare, T. R. Deshmukh, J. N. Sangshetti, V. S. Krishna, D. Sriram, V. M. Khedkar and B. B. Shingate, ChemistrySelect, 2018, 3, 13113 CrossRef CAS; (c) A. B. Danne, A. S. Choudhari, D. Sarkar, J. N. Sangshetti, V. M. Khedkar and B. B. Shingate, Res. Chem. Intermed., 2018, 44, 6283 CrossRef CAS; (d) M. H. Shaikh, D. D. Subhedar, M. Arkile, V. M. Khedkar, N. Jadhav, D. Sarkar and B. B. Shingate, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 2016, 26, 561 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (e) M. H. Shaikh, D. D. Subhedar, B. B. Shingate, F. A. K. Khan, J. N. Sangshetti, V. M. Khedkar, L. Nawale, D. Sarkar, G. R. Navale and S. S. Shinde, Med. Chem. Res., 2016, 25, 790 CrossRef CAS; (f) M. H. Shaikh, D. D. Subhedar, F. A. K. Khan, J. N. Sangshetti and B. B. Shingate, Chin. Chem. Lett., 2016, 27, 295 CrossRef CAS; (g) M. H. Shaikh, D. D. Subhedar, V. M. Khedkar, P. C. Jha, F. A. K. Khan, J. N. Sangshetti and B. B. Shingate, Chin. Chem. Lett., 2016, 27, 1058 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) D. D. Subhedar, M. H. Shaikh, B. B. Shingate, L. Nawale, D. Sarkar, V. M. Khedkar, F. A. K. Khan and J. N. Sangshetti, Eur. J. Med. Chem., 2017, 125, 385 CrossRef CAS; (b) D. D. Subhedar, M. H. Shaikh, F. A. K. Khan, J. N. Sangshetti, V. M. Khedkar and B. B. Shingate, New J. Chem., 2016, 40, 3047 RSC; (c) D. D. Subhedar, M. H. Shaikh, B. B. Shingate, L. Nawale, D. Sarkar and V. M. Khedkar, Med. Chem. Commun., 2016, 7, 1832 RSC; (d) D. D. Subhedar, M. H. Shaikh, L. Nawale, A. Yeware, D. Sarkar, F. A. K. Khan, J. N. Sangshetti and B. B. Shingate, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 2016, 26, 2278 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (e) D. D. Subhedar, M. H. Shaikh, M. A. Arkile, A. Yeware, D. Sarkar and B. B. Shingate, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 2016, 26, 1704 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (f) M. H. Shaikh, D. D. Subhedar, F. A. Kalam Khan, J. N. Sangshetti and B. B. Shingate, Res. Chem. Intermed., 2016, 42, 5115 CrossRef CAS; (g) D. D. Subhedar, M. H. Shaikh, L. Nawale, A. Yeware, D. Sarkar and B. B. Shingate, Res. Chem. Intermed., 2016, 42, 6607 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) S. T. Dhumal, A. R. Deshmukh, K. R. Kharat, B. R. Sathe, S. S. Chavan and R. A. Mane, New J. Chem., 2019, 43, 7663 RSC; (b) C. P. Kaushik, R. Luxmi, M. Kumar, D. Singh, K. Kumar and A. Pahwa, Synth. Commun., 2019, 49, 118 CrossRef CAS; (c) G. Wang, Z. Peng, J. Wang, X. Li and J. Li, Eur. J. Med. Chem., 2017, 125, 423 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (d) P. Neeraja, S. Srinivas, K. Mukkanti, P. K. Dubey and S. Pal, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 2016, 26, 5212 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (e) G. Wang, Z. Peng, J. Wang, J. Li and X. Li, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 2016, 26, 5719 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Ferroni, A. Pepe, Y. Sang Kim, S. Lee, A. Guerrini, M. D. Parenti, A. Tesei, A. Zamagni, M. Cortesi, N. Zaffaroni, M. De Cesare, G. L. Beretta, J. B. Trepel, S. V. Malhotra and G. Varchi, J. Med. Chem., 2017, 60, 3082 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) K. Khan, In vitro and In vivo Screening Techniques for Bioactivity Screening and Evaluation, Proc. Int. Workshop UNIDO-CDRI, 1997, p. 210 Search PubMed; (b) A. H. Collins, Microbiological Methods, Butterworth, London, 2nd edn, 1976 Search PubMed.
- M. Burits and F. Bucar, Phytother. Res., 2000, 14, 323 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Li, D. Li, T. Xiao, S. Zhang, Z. Song and H. Ma, J. Agric. Food Chem., 2016, 23, 8927 CrossRef PubMed.
- V. S Dofe, A. P. Sarkate, D. K. Lokwani, S. H. Kathwate and C. H. Gill, Res. Chem. Intermed., 2017, 43, 15 CrossRef.
- S. G. Franzblau, R. S. Witzig and J. C. McLaughlin, J. Clin. Microbiol., 1998, 36, 362 CAS.
- (a) J. N. Sangshetti, F. A. Kalam Khan, R. S. Chouthe, M. G. Damale and D. B. Shinde, Chin. Chem. Lett., 2014, 25, 1033 CrossRef CAS; (b) R. W. Hooft, G. Vriend, C. Sander and E. E. Abola, Nature, 1996, 381, 272 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available. See DOI: 10.1039/c9ra03425k |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2019 |