Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleActivatable near-infrared emission-guided on-demand administration of photodynamic anticancer therapy with a theranostic nanoprobe†
Rongchen
Wang‡
a,
Kaikai
Dong‡
b,
Ge
Xu
a,
Ben
Shi
a,
Tianli
Zhu
a,
Ping
Shi
 *b,
Zhiqian
Guo
*b,
Zhiqian
Guo
 a,
Wei-Hong
Zhu
a,
Wei-Hong
Zhu
 a and
Chunchang
Zhao
a and
Chunchang
Zhao
 *a
*a
aKey Laboratory for Advanced Materials and Institute of Fine Chemicals, School of Chemistry and Molecular Engineering, East China University of Science & Technology, Shanghai 200237, P. R. China. E-mail: zhaocchang@ecust.edu.cn
bState Key Laboratory of Bioreactor Engineering, East China University of Science and Technology, Shanghai 200237, P. R. China. E-mail: ship@ecust.edu.cn
First published on 9th January 2019
Abstract
Development of theranostic probes that can be used to identify tumors and direct the on-demand drug administration to cancers is ongoing but remains challenging. Herein, we report a theranostic platform composed of a H2S-activated imaging probe and a light-sensitive drug. The designed probe affords advantages of H2S-activated NIR emission light-up and efficient 1O2 generation, enabling the selective visualization of H2S-rich cancers and the subsequent imaging-directed on-demand light exposure to the detected cancers while leaving normal tissues untouched. Such controllable administration of photodynamic anticancer therapy maximizes the therapeutic efficiency and minimizes side effects. This work should facilitate significant advances toward precise diagnosis and treatment of cancer.
Introduction
Precise cancer treatment relies on maximizing the toxic effect of anticancer drugs to tumor sites while minimizing the side effects to normal regions.1 To date, theranostic prodrug systems with integrated diagnostic and therapeutic functions have been developed as promising tools in precision cancer medicine.2 These systems are particularly useful for cancer therapy, providing activated release of drugs and concomitant in situ drug tracking capability in response to endogenous stimuli (including pH,3 hypoxia,4 increased glutathione levels,5 elevated oxidative stress,6 and specific enzyme overexpression7) and/or exogenous stimuli (including light8 and heat9). However, concurrent events including the diagnostic and therapeutic capabilities of the available theranostic prodrugs do not allow for diagnosis-directed on-demand therapy. Thus the search for image-guided prodrugs, in which the tumor can be diagnosed and the subsequent diagnosis controlled on-demand drug administration to the detected region could be realized, is ongoing but remains challenging.Photodynamic therapy (PDT) is a potent noninvasive therapeutic modality for a variety of cancers.10 PDT treatment utilizes a photosensitizer that serves as a light-sensitive drug to generate cytotoxic ROS upon light irradiation for disrupting cellular function and killing the cells in the exposed area.11 As light can provide the advantages of a noninvasiveness mode and precise spatiotemporal controllability, light-sensitive photosensitizers will cause less treatment-related toxicity and fewer side effects on adjacent normal tissues when compared with conventional chemotherapeutic reagents.12 Thus, a theranostic prodrug that integrates a diagnostic probe and a light-sensitive drug would be rather attractive because the tumor can be monitored and then diagnosis can precisely guide the on-demand light exposure to the detected region while leaving normal tissues untouched. Notably, the precise spatial location of the PDT agent and the timing of implementation of the light illumination are critical to maximize the therapeutic effect.
Herein, in this work, we reported a theranostic prodrug for activatable near-infrared emission-guided on-demand administration of photodynamic anticancer therapy. Although the appealing strategy for developing activatable PDT agents has been demonstrated to be an efficient way to control PDT selectivity to cancer cells while leaving normal cells unharmed, the construction of such an activatable photosensitizer requires judicious molecular design and is nontrivial.13 The theranostic prodrug (TNP-SO) platform here was composed of a H2S-activated imaging probe, NIR-BSO and a light-sensitive drug, 3I-BOD. The two units were linked by a short diethylene glycolamine spacer. Interestingly, NIR-BSO displayed H2S-dependent NIR emission light up, thus enabling the selective detection of H2S-rich cancer cells. More importantly, such cancer imaging precisely directed when and where to implement the light illumination of 3I-BOD to produce cytotoxic ROS for on-demand cancer therapy, thus maximizing the therapeutic efficiency and minimizing side effects.
Results and discussion
The target compound TNP-SO was readily synthesized in a sequence of steps, as illustrated in Schemes 1 and S1.† The light-sensitive drug 3I-BOD was modified with compound 3 to afford 4 with the requisite cyanoacetamide function, which was incorporated into p-thiocresol substituted BODIPY via a Knoevenagel condensation reaction with aldehyde BODIPY 5,14 thus affording an intermediate 6. Finally, conversion of a thioether unit with m-CPBA to a sulfoxide functional group produced the target theranostic prodrug TNP-SO in good yield. The identity and purity of all new compounds were verified by NMR and mass spectrometry.It is known that elevated H2S production is closely related to various cancers, such as ovarian, breast, and colorectal cancers.15 Accordingly, H2S-activated NIR emissions could provide a powerful tool for the accurate identification of these cancers. We first investigated the capability of TNP-SO as an activatable fluorescent probe toward H2S under physiological conditions (CH3CN/PBS, 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1, v/v, 20 mM, pH 7.4, and room temperature). As shown in Fig. 1, TNP-SO showed a mild absorption and a strong absorption with maxima at 500 and 533 nm, corresponding to NIR-BSO and 3I-BOD, respectively. Notably, the absorption of 3I-BOD partially obscures that of NIR-BSO owing to spectral overlap. Upon the treatment with 100 μM H2S, the absorption band at 500 nm decreased obviously accompanied by the emergence of a new absorption band around 655 nm, affording a dramatic red-shift of 155 nm. More importantly, this process activated a robust NIR fluorescence at 712 nm that produced about 137-fold enhancement upon excitation at 640 nm. Such optical changes were ascribed to the conversion of TNP-SO into corresponding TNP-HS, proven by HRMS analysis (Fig. S1†). Collectively, TNP-SO exhibited H2S-triggered NIR emission light up, and thus preferable for in vivo visualization of H2S-rich cancers due to the deep penetration ability, minimal tissue absorption and low background autofluorescence in the NIR region.16
1, v/v, 20 mM, pH 7.4, and room temperature). As shown in Fig. 1, TNP-SO showed a mild absorption and a strong absorption with maxima at 500 and 533 nm, corresponding to NIR-BSO and 3I-BOD, respectively. Notably, the absorption of 3I-BOD partially obscures that of NIR-BSO owing to spectral overlap. Upon the treatment with 100 μM H2S, the absorption band at 500 nm decreased obviously accompanied by the emergence of a new absorption band around 655 nm, affording a dramatic red-shift of 155 nm. More importantly, this process activated a robust NIR fluorescence at 712 nm that produced about 137-fold enhancement upon excitation at 640 nm. Such optical changes were ascribed to the conversion of TNP-SO into corresponding TNP-HS, proven by HRMS analysis (Fig. S1†). Collectively, TNP-SO exhibited H2S-triggered NIR emission light up, and thus preferable for in vivo visualization of H2S-rich cancers due to the deep penetration ability, minimal tissue absorption and low background autofluorescence in the NIR region.16
The photosensitizing generation of 1O2 induced by the light-sensitive drug 3I-BOD in TNP-SO under 530 nm light irradiation was evaluated using 1,3-diphenylbenzofuran (DPBF) as the 1O2 indicator and MB as the standard (ΦΔ = 52%).17 It was found that TNP-SO showed a relatively high singlet-oxygen yield (ΦΔ = 49%) because of the heavy atom effect that facilitates intersystem crossing (ISC) of the excited energy (Fig. S2†). Notably, the formation of TNP-SH had minimal effect on the production efficiency of 1O2. Therefore, the theranostic TNP-SO would be suitable for imaging-guided on-demand administration of photodynamic therapy of cancers expressing elevated levels of H2S.
In light of the low solubility of TNP-SO in aqueous solution, the nanoplatform Nano-TNP-SO was generated by encapsulating TNP-SO into the hydrophobic interior of water-dispersible silica nanocomposites according to a previously established method (Scheme 2).18 The loading efficiency of TNP-SO was determined with UV/vis absorbance spectra to be 0.96 wt%. Characterization of the resulting Nano-TNP-SO was performed by dynamic light scattering (DLS) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) (Scheme 2), which showed that the hydrodynamic diameter of Nano-TNP-SO remained at 98 nm and negligible aggregation was observed in aqueous solutions for days (Fig. S3†).
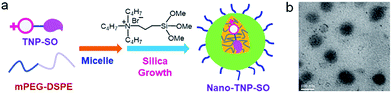 | ||
| Scheme 2 (a) Schematic illustration of the generation of Nano-TNP-SO. (b) Characterization of Nano-TNP-SO by TEM. Scale bars: 100 nm. | ||
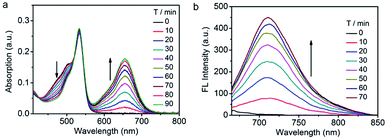
Next, the photophysical response of Nano-TNP-SO toward H2S was evaluated in PBS buffer solutions (pH 7.4). As shown in Fig. 2, the absorption maxima at 509 and 537 nm of NIR-BSO and 3I-BOD in silica nanocomposites showed a slightly bathochromic shift when compared to those in CH3CN/PBS. Interestingly, H2S-induced dramatic optical changes remained after the encapsulation of TNP-SO. The addition of NaHS elicited the generation of the NIR absorption at 677 nm and reduction of the absorption at 509 nm (Fig. 2a). Specifically, a significant increase in the fluorescence intensity at 712 nm was noted upon excitation at 640 nm (Fig. 2b). Notably, the reaction time of 70 min between TNP-SO and H2S in CH3CN/PBS was relatively slow. In contrast, the reaction of TNP-SO with H2S in Nano-TNP-SO was markedly accelerated, reaching completion within 20 min (Fig. 2c). Moreover, the NIR fluorescence exhibited a linear increase with H2S concentration (0–20 μM), determining the detection limit to be 21 nM which indicates the high sensitivity of Nano-TNP-SO for the detection of H2S (Fig. 2d). Minimal optical responsiveness was observed in the presence of biologically related reactive sulfur (RSS), oxygen (ROS), and nitrogen species (RNS), indicative of its high selectivity for H2S (Fig. 2e). Importantly, Nano-TNP-SO could also act as a good photosensitizer for the production of 1O2 (ΦΔ = 32%) in PBS upon exposure to 530 nm light (Fig. 2f and S4†). In addition, Nano-TNP-SO exhibited good photostability (Fig. S5†) in aqueous solution, a critical factor for biomedical applications. Taken together, these advantages, including H2S-activated NIR emission light-up and efficient 1O2 generation, make Nano-TNP-SO a promising tool for the identification of cancers and the subsequent imaging-directed on-demand administration of photodynamic anticancer therapy.
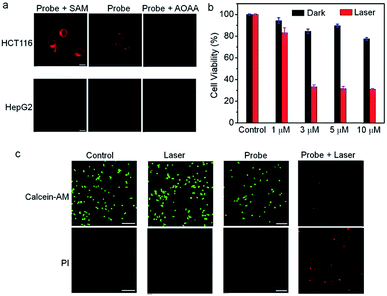
To explore the capability of Nano-TNP-SO as an imaging probe for guiding where to implement the light illumination of 3I-BOD to produce cytotoxic ROS, the ability to selectively visualize H2S-rich cancer cells was investigated. As shown in Fig. 3, HCT116 cells that express high levels of H2S gave strong NIR fluorescence signals upon incubation with Nano-TNP-SO for 1 h. The presence of a CBS inhibitor aminooxyacetic acid (AOAA) significantly attenuated the fluorescence image due to the inhibition of cellular generation of H2S. In contrast, increase of H2S levels via stimulation with an allosteric CBS activator S-adenosyl-L-methionine (SAM) led to much stronger fluorescence. As expected, HepG2 cells with the minimized level of H2S afford weak NIR fluorescence. AOAA and SAM also displayed a negligible effect on the fluorescence images (Fig. 3a). On this basis, it can be concluded that Nano-TNP-SO is selectively activated to light up NIR fluorescence in H2S-rich cancer cells, thus facilitating the accurate administration of PDT. According to the aforementioned imaging result, the cytotoxicity of Nano-TNP-SO toward HCT116 cells was then studied in the absence and presence of 530 nm light irradiation. MTT assay clearly demonstrated that Nano-TNP-SO showed low cytotoxicity in the absence of light. In contrast, greater cell death was seen in the case of HCT116 cells upon simultaneous treatment with Nano-TNP-SO and light irradiation at 530 nm (100 mW cm−2) for 10 min (Fig. 3b). The cell death induced by the Nano-TNP-SO mediated PDT was also evaluated using staining experiments with calcein acetoxymethyl ester/propidium iodide (calcein-AM/PI). As shown in Fig. 3c, treatment of cells with either Nano-TNP-SO or a 530 nm laser alone resulted in predominantly calcein AM-dependent green fluorescence, whereas PI-positive red signals were noted in cells upon treatment with Nano-TNP-SO (TNP-SO 5 μM) plus a 530 nm laser. These imaging results further demonstrated the low dark cytotoxicity and high photocytotoxicity of Nano-TNP-SO. Costaining experiments were employed to identify the location of Nano-TNP-SO utilizing commercially available Mito-Tracker Green and Lyso-Tracker Green (Fig. S6†). It was found that H2S-activated red fluorescence from Nano-TNP-SO showed good overlap with green fluorescence from Mito-Tracker Green or Lyso-Tracker Green, indicative of nonspecific intracellular localization.
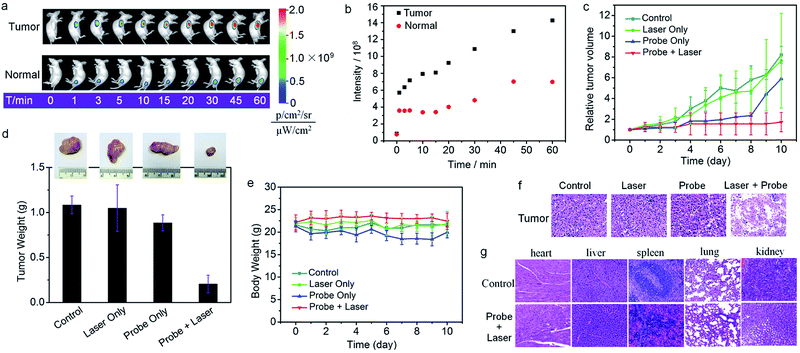
Inspired by the aforementioned promising results, in vivo imaging-guided on demand PDT was evaluated. As shown in Fig. 4, a HCT116 tumor-bearing mouse treated with Nano-TNP-SO displayed tumor-specific activation of NIR fluorescence as early as 1 min post-injection, whereas injection of Nano-TNP-SO into the normal muscle gave weak fluorescence. Region of interest measurements gave a NIR fluorescence signal ratio between the tumor and the normal site of 1.9 (5 min), 2.3 (10 min), 2.2 (30 min) and 2.0 (60 min). In addition, such specific NIR fluorescence signals in the tumor region were significantly reduced upon the pretreatment of the tumor with aminooxyacetic acid (AOAA), a cystathionine-β-synthase (CBS) inhibitor. Since the overexpression of CBS contributes to increased H2S levels in colon cancer, the inhibition of CBS activity by AOAA attenuated H2S levels and thus led to the reduction of NIR fluorescence signals (Fig. S7†). All these results indicated that Nano-TNP-SO can be specifically lit up in H2S-rich colorectal cancers, correspondingly identifying the spatial location of the PDT agent and the timing of implementation of the light illumination. We next assessed the PDT effect of Nano-TNP-SO on tumors in HCTT116 tumor-bearing mice. After intratumor administration of Nano-TNP-SO and light irradiation, tumor growth was remarkably suppressed (Fig. 4c). As a control, minimal tumor growth inhibition was observed in mice treated with Nano-TNP-SO or laser exposure alone. The tumor inhibition efficiency of PDT was calculated to be around 82% at 10 d after treatment (Fig. 4d). The H&E staining analysis demonstrated that significant cancer cell necrosis was noticed in the tumor section with both Nano-TNP-SO administration and light irradiation, indicative of high therapeutic efficiency toward the tumor cells by the PDT with Nano-TNP-SO. The tumor tissues in control groups including no treatment and treatment with a laser or Nano-TNP-SO alone showed indiscernible necrosis, suggesting that Nano-TNP-SO has negligible dark toxicity. In addition to no obvious changes of the body weights in mice with various treatments (Fig. 4e), no noticeable organ damage was observed in mice using H&E stained images of major organs (heart, liver, spleen, lung, and kidney). These results clearly indicate the low toxic effect of PDT using Nano-TNP-SO.
Live subject statement
All animal experiments were performed in compliance with Chinese legislation on the Use and Care of Research Animals, and institutional guidelines for the Care and Use of laboratory animals established by the East China University of Science and Technology Animal Studies Committee. The experimental procedures and protocols were approved by this committee.Conclusions
In conclusion, we have designed and synthesized a theranostic probe for activatable near-infrared emission-guided on-demand administration of PDT. The new obtained small molecule probe was encapsulated into the hydrophobic interior of silica nanocomposites for the fabrication of a nanoprobe with good aqueous solubility and photostability. This nanoprobe displayed H2S-dependent NIR emission light up, preferable for in vivo visualization of H2S-rich cancers. In addition, the nanoprobe could also act as a good photosensitizer for efficient production of 1O2. By exploiting these advantages, we employed such a probe for in vivo PDT, which revealed that cancer imaging precisely directed where to implement the light illumination to produce cytotoxic ROS for on-demand cancer therapy, thus maximizing the therapeutic efficiency and minimizing side effects. We expect that our design approach could promote new advancements in the areas of cancer diagnosis and therapy.Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no competing financial interest.Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge the financial support by the National Science Foundation of China (grant numbers 21672062, 31671309).Notes and references
- A. Umar, B. K. Dunn and P. Greenwald, Nat. Rev. Cancer, 2012, 12, 835 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) M. H. Lee, Z. Yang, C. W. Lim, Y. H. Lee, S. Dongbang, C. Kang and J. S. Kim, Chem. Rev., 2013, 113, 5071 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) Q. Hu, M. Gao, G. Feng and B. Liu, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2014, 53, 14225 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) S. S. Kelkar and T. M. Reineke, Bioconjugate Chem., 2011, 22, 1879 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (d) X. Chen, S. S. Gambhir and J. Cheon, Acc. Chem. Res., 2011, 44, 841 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (e) H. Shi, R. T. K. Kwok, J. Liu, B. Xing, B. Z. Tang and B. Liu, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2012, 134, 17972 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (f) J. V. Jokerst and S. S. Gambhir, Acc. Chem. Res., 2011, 44, 1050 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (g) M. Gao, F. Yu, C. Lv, J. Choo and L. Chen, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2017, 46, 2237 RSC; (h) M. H. Lee, A. Sharma, M. J. Chang, J. Lee, S. Son, J. L. Sessler, C. Kang and J. S. Kim, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2018, 47, 28 RSC.
- (a) X. He, J. Li, S. An and C. Jiang, Ther. Delivery, 2013, 4, 1499 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) J. Tian, L. Ding, H.-J. Xu, Z. Shen, H. Ju, L. Jia, L. Bao and J.-S. Yu, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2013, 135, 18850 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) M. R. Ke, D. K. P. Ng and P. C. Lo, Chem. Commun., 2012, 48, 9065 RSC; (d) Z. Dong, L. Feng, Y. Hao, M. Chen, M. Gao, Y. Chao, H. Zhao, W. Zhu, J. Liu, C. Liang, Q. Zhang and Z. Liu, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2018, 140, 2165 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) Q. Lin, C. Bao, Y. Yang, Q. Liang, D. Zhang, S. Cheng and L. Zhu, Adv. Mater., 2013, 25, 1981 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) Y. Li, Y. Sun, J. Li, Q. Su, W. Yuan, Y. Dai, C. Han, Q. Wang, W. Feng and F. Li, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2015, 137, 6407 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) H. S. Jung, J. Han, H. Shi, S. Koo, H. Singh, H.-J. Kim, J. L. Sessler, J. Y. Lee, J.-H. Kim and J. S. Kim, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2017, 139, 7595 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) Z. Yang, J. H. Lee, H. M. Jeon, J. H. Han, N. Park, Y. He, H. Lee, K. S. Hong, C. Kang and J. S. Kim, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2013, 135, 11657 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) F. Wang, L. Zhou, C. Zhao, R. Wang, Q. Fei, S. Luo, Z. Guo, H. Tian and W. Zhu, Chem. Sci., 2015, 6, 2584 RSC; (c) Z. Zhao, H. Meng, N. Wang, M. J. Donovan, T. Fu, M. You, Z. Chen, X. Zhang and W. Tan, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2013, 52, 7487 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (d) J. Zhang, Z. F. Yuan, Y. Wang, W. H. Chen, G. F. Luo, S. X. Cheng, R. X. Zhuo and X. Z. Zhang, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2013, 135, 5068 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (e) X. Wu, X. Sun, Z. Guo, J. Tang, Y. Shen, T. D. James, H. Tian and W. Zhu, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2014, 136, 3579 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (f) S. Bhuniya, S. Maiti, E.-J. Kim, H. Lee, J. L. Sessler, K. S. Hong and J. S. Kim, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2014, 53, 4469 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (g) C. Yan, Z. Guo, Y. Shen, Y. Chen, H. Tian and W.-H. Zhu, Chem. Sci., 2018, 9, 4959 RSC; (h) G. Yu, Z. Yang, X. Fu, B. C. Yung, J. Yang, Z. Mao, L. Shao, B. Hua, Y. Liu, F. Zhang, Q. Fan, S. Wang, O. Jacobson, A. Jin, C. Gao, X. Tang, F. Huang and X. Chen, Nat. Commun., 2018, 9, 766 CrossRef PubMed.
- (a) H.-W. Liu, X.-X. Hu, K. Li, Y. Liu, Q. Rong, L. Zhu, L. Yuan, F.-L. Qu, X.-B. Zhang and W. Tan, Chem. Sci., 2017, 8, 7689 RSC; (b) R. Kumar, J. Han, H. Lim, W. X. Ren, J.-Y. Lim, J.-H. Kim and J. S. Kim, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2014, 136, 17836 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) G. Saravanakumar, J. Kim and W. J. Kim, Adv. Sci., 2017, 4, 1600124 CrossRef PubMed; (d) E.-J. Kim, S. Bhuniya, H. Lee, H. M. Kim, C. Cheong, S. Maiti, K. S. Hong and J. S. Kim, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2014, 136, 13888 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (e) X. Xu, P. E. Saw, W. Tao, Y. Li, X. Ji, S. Bhasin, Y. Liu, D. Ayyash, J. Rasmussen, M. Huo, J. Shi and O. C. Farokhzad, Adv. Mater., 2017, 29, 1700141 CrossRef PubMed; (f) C. Chu, H. Lin, H. Liu, X. Wang, J. Wang, P. Zhang, H. Gao, C. Huang, Y. Zeng, Y. Tan, G. Liu and X. Chen, Adv. Mater., 2017, 29, 1605928 CrossRef PubMed.
- (a) X. Li, Y. Hou, X. Meng, C. Ge, H. Ma, J. Li and J. Fang, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2018, 57, 6141 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) J. B. Wu, T.-P. Lin, J. D. Gallagher, S. Kushal, L. W. K. Chung, H. E. Zhau, B. Z. Olenyuk and J. C. Shih, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2015, 137, 2366 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) G. Zheng, J. Chen, K. Stefflova, M. Jarvi, H. Li and B. C. Wilson, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., 2007, 104, 8989 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (d) M. Chiba, Y. Ichikawa, M. Kamiya, T. Komatsu, T. Ueno, K. Hanaoka, T. Nagano, N. Lange and Y. Urano, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2017, 56, 10418 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (e) X. Zhen, J. Zhang, J. Huang, C. Xie, Q. Miao and K. Pu, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2018, 57, 1 CrossRef.
- (a) G. Collet, T. Lathion, C. Besnard, C. Piguet and S. Petoud, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2018, 140, 10820 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) K. Mitra, C. E. Lyons and M. C. T. Hartman, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2018, 57, 10263 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) S. Luo, X. Tan, S. Fang, Y. Wang, T. Liu, X. Wang, Y. Yuan, H. Sun, Q. Qi and C. Shi, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2016, 26, 2826 CrossRef CAS; (d) Y. Min, J. Li, F. Liu, E. K. L. Yeow and B. Xing, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2014, 53, 1012 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (e) M. Karimi, P. S. Zangabad, S. B.-R. M. Ghazadeh, H. Mirshekari and M. R. Hamblin, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2017, 139, 4584 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (f) L. Zhao, J. Peng, Q. Huang, C. Li, M. Chen, Y. Sun, Q. Lin, L. Zhu and F. Li, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2014, 24, 363 CrossRef CAS; (g) R.-F. Wang, H.-Q. Peng, P.-Z. Chen, L.-Y. Niu, J.-F. Gao, L.-Z. Wu, C.-H. Tung, Y.-Z. Chen and Q.-Z. Yang, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2016, 26, 5419 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) W. Tang, Z. Yang, S. Wang, Z. Wang, J. Song, G. Yu, W. Fan, Y. Dai, J. Wang, L. Shan, G. Niu, Q. Fan and X. Chen, ACS Nano, 2018, 12, 2610 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) C. Zhu, D. Huo, Q. Chen, J. Xue, S. Shen and Y. Xia, Adv. Mater., 2017, 1703702 CrossRef PubMed.
- (a) L. Cheng, C. Wang, L. Feng, K. Yang and Z. Liu, Chem. Rev., 2014, 114, 10869 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) X. Li, N. Kwon, T. Guo, Z. Liu and J. Yoon, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2018, 57, 11522 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) M. Triesscheijn, P. Baas, J. H. Schellens and F. A. Stewart, Oncologist, 2006, 11, 1034 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) C. Robertson, D. H. Evans and H. Abrahamse, J. Photochem. Photobiol., B, 2009, 96, 1 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) S. S. Lucky, K. C. Soo and Y. Zhang, Chem. Rev., 2015, 115, 1990 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) L. Huang, Z. Li, Y. Zhao, Y. Zhang, S. Wu, J. Zhao and G. Han, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2016, 138, 14586 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) D. E. J. G. J. Dolmans, D. Fukumura and R. K. Jain, Nat. Rev. Cancer, 2003, 3, 380 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) X. Li, S. Lee and J. Yoon, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2018, 47, 1174 RSC.
- (a) X. Li, D. Lee, J. Huang and J. Yoon, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2018, 57, 9885 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) X. Li, C.-Y. Kim, S. Lee, D. Lee, H. Chung, G. Kim, S.-H. Heo, C. Kim, K. Hong and J. Yoon, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2017, 139, 10880 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) Y. Ma, X. Li, A. Li, P. Yang, C. Zhang and B. Tang, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2017, 56, 13752 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (d) F. Hu, Y. Yuan, D. Mao, W. Wu and B. Liu, Biomaterials, 2017, 144, 53 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (e) W. Wu, D. Mao, F. Hu, S. Xu, C. Chen, C. Zhang, X. Cheng, Y. Yuan, D. Ding, D. Kong and B. Liu, Adv. Mater., 2017, 29, 1700548 CrossRef PubMed; (f) Z. Zhou, J. Song, R. Tian, Z. Yang, G. Yu, L. Lin, G. Zhang, W. Fan, F. Zhang, G. Niu, L. Nie and X. Chen, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2017, 56, 6492 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (g) M. Li, X. Li, Z. Cao, Y. Wu, J.-A. Chen, J. Gao, Z. Wang, W. Guo and X. Gu, Eur. J. Med. Chem., 2018, 157, 599 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) F. Wang, G. Xu, X. Gu, Z. Wang, Z. Wang, B. Shi, C. Lu, X. Gong and C. Zhao, Biomaterials, 2018, 159, 82 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) C. Zhao, X. Zhang, K. Li, S. Zhu, Z. Guo, L. Zhang, F. Wang, Q. Fei, S. Luo, P. Shi, H. Tian and W. Zhu, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2015, 137, 8490 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) G. Xu, Q. Yan, X. Lv, Y. Zhu, K. Xin, B. Shi, R. Wang, J. Chen, W. Gao, P. Shi, C. Fan, C. Zhao and H. Tian, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2018, 57, 3626 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) B. Shi, X. Gu, Q. Fei and C. Zhao, Chem. Sci., 2017, 8, 2150 RSC; (c) C. Szabo, C. Coletta, C. Chao, K. Módis, B. Szczesny, A. Papapetropoulos and M. R. Hellmich, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., 2013, 110, 12474 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (d) B. Shi, Q. Yan, J. Tang, K. Xin, J. Zhang, Y. Zhu, G. Xu, R. Wang, J. Chen, W. Gao, T. Zhu, J. Shi, C. Fan, C. Zhao and H. Tian, Nano Lett., 2018, 18, 6411 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (e) K. Zhang, J. Zhang, Z. Xi, L.-Y. Li, X. Gu, Q.-Z. Zhang and L. Yi, Chem. Sci., 2017, 8, 2776 RSC.
- (a) Y. M. Yang, Q. Zhao, W. Feng and F. Y. Li, Chem. Rev., 2012, 113, 192 CrossRef PubMed; (b) Q. Miao, D. C. Yeo, C. Wiraja, J. Zhang, X. Ning, C. Xu and K. Pu, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2018, 57, 1256 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) Z. Guo, S. Park, J. Yoon and I. Shin, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2014, 43, 16 RSC; (d) L. Yuan, W. Lin, K. Zheng, L. He and W. Huang, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2013, 42, 622 RSC; (e) Q. Fei, X. Gu, Y. Liu, B. Shi, H. Liu, G. Xu, C. Li, P. Shi and C. Zhao, Org. Biomol. Chem., 2017, 15, 4072 RSC; (f) L.-Y. Niu, Y.-Z. Chen, H.-R. Zheng, L.-Z. Wu, C.-H. Tung and Q.-Z. Yang, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2015, 44, 6143 RSC.
- N. Adarsh, R. R. Avirah and D. Ramaiah, Org. Lett., 2010, 12, 5720 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) B. Shi, X. Gu, Z. Wang, G. Xu, Q. Fei, J. Tang and C. Zhao, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2017, 9, 35588 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) B. M. Weckhuysen and J. Yu, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2015, 44, 7022 RSC.
Footnotes |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available: Procedures for synthesis, characterization data, and supplementary figures. See DOI: 10.1039/c8sc04854a |
| ‡ These authors contributed equally to this work. |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2019 |