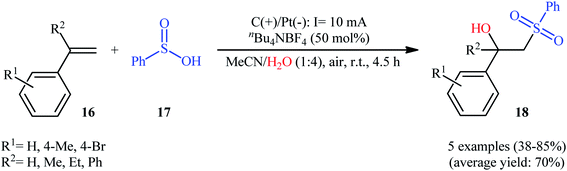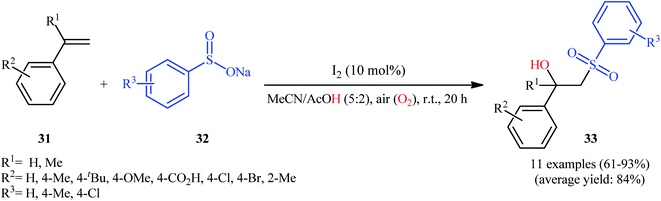Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleHydroxysulfonylation of alkenes: an update
Zinatossadat Hossaini
 *a,
Evan Abdulkareem Mahmood
b,
Mohammad Reza Poor Heravi
*a,
Evan Abdulkareem Mahmood
b,
Mohammad Reza Poor Heravi
 c,
Abdol Ghaffar Ebadi
d and
Esmail Vessally
c,
Abdol Ghaffar Ebadi
d and
Esmail Vessally
 c
c
aDepartment of Chemistry, Qaemshahr Branch, Islamic Azad University, Qaemshahr, Iran. E-mail: zs.hossaini@qaemiau.ac.ir; zshossaini@yahoo.com
bMedical Laboratory Science Department, College of Health Science, University of Human Development, Sulaimanyiah, Kurdistan region of Iraq
cDepartment of Chemistry, Payame Noor University, P.O. Box 19395-3697, Tehran, Iran. E-mail: vessally@pnu.ac.ir
dDepartment of Agriculture, Jouybar Branch, Islamic Azad University, Jouybar, Iran
First published on 18th June 2021
Abstract
The direct difunctionalization of inexpensive and widely available alkenes has been recognized as a strong and straightforward tool for the rapid fabrication of complex molecules and pharmaceutical targets by introducing two different functional groups on adjacent carbon atoms of common alkene moieties in a single operation. This synthetic strategy avoids the purification and isolation of the intermediates and thus makes synthetic schemes shorter, simpler and cleaner. In this family of reactions, the hydroxysulfonylation of alkenes has emerged as an increasingly promising strategy for the synthesis of β-hydroxysulfones, which are found in many biologically important molecules and widespread applications in organic synthesis. The objective of this review is to illustrate the advancements in the field of hydroxysulfonylation of alkenes with special emphasis on the mechanistic details of the reaction pathways.
1. Introduction
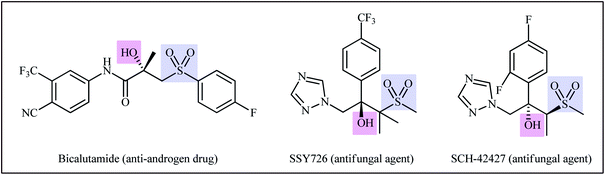
Sulfones are an important class of pharmacophores which are widely found in human and veterinary medicine.1 About ten FDA-approved drugs contain a sulfone unit in their structure and are used to treat various diseases such as leprosy, lung cancer, trichomoniasis, psoriatic arthritis, migraine headaches, and muscle spasms.2 In this family of organosulfur compounds, β-hydroxysulfones not only exhibit a range of pharmacological activities (Scheme 1)3 but are also used as versatile intermediates in organic synthesis.4 Traditionally, β-hydroxysulfones are obtained through reduction of β-keto-sulfones,5 hydroxylation of α,β-unsaturated sulfones,6 and nucleophilic ring opening of epoxides with sulfinate salts.7 However, these transformations suffer from certain drawbacks, such as production of unwanted byproducts, requirement of pre-functionalized starting materials and harsh reaction conditions.8 Therefore, development of efficient, straightforward, and environmentally benign synthetic strategies for the preparation of the titled compounds from inexpensive and easily available starting materials is highly desirable.The vicinal difunctionalization of alkenes has evolved to be one of the most effective and straightforward strategies to integrate small molecules toward structurally complex architectures via introduction of two different functional groups within a single click.9,10 In this regard, the direct hydroxysulfonylation of alkenes has emerged as a promising strategy for the construction of β-hydroxysulfone derivatives (Fig. 1). Recently Terent'ev and colleagues briefly highlighted this novel page of β-hydroxysulfone synthesis in their appealing review paper entitled “oxidative sulfonylation of multiple carbon–carbon bonds with sulfonyl hydrazides, sulfinic acids and their salts”.11 However, only eight works were cited in the relevant section and a significant number of recent examples were omitted. Therefore, of course, there is still a need for summarization of available literature on this chemistry in a comprehensive review with insightful mechanistic discussions, which can be helpful to compare efficiency of various protocols and inspire further research efforts on the field. In connection with our review articles on organosulfur chemistry12 and modern organic synthesis,13 herein, we will summarize a variety of methods for the synthesis of β-hydroxysulfones via the one-pot hydroxysulfonylation of alkenes. For clarity, we structured this topic based on the type of sulfonylating agents. It is worth mentioning that a special emphasis is placed on mechanistic aspects of reactions. Of note, we have not discussed oxosulfonylation reactions, since it has recently been described in another publication.14
2. Sulfonyl chlorides as sulfonylating agents
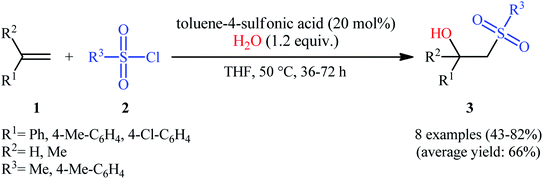
The first successful synthesis of β-hydroxysulfones via the direct hydroxysulfonylation of corresponding alkenes was disclosed in 2004 by Xi and co-workers,15 who reported an acid-promoted three-component reaction between terminal alkenes 1, sulfonyl chlorides 2, and water in THF (Scheme 2). In this preliminary work, eight β-hydroxysulfone derivatives 3 were synthesized in moderate to high yields, ranging from 43% to 82%. Various mono- and 1,1-di-substituted alkenes and both alkyl and aryl sulfonyl chlorides were compatible substrates in this difunctionalization reaction. However, no internal alkene was exemplified in the protocol. It should be mentioned that the reaction demonstrated an excellent level of regioselectivity, in which the hydroxyl group was predominantly introduced to the more hindered carbon atom of the double bond. The authors described a plausible mechanism for this transformation as illustrated in Scheme 3. It consists of the following key steps: (i) protonation of the oxygen atom in sulfonyl chloride 2 with acid to form the electrophilic intermediate A; (ii) nucleophilic attack of alkene 1 to this intermediate A to produce carbocationic intermediate B; (iii) intramolecular cyclization of B to yield intermediate C; (iv) deprotonation of C to generate oxathietane D; (v) cleavage of the O–S bond of D by water to produce the intermediate E; (vi) intramolecular H-transfer of E to give sulfurochloridous acid F; and (vii) elimination of HCl from F to give the desired β-hydroxysulfone 3.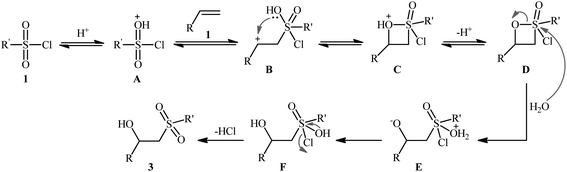 | ||
| Scheme 3 Possible mechanism for the reaction in Scheme 2. | ||
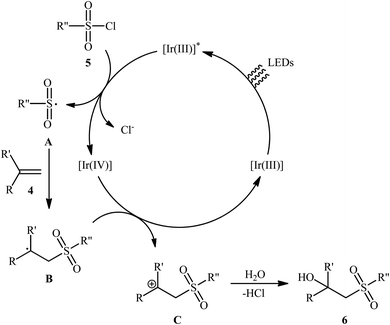
Twelve years later, Reiser's research team developed the photoredox-catalyzed version of this hydroxysulfonylation reaction using [fac-Ir(ppy)3] as the photocatalyst.16 The reaction of various α- and β-substituted styrenes 4 with sulfonyl chlorides 5 in the presence of only 1 mol% of catalyst in binary solvent MeCN/H2O with ratio 5![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 under the irradiation of blue LEDs at ambient temperature could give the highly functionalized β-hydroxysulfones 6 in good to almost quantitative yields within 10–24 h (Scheme 4). The catalyst was, however, not effective for aliphatic and benzylic alkenes. In Scheme 5 a plausible mechanism for this transformation is depicted. In the beginning, the ground state Ir(III) photoredox catalyst undergoes excitation by irradiation with blue light to produce the excited state *Ir(III), which after a single-electron transfer (SET) to sulfonyl chloride 5 leads to the formation of the sulfonyl chloride A and strongly oxidizing Ir(IV). Next, regioselective sulfonyl radical A addition to styrene 4 takes place to form the carbon-centered radical intermediate B that, after oxidization by Ir(IV) produces the carbocation intermediate C and regenerates Ir(III) catalyst. Finally, nucleophilic addition of H2O on the carbocation C provides the desired β-hydroxysulfone 6.
1 under the irradiation of blue LEDs at ambient temperature could give the highly functionalized β-hydroxysulfones 6 in good to almost quantitative yields within 10–24 h (Scheme 4). The catalyst was, however, not effective for aliphatic and benzylic alkenes. In Scheme 5 a plausible mechanism for this transformation is depicted. In the beginning, the ground state Ir(III) photoredox catalyst undergoes excitation by irradiation with blue light to produce the excited state *Ir(III), which after a single-electron transfer (SET) to sulfonyl chloride 5 leads to the formation of the sulfonyl chloride A and strongly oxidizing Ir(IV). Next, regioselective sulfonyl radical A addition to styrene 4 takes place to form the carbon-centered radical intermediate B that, after oxidization by Ir(IV) produces the carbocation intermediate C and regenerates Ir(III) catalyst. Finally, nucleophilic addition of H2O on the carbocation C provides the desired β-hydroxysulfone 6.
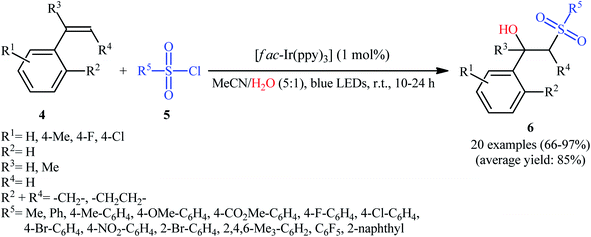 | ||
| Scheme 4 Visible light mediated synthesis of β-hydroxysulfones 6 through the reaction of styrenes 4 and sulfonyl chlorides 5 in the presence of water. | ||
Very recently, in a related investigation, Li and Wang along with their co-workers reported the use of [Ru(bpy)3]Cl2·6H2O in combination with K2HPO4 for regioselective hydroxysulfonylation of alkylidenecyclopropanes 7 with sulfonyl chloride 8 and water under the irradiation of 12 W blue LEDs.17 The reactions were implemented under an inert atmosphere (N2) at room temperature, tolerated a wide range of important functional groups on both the substrates, and afforded the target cyclopropane-containing β-hydroxysulfones 9 in fair to excellent yields (Scheme 6). The authors further demonstrated that cyclobutane-containing β-hydroxysulfones could also be achieved in modest yields when alkylidenecyclobutanes were used as substrates. Noteworthy, the protocol was also applicable for gram-scale synthesis of cyclopropane-containing β-hydroxysulfones as exemplified by the formation of diphenyl(1-tosylcyclopropyl)methanol on a 1.59 g scale (84%).
3. Sulfinic acids as sulfonylating agents
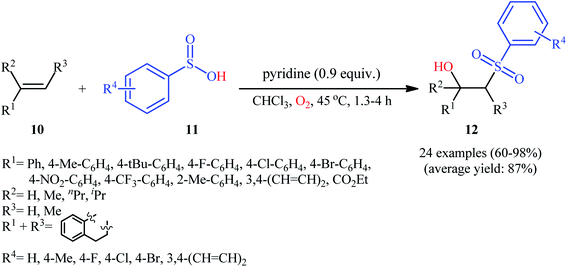
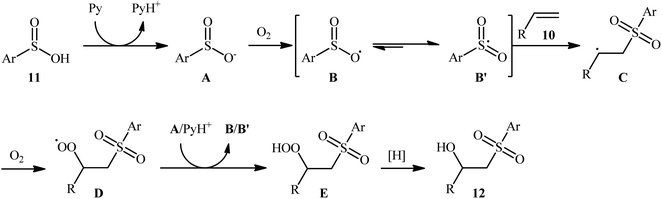
In 2013, Lei and co-workers disclosed the first direct oxidative difunctionalization of alkenes 10 with sulfinic acids 11 through dioxygen activation to construct β-hydroxysulfone derivatives 12 (Scheme 7).18 A near stoichiometric amount of pyridine was used as base and CHCl3 as solvent. Terminal, 1,1- and 1,2-disubstituted alkenes reacted well with various aromatic sulfinic acids bearing electron-withdrawing or -donating groups to generate the corresponding products in good to excellent yields. To elucidate the origination of the hydroxyl oxygen atom of the products, the authors performed a 18O2 isotope labeling experiment. The results demonstrated that the oxygen atom in β-hydroxysulfones came from O2. Furthermore, the radical trapping experiments with TEMPO (2,2,6,6-tetramethyl-1-piperidinyloxy) and BHT (2,4-di-tert-butyl-4-methylphenol) revealed that the radical processes might be involved in this difunctionalization reaction (Scheme 8). In the presence of pyridine and oxygen, the sulfonyl radical B′ was formed from benzenesulfinic acid 11 by a single-electron transfer process through the intermediate A. Addition of this radical B′ to alkene 10 provided carbon-centered radical C, followed by a redox-transfer process to generate alkylhydroperoxy radical intermediate D. Thereafter, the newly formed radical D was converted to β-peroxylsulfone intermediate E through a SET process and concomitant proton transfer from A and pyridium benzenesulfonate. And then, reduction of E by benzenesulfinic acid 11 or workup with PPh3 furnished the difunctionalized product 12.Three years later, the same group disclosed that synthetically challenging 2-sulfonyl allylic alcohols 15 could be effectively prepared in highly regio- and stereoselective manner from the reaction of allenes 13 with arenesulfinic acids 14 in the presence of 3.5 equiv. of pyridine under air atmosphere (Scheme 9).19 In the investigation of the scope of this transformation, it was found that the presence of an aryl substituent on the double bond was vital for the success of the reaction. When ester-substituted allenes were used as substrates under the identical conditions, terminal alkene products were generated instead. Moreover, the concentration of dioxygen had a great influence on the reaction. When the reaction was carried out under O2 atmosphere instead of air, it turned generated a complex product mixture.
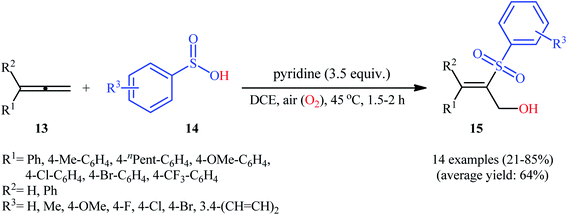 | ||
| Scheme 9 Regio- and stereoselective hydroxysulfonylation allenes 13 with arenesulfinic acids 14 reported by Lei. | ||
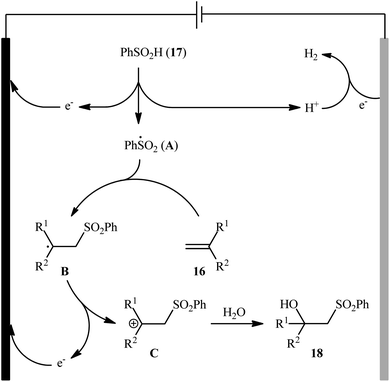
Very recently, Sun and colleagues developed an interesting electrochemical approach for regioselective hydroxysulfonylation of styrene derivatives 16 employing benzenesulfinic acid 17 as the sulfonylating reagent and water as hydroxylating agent.20 The optimal system was identified using nBu4NBF4 (tetrabutylammonium tetrafluoroborate) as an electrolyte with an undivided graphite/Pt-cell in a 4![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 mixture of MeCN and H2O under an inert atmosphere at room temperature. This electrochemical method efficiently provided the target β-hydroxysulfones 18 in fair to high yields under catalyst-free conditions and without consuming any oxidizing agent or additive (Scheme 10). The authors depicted a plausible mechanism for this transformation, which is shown in Scheme 11.
1 mixture of MeCN and H2O under an inert atmosphere at room temperature. This electrochemical method efficiently provided the target β-hydroxysulfones 18 in fair to high yields under catalyst-free conditions and without consuming any oxidizing agent or additive (Scheme 10). The authors depicted a plausible mechanism for this transformation, which is shown in Scheme 11.
4. Sulfonylhydazides as sulfonylating agents
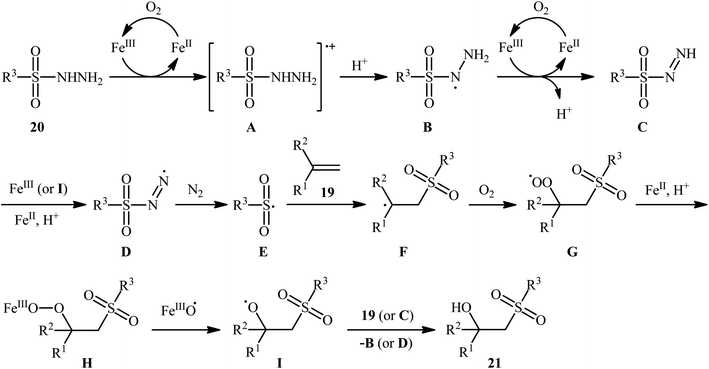
In 2011, Taniguchi's research team reported the first example of metal-catalyzed direct hydroxysulfonylation of alkenes 19 using sulfonylhydazides 20 as easily available and powerful sulfonyl sources.21 The reactions were carried out in the presence of a catalytic amount of FeCl3 in THF under air, completed within 6–24 h at 65 °C, and afforded the corresponding β-hydroxysulfones 21 in moderate to excellent yields (Scheme 12). The method showed a broad substrate scope including both aliphatic and aromatic sulfonylhydazides and various aryl-, ester-, and acetylene-substituted alkenes. However, the reaction failed in the case of an internal alkene. Moreover, 1,1-dialkyl substituted substrates did not work well in this synthetic strategy. A possible mechanism was also proposed (Scheme 13), whereby the reaction is initiated with oxidation of sulfonylhydrazide 20 by Fe(III) to give diazene C via the intermediates A and B, which undergoes further oxidation by iron catalyst affording nitrogen-centered radical D. Subsequently, this radical D releases a molecular nitrogen to deliver the sulfonyl radical E. The newly formed radical E is then reacting with alkene 19 to form alkyl radical F, which after interaction with the dioxygen dissolved in THF converts to the peroxy radical G. Thereafter, reduction of peroxy radical G by Fe(II) yields the alkoxyl radical I through the intermediate H. Finally, alkoxyl radical I abstracts a hydrogen atom from diazene intermediate C or another molecule of sulfonylhydrazide 20 to furnish the desired β-hydroxysulfone product 21.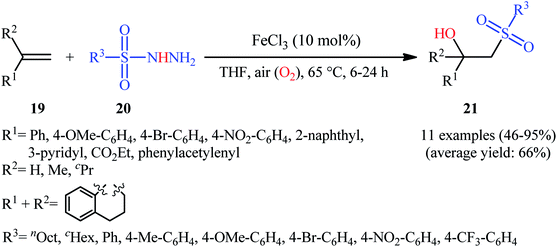 | ||
| Scheme 12 Fe-catalyzed direct synthesis of β-hydroxysulfones 21 from alkenes 19 and sulfonylhydazides 20. | ||
In 2016, Terent'ev and co-workers reported an analogous methodology for the direct hydroxysulfonylation of α-substituted styrenes 22 with arylsulfonyl hydrazides 23 under O2 atmosphere in the presence of a copper salt (Scheme 14).22 In their optimization study, the authors found that the use of 2.0 equiv. of CuBr as mediator in MeCN–H2O (5![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) gave the best results. Examination of the scope of the reaction revealed that a range of α-substituted styrenes bearing either electron-withdrawing or electron-donating groups and a variety of electron rich- and deficient-substituted arylsulfonyl hydrazide analogues were compatible substrates and afforded the β-hydroxysulfones 24 in moderate to excellent yields. However, the use of α-unsubstituted styrenes as substrates under the identical conditions led to the mixture of corresponding β-hydroxysulfones and β-sulfonyl ketones.
1) gave the best results. Examination of the scope of the reaction revealed that a range of α-substituted styrenes bearing either electron-withdrawing or electron-donating groups and a variety of electron rich- and deficient-substituted arylsulfonyl hydrazide analogues were compatible substrates and afforded the β-hydroxysulfones 24 in moderate to excellent yields. However, the use of α-unsubstituted styrenes as substrates under the identical conditions led to the mixture of corresponding β-hydroxysulfones and β-sulfonyl ketones.
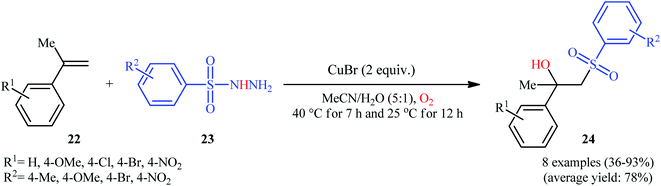 | ||
| Scheme 14 Cu-mediated synthesis of β-hydroxysulfones 24 from styrenes 22 and sulfonylhydrazides 23 in the presence of O2. | ||
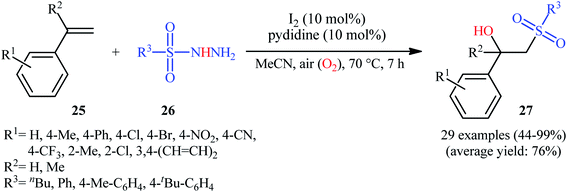
With the objective of designing a metal-free protocol to β-hydroxylated sulfones through the direct hydroxysulfonylation of the alkenes with sulfonylhydazides, Mal and colleagues were able to reveal that a divers set of functionalized β-hydroxysulfones 27 could be prepared in moderate to quantitative yields from the reaction of styrene derivatives 25 with sulfonylhydazides 26 under ambient atmosphere employing molecular iodine as a catalyst and pyridine as an additive in MeCN (Scheme 15).23 Noteworthy, when pyridine was solely used as a catalyst no product formation was observed. The results also proved that other halide ion sources such as TBAI and TBAB were not able to promote this reaction. Some important information of the reactions is listed below: (i) both aromatic and aliphatic sulfonylhydazides were suitable substrates under the optimal condition; (ii) not only α-substituted styrenes but also α-unsubstituted styrenes afforded the desired products with excellent selectivity; (iii) the protocol was not successful in the case of aliphatic alkenes; and (iv) the process could be easily scaled up to the gram quantities without loss of the yields. Along this line, recently, the Zhu group has identified methylene blue (MB) as an efficient photoredox catalyst for hydroxysulfonylation of α-substituted styrenes with 4-methylbenzenesulfonohydrazide under aerobic conditions.24 In this report, seven β-hydroxysulfones were synthesized in good yields (63–81%) by means of 2 mol% of MB and 1 equiv. of DABCO in EtOH at room temperature under the irradiation of 7 W blue LEDs. However, under the identical conditions, α-unsubstituted styrenes afforded the corresponding β-keto sulfones instead of β-hydroxysulfone products.
Recently, Ye, Wu, and co-workers disclosed an innovative Cu-catalyzed aerobic oxidative three-component reaction of alkenes 28, arylhydrazines 29, and DABCO·(SO2)2 to prepare the corresponding β-hydroxysulfones 30 through hydroxysulfonylation of C–C double bonds with the insertion of sulfur dioxide (Scheme 16).25 Here, arylhydrazines served as the precursors of aryl radicals under aerobic atmosphere, which initiated the reaction. During the reaction process, aryl radicals react with sulfur dioxide leading to arylsulfonyl radicals, which subsequently undergo hydroxysulfonylation of alkenes with oxygen to provide β hydroxysulfones.
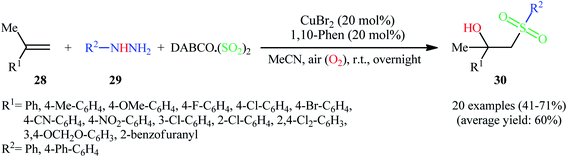 | ||
| Scheme 16 Cu-catalyzed synthesis of β-hydroxysulfones 30 through the aerobic oxidative reaction of alkenes 28, arylhydrazines 29, and DABCO·(SO2)2. | ||
5. Sodium sulfinates as sulfonylating agents
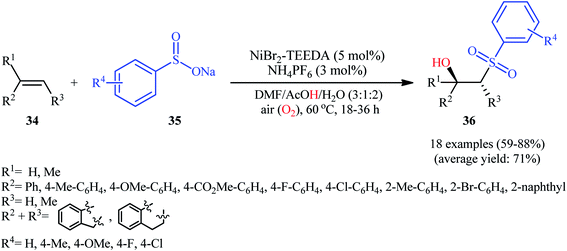
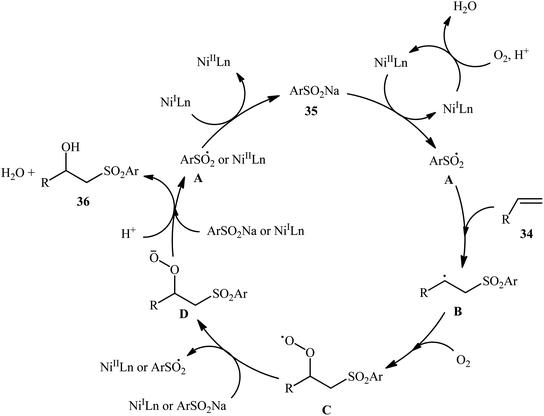
One of the earliest reports on the utilization of sodium sulfinates as sulfonylationg agents in the direct hydroxysulfonylation of alkenes under oxidative conditions was published by Itoh and colleagues in 2014,26 who showed that the treatment of styrene derivatives 31 with sodium arylsulfinates 32 in the presence of a catalytic amount of molecular iodine in MeCN/AcOH mixture under air without any additional oxidants, resulted in the formation of the corresponding β-hydroxysulfones 33 in good to excellent yields (Scheme 17). Unfortunately, cyclohexene did not take part in the reaction and therefore no other aliphatic alkenes were examined in the protocol. In their optimization study, the authors found that other iodine sources such as NIS, NaI, MgI2, CaI2, and CI4 could also promote this transformation; albeit, at lower efficiencies. Notably, sulfonylhydazides did not respond to this difunctionalization reaction using I2 catalyst alone and the presence of a basic additive such as pyridine was crucial for the success of this conversion.23 Later, Chen and Chang along with their co-workers improved the efficiency of this transformation in the terms of reaction time and yield by switching the iodine source to KI and performing the process in a GCE-Pt electrochemical cell.27In 2015, Taniguchi disclosed the usefulness of nickel catalysts for hydroxysulfonylation of alkenes using sodium sulfinates under air atmosphere.28 Thus, in the presence of a combination of NiBr2-TEEDA (N,N,N′,N′-tetraethylethylenediamine) complex and NH4PF6 in DMF–AcOH–H2O at 60 °C, the reaction of various terminal and internal aklenes 34 with aromatic sodium sulfinates 35 furnished the corresponding β-hydroxysulfones 36 in good to high yields, ranging from 59% to 88% (Scheme 18). However, in the majority of cases, β-ketosulfones were obtained as side products. In this study, the authors found some limitation in their methodology, when they attempted to react heteroaromatic and aliphatic alkenes. Unfortunately, these compounds were ineffective under standard condition. NMR analysis revealed that in the cases of internal alkenes anti-adducts were selectively formed. Furthermore, reactions using cis and trans alkenes gave the same products. A plausible mechanism proposed by the authors was started with Ni(II)-mediated oxidation of sodium sulfinate 35 by air to form sulfonyl radical A which was then trapped by alkene 34 to generate C-centered radical B. Subsequently, the radical B attacked air oxygen to achieve peroxy radical C. After that, this radical C was reduced to peroxy anion D by nickel(I) or a sulfonyl anion. Finally, anion intermediate D afforded the desired product 36 by reduction with a proton (Scheme 19). In a related investigation, Menezes's research team demonstrated that the merge of 1.0 equiv. of FeCl3 with (NH4)2S2O8 could also promote this difunctionalization reaction.29 However, selectivity and yield was modest at best.
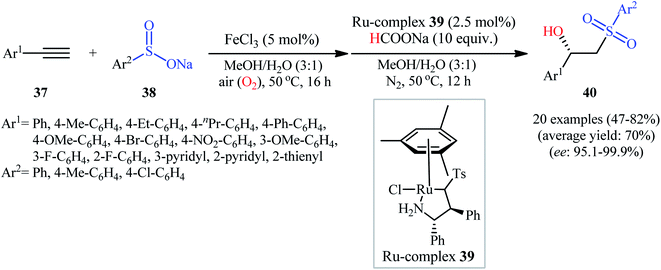
Recently, Zhou's research team demonstrated an innovative protocol for highly enantioselective synthesis of β-hydroxysulfones from terminal alkynes and sodium sulfinates via Fe-catalyzed aerobic oxysulfonylation and consecutive Ru-catalyzed asymmetric transfer hydrogenation in an aqueous medium under mild conditions.30 Thus, in the presence of 20 mol% of FeCl3 as a catalyst in MeOH/H2O, aerobic oxysulfonylation of (hetero)aromatic terminal alkynes 37 with sodium arylsulfinates 38 furnished the corresponding β-keto sulfones which subsequently reduced by HCOONa as a hydrogen source employing 2.5 mol% of ruthenium complex 39 as a chiral catalyst to give enantiomerically enriched β-hydroxysulfones 40 in moderate to high yields and up to 99.9% ee values (Scheme 20). Various important functional groups in the phenyl ring periphery of either alkynes or sulfinates were well tolerated by this reaction, thus indicating its broad applicability. The reaction could also be easily conducted on a gram scale (78% yield and 98.7% ee on 10 mmol scale). Drawing inspiration from this work, quite recently, Liu and co-workers designed and synthesized the yolk–shell-structured magnetic nanoparticles with the chiral Ru/diamine species with in the nanochannels of the outer mesoporous silica shell and the FeCl3 species on the inner magnet core, [Fe]@Fe3O4@[Ru]@[Si] ([Ru] = MesRuArDPEN : Mes = Mesitylene, and ArDPEN = (S,S)-4-((trimethoxysilyl)ethyl)phenylsulfonyl-1,2-diphenylethylene–diamine; [Fe] = FeCl3), and successfully applied the prepared nanocomposite system as an efficient catalyst for high yielding synthesis of a wide variety of chiral β-hydroxysulfones from the corresponding aryl-substituted terminal alkynes and sodium arylsulfinates via the one-pot aerobic oxysulfonylation/asymmetric transfer hydrogenation cascade process.31
6. Thiosulfonates as sulfonylating agents
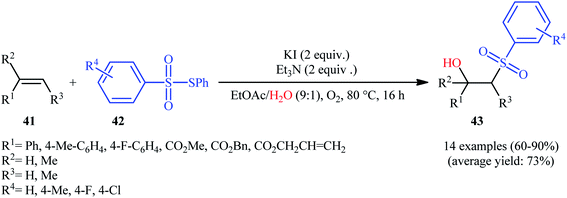
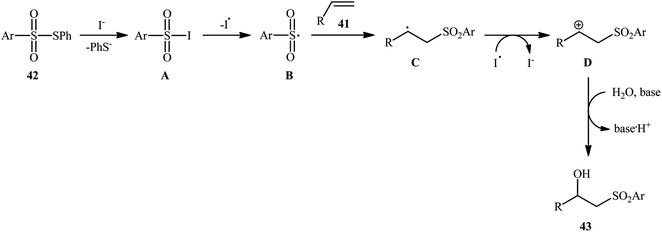
Recently, Jang and colleagues reported a new methodology for high yielding preparation of β-hydroxyl sulfone derivatives 43 shown in Scheme 21.32 These compounds were synthesized by the treatment of the corresponding alkenes 41 with thiosulfonates 42 as aryl sulfonyl sources and water as the source of the hydroxyl group through an KI-catalyzed regioselective vicinal hydroxysulfonylation reaction. The reaction is noteworthy in that both electron-rich alkenes such as styrene and electron-deficient alkenes such as methyl methacrylate and benzyl methacrylate were well tolerated. In addition, the scope of thiosulfonates that underwent reaction was broad enough to include electron-neutral, electron-rich and electron-poor thiosulfonate derivatives. A plausible mechanism proposed by the authors was started with reaction of thiosulfonate 42 with iodide to form sulfonyl iodide A which was then dissociated into sulfonyl radical B and iodide radical. Subsequently, the sulfonyl radical B attacked the alkene 41 to afford carbon-centered radical C. After that, radical C was oxidized to carbocationic intermediate D by I˙. Finally, the addition of water to the carbocation afforded the desired product 43 (Scheme 22). To the best of our knowledge, this is the only example reported on the hydroxysulfonylation of alkenes with thiosulfonates.7. Sulfonamides as sulfonylating agents
Recently, in a report by Bi, Feng, and co-workers, a library of 2-(tert-butylsulfonyl)-1-arylylethanols 46 were synthesized in moderate to good yields by treatment of styrene derivatives 44 with a slight excess of t-butylsulfinamide 45 under open-air conditions (Scheme 23).33 The reaction was performed in the presence of 20 mol% of CuSO4·5H2O as a catalyst and 2 equiv. of H3PO3 as an additive at 40 °C. Although other copper salts (e.g., CuI, CuBr, Cu(OAc)2, CuSO4) and additives (e.g., DMPH, DEPH, DIPPH, DPPH) also allowed for the reaction to proceed, the efficiency was optimal using the aforementioned conditions. The best results were obtained in the case of aromatic alkenes with electron-withdrawing groups. On the contrary, electron-donating groups were unfavorable for the reaction and led to lower yields. Unfortunately, styrenes with strong electron-donating groups (OMe) as well as disubstituted styrenes completely failed to participate in this reaction. The plausible mechanistic pathway suggested by the authors for this transformation is depicted in Scheme 24. It is worthy of note that when the same reaction was carried out at 120 °C, instead of β-hydroxysulfone compounds, vinyl sulfones were obtained as the sole products. The authors proved that the formation of vinyl sulfones did not proceed through the simple dehydration of β-hydroxysulfones under high temperatures as evidenced by an unsuccessful intermolecular transformation of a β-hydroxysulfone to the corresponding vinyl sulfone by heating at 120 °C for 5 h.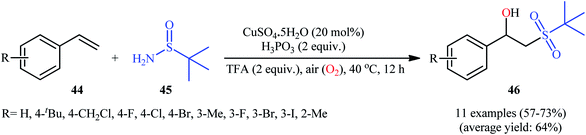 | ||
| Scheme 23 Synthesis of 2-(tert-butylsulfonyl)-1-arylylethanols 46 from styrenes 44 and t-butylsulfinamide 45 under aerobic Cu-catalyzed conditions. | ||
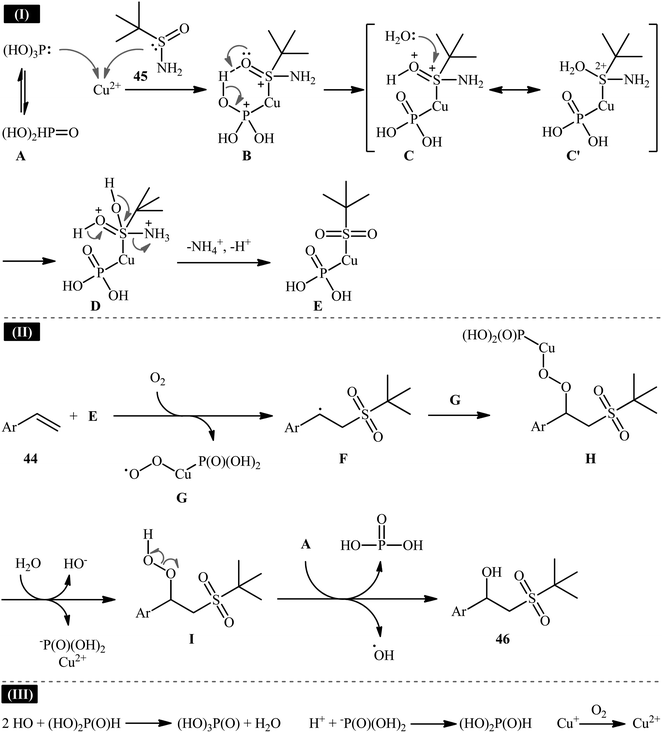 | ||
| Scheme 24 A plausible reaction mechanism for the formation of 2-(tert-butylsulfonyl)-1-arylylethanols 46. | ||
8. Thiols as sulfonylating agents
In 2017, the Huo group developed an elegant one-pot multi-step method for the synthesis of β-hydroxysulfones 49 from alkenes 47 and thiols 48 under catalyst-free and mild conditions (Scheme 25).34 This sequential approach involving an auto-oxidative difunctionalization reaction of alkenes and thiols under oxygen atmosphere, oxidation of generated β-hydroperoxysulfide to β-hydroperoxysulfone using oxone as a sustainable oxidant followed by reduction with NaBH4. The optimization of the one-pot process has allowed the preparation of a diverse range of secondary and tertiary β-hydroxysulfones in moderate to excellent yields with outstanding regioselectivities. Notably, the authors nicely applied their methodology in the high yielding multi-gram scale (2.92 g) preparation of bicalutamide, anti-cancer drug.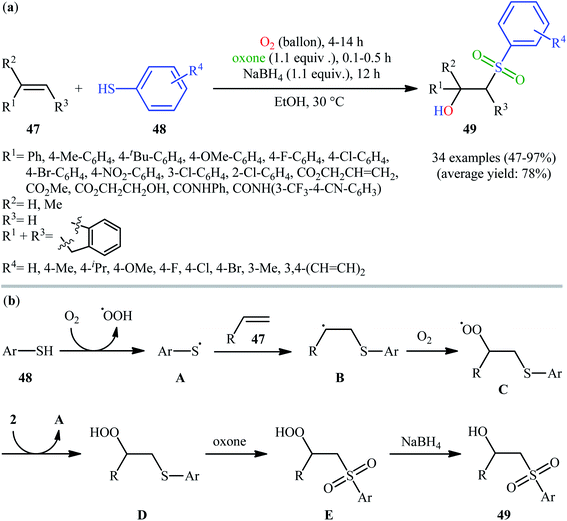 | ||
| Scheme 25 (a) Huo's synthesis of β-hydroxysulfones 49; (b) mechanistic explanation for the formation of β-hydroxysulfones 49. | ||
Finally, it should be noted that transition metal complexes play important role in the hydroxysulfonylation of alkenes and other compounds.35–42
9. Conclusion
β-Hydroxysulfones are valuable skeletons found in many biologically active molecules, and provide useful building blocks in organic synthesis. Traditionally, these compounds are synthesized through reduction of β-keto-sulfones, hydroxylation of α,β-unsaturated sulfones, and nucleophilic ring opening of epoxides with sulfinate salts. However, these transformations suffer from certain drawbacks, such as production of unwanted byproducts, requirement of pre-functionalized starting materials as well as harsh reaction conditions. In order to bypass these limitations, direct hydroxysulfonylation of inexpensive and easily accessible alkenes was recently developed as an efficient and straightforward one-pot approach to the titled compounds. Majority of these difunctionalization reactions have been carried out under metal-free and mild conditions and can be also scaled up to gram levels without difficulty. Nevertheless, the area still needs much more investigation due to some challenges and limitations in the current reports. For instance: (i) the substrate scope of alkenes is narrow and generally limited to the activated alkenes (e.g. styrenes, acrylates). Thus, of course, expanding of substrate scope of this page of β-hydroxysulfone synthesis to unactivated alkenes are necessary; (ii) the hydroxysulfonylation of alkynes still almost remains unexplored and there is a need for further studies the scope and limitations of alkynes in this transformation; and (iii) the exploration of asymmetric hydroxysulfonylations for the synthesis of enantioenriched β-hydroxysulfones still remains an elusive goal. We hope this review will be helpful in the development of improved methods for the synthesis of β-hydroxysulfones as well as other organosulfur compounds.Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.References
- M. Feng, B. Tang, S. H. Liang and X. Jiang, Curr. Top. Med. Chem., 2016, 16, 1200–1216 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. A. Scott and J. T. Njardarson, Top. Curr. Chem., 2019, 376, 5 CrossRef PubMed.
- (a) I. D. Cockshott, Clin. Pharmacokinet., 2004, 43, 855–878 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) D. Loebenberg, A. Cacciapuoti, R. Parmegiani, E. Moss, F. Menzel, B. Antonacci, C. Norris, T. Yarosh-Tomaine, R. Hare and G. Miller, Antimicrob. Agents Chemother., 1992, 36, 498–501 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) T. Walsh, J. Lee, J. Lecciones, P. Kelly, J. Peter, V. Thomas, J. Bacher and P. Pizzo, Antimicrob. Agents Chemother., 1990, 34, 1560–1564 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- (a) T. Mandai, T. Yanagi, K. Araki, Y. Morisaki, M. Kawada and J. Otera, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1984, 106, 3670–3672 CrossRef CAS; (b) G. Solladie, C. Frechou, G. Demailly and C. Greck, J. Org. Chem., 1986, 51, 1912–1914 CrossRef CAS; (c) R. Tanikaga, K. Hosoya, K. Hamamura and A. Kaji, Tetrahedron Lett., 1987, 28, 3705–3706 CrossRef CAS; (d) S. Robin, F. Huet, A. Fauve and H. Veschambre, Tetrahedron: Asymmetry, 1993, 4, 239–246 CrossRef CAS; (e) M.-Y. Chang, Y.-J. Lu and Y.-C. Cheng, Tetrahedron, 2015, 71, 1192–1201 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) M. C. Bernabeu, P. Bonete, F. Caturla, R. Chinchilla and C. Nájera, Tetrahedron: Asymmetry, 1996, 7, 2475–2478 CrossRef CAS; (b) P. Bertus, P. Phansavath, V. Ratovelomanana-Vidal, J.-P. Genêt, A. Touati, T. Homri and B. B. Hassine, Tetrahedron Lett., 1999, 40, 3175–3178 CrossRef CAS.
- A. L. Moure, R. G. Arrayás and J. C. Carretero, Chem. Commun., 2011, 47, 6701–6703 RSC.
- (a) A. Maiti and P. Bhattacharyya, Tetrahedron, 1994, 50, 10483–10490 CrossRef CAS; (b) D. J. Berrisford, P. A. Lovell, N. R. Suliman and A. Whiting, Chem. Commun., 2005, 5904–5906 RSC; (c) S. N. Murthy, B. Madhav, V. P. Reddy, K. R. Rao and Y. Nageswar, Tetrahedron Lett., 2009, 50, 5009–5011 CrossRef.
- M. Z. Zhang, P. Y. Ji, Y. F. Liu, J. W. Xu and C. C. Guo, Adv. Synth. Catal., 2016, 358, 2976–2983 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) H. Mei, Z. Yin, J. Liu, H. Sun and J. Han, Chin. J. Chem., 2019, 37, 292–301 CAS; (b) Z.-L. Li, G.-C. Fang, Q.-S. Gu and X.-Y. Liu, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2020, 49, 32–48 RSC; (c) J. B. Peng, Adv. Synth. Catal., 2020, 362, 3059–3080 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) N. Yue and F. R. Sheykhahmad, J. Fluorine Chem., 2020, 109629 CrossRef CAS; (b) A. Bakhtiary, M. R. P. Heravi, A. Hassanpour, I. Amini and E. Vessally, RSC Adv., 2020, 11, 470–483 RSC.
- O. M. Mulina, A. I. Ilovaisky, V. D. Parshin and A. O. Terent'ev, Adv. Synth. Catal., 2020, 362, 4579–4654 CrossRef CAS.
- (a) S. Arshadi, E. Vessally, L. Edjlali, R. Hosseinzadeh-Khanmiri and E. Ghorbani-Kalhor, Beilstein J. Org. Chem., 2017, 13, 625–638 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) E. Vessally, K. Didehban, R. Mohammadi, A. Hosseinian and M. Babazadeh, J. Sulfur Chem., 2018, 39, 332–349 CrossRef CAS; (c) E. Vessally, R. Mohammadi, A. Hosseinian, K. Didehban and L. Edjlali, J. Sulfur Chem., 2018, 39, 443–463 CrossRef CAS; (d) A. Hosseinian, L. Zare Fekri, A. Monfared, E. Vessally and M. Nikpassand, J. Sulfur Chem., 2018, 39, 674–698 CrossRef CAS; (e) A. Hosseinian, S. Ahmadi, F. A. H. Nasab, R. Mohammadi and E. Vessally, Top. Curr. Chem., 2018, 376, 39 CrossRef PubMed; (f) A. Hosseinian, P. D. K. Nezhad, S. Ahmadi, Z. Rahmani and A. Monfared, J. Sulfur Chem., 2019, 40, 88–112 CrossRef CAS; (g) A. Monfared, S. Ahmadi, Z. Rahmani, P. D. K. Nezhad and A. Hosseinian, J. Sulfur Chem., 2019, 40, 209–231 CrossRef CAS; (h) A. Hosseinian, S. Arshadi, S. Sarhandi, A. Monfared and E. Vessally, J. Sulfur Chem., 2019, 40, 289–311 CrossRef CAS; (i) A. Monfared, S. Ebrahimiasl, M. Babazadeh, S. Arshadi and E. Vessally, J. Fluorine Chem., 2019, 220, 24–34 CrossRef CAS; (j) A. Hosseinian, Y. J. Sadeghi, S. Ebrahimiasl, A. Monfared and E. Vessally, J. Sulfur Chem., 2019, 40, 565–585 CrossRef CAS; (k) M. Hamzehloo, A. Hosseinian, S. Ebrahimiasl, A. Monfared and E. Vessally, J. Fluorine Chem., 2019, 224, 52–60 CrossRef CAS; (l) N. H. Jabarullah, K. Jermsittiparsert, P. A. Melnikov, A. Maseleno, A. Hosseinian and E. Vessally, J. Sulfur Chem., 2020, 41, 96–115 CrossRef CAS; (m) X. Guo-Liang, J. Shang-Hua, S. Xiangdong and F. Behmagham, J. Fluorine Chem., 2020, 29, 109524 CrossRef; (n) Z. Liu, A. Ebadi, M. Toughani, N. Mert and E. Vessally, RSC Adv., 2020, 10, 37299–37313 RSC; (o) S. Majedi, S. Majedi and F. Behmagham, Chem. Rev. Lett., 2019, 2, 187–192 Search PubMed; (p) E. A. Mahmood, B. Azizi and S. Majedi, Chem. Rev. Lett., 2020, 3, 2–8 Search PubMed; (q) S. Shahidi, P. Farajzadeh, P. Ojaghloo, A. Karbakhshzadeh and A. Hosseinian, Chem. Rev. Lett., 2018, 1, 37–44 Search PubMed; (r) M. R. J. Sarvestani, N. Mert, P. Charehjou and E. Vessally, J. Chem. Lett., 2020, 1, 93–102 Search PubMed.
- (a) A. Hosseinian, S. Farshbaf, L. Z. Fekri, M. Nikpassand and E. Vessally, Top. Curr. Chem., 2018, 376, 23 CrossRef PubMed; (b) A. Hosseinian, F. A. H. Nasab, S. Ahmadi, Z. Rahmani and E. Vessally, RSC Adv., 2018, 8, 26383–26398 RSC; (c) A. Hosseinian, R. Mohammadi, S. Ahmadi, A. Monfared and Z. Rahmani, RSC Adv., 2018, 8, 33828–33844 RSC; (d) W. Peng, E. Vessally, S. Arshadi, A. Monfared, A. Hosseinian and L. Edjlali, Top. Curr. Chem., 2019, 377, 20 CrossRef PubMed; (e) S. Ebrahimiasl, F. Behmagham, S. Abdolmohammadi, R. N. Kojabad and E. Vessally, Curr. Org. Chem., 2019, 23, 2489–2503 CrossRef CAS; (f) Y. Liu, A. G. Ebadi, L. Youseftabar-Miri, A. Hassanpour and E. Vessally, RSC Adv., 2019, 9, 25199–25215 RSC; (g) C. Yang, A. Hassanpour, K. Ghorbanpour, S. Abdolmohammadi and E. Vessally, RSC Adv., 2019, 9, 27625–27639 RSC; (h) Y. Yang, D. Zhang and E. Vessally, Top. Curr. Chem., 2020, 378, 37 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (i) Z. He, D. Wu and E. Vessally, Top. Curr. Chem., 2020, 378, 46 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (j) L. Feng, X. Li, B. Liu and E. Vessally, J. CO2 Util., 2020, 40, 101220 CrossRef CAS; (k) W. Xu, A. G. Ebadi, M. Toughani and E. Vessally, J. CO2 Util., 2020, 101358 Search PubMed; (l) S. Sarhandi, M. Daghagheleh, M. Vali, R. Moghadami and E. Vessally, Chem. Rev. Lett., 2018, 1, 9–15 Search PubMed; (m) L. Sreerama, E. Vessally and F. Behmagham, J. Chem. Lett., 2020, 1, 9–18 Search PubMed; (n) S. Mohammadi, M. Musavi, F. Abdollahzadeh, S. Babadoust and A. Hosseinian, Chem. Rev. Lett., 2018, 1, 49–55 Search PubMed; (o) M. Daghagheleh, M. Vali, Z. Rahmani, S. Sarhandi and E. Vessally, Chem. Rev. Lett., 2018, 1, 23–30 Search PubMed; (p) S. Farshbaf, L. Sreerama, T. Khodayari and E. Vessally, Chem. Rev. Lett., 2018, 1, 56–67 Search PubMed; (q) S. Majedi, L. Sreerama, E. Vessally and F. Behmagham, J. Chem. Lett., 2020, 1, 25–31 Search PubMed.
- S. Ghosh, S. Samanta, A. K. Ghosh, S. Neogi and A. Hajra, Adv. Synth. Catal., 2020, 362, 4552–4578 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Xi, C. Lai, C. Chen and R. Wang, Synlett, 2004, 1595–1597 CrossRef CAS.
- S. K. Pagire, S. Paria and O. Reiser, Org. Lett., 2016, 18, 2106–2109 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Liu, Y. J. Yang, J. Y. Dong, M. D. Zhou, L. Li and H. Wang, Org. Chem. Front., 2019, 6, 3944–3949 RSC.
- Q. Lu, J. Zhang, F. Wei, Y. Qi, H. Wang, Z. Liu and A. Lei, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2013, 125, 7297–7300 CrossRef.
- Z. Huang, Q. Lu, Y. Liu, D. Liu, J. Zhang and A. Lei, Org. Lett., 2016, 18, 3940–3943 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Z. Zhang, J. Yan, D. Ma and J. Sun, Chin. Chem. Lett., 2019, 30, 1509–1511 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Taniguchi, A. Idota and H. Ishibashi, Org. Biomol. Chem., 2011, 9, 3151–3153 RSC.
- A. O. Terent'ev, O. M. Mulina, D. A. Pirgach, D. V. Demchuk, M. A. Syroeshkin and G. I. Nikishin, RSC Adv., 2016, 6, 93476–93485 RSC.
- K. Choudhuri, T. K. Achar and P. Mal, Adv. Synth. Catal., 2017, 359, 3566–3576 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Wu, Y. Zhang, X. Gong, Y. Meng and C. Zhu, Org. Biomol. Chem., 2019, 17, 3507–3513 RSC.
- J. Zhang, W. Xie, S. Ye and J. Wu, Org. Chem. Front., 2019, 6, 2254–2259 RSC.
- A. Kariya, T. Yamaguchi, T. Nobuta, N. Tada, T. Miura and A. Itoh, RSC Adv., 2014, 4, 13191–13194 RSC.
- C. K. Chan, N. C. Lo, P. Y. Chen and M. Y. Chang, Synthesis, 2017, 28, 4469–4477 CrossRef.
- N. Taniguchi, J. Org. Chem., 2015, 80, 7797–7802 CrossRef CAS.
- Q. P. Freitas, R. A. Lira, J. J. Freitas, G. Zeni and P. H. Menezes, J. Braz. Chem. Soc., 2018, 29, 1167–1174 CrossRef CAS.
- P. Cui, Q. Liu, J. Wang, H. Liu and H. Zhou, Green Chem., 2019, 21, 634–639 RSC.
- S. Wang, C. Wang, N. Lv, C. Tan, T. Cheng and G. Liu, ChemCatChem, 2021, 13, 909–915 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Son, P. K. Shyam, H. Park, I. Jeong and H. Y. Jang, Eur. J. Org. Chem., 2018, 3365–3371 CrossRef CAS.
- W. Z. Bi, W. J. Zhang, S. X. Feng, Z. J. Li, H. L. Ma, S. H. Zhu, X. L. Chen, L. B. Qu and Y. F. Zhao, New J. Chem., 2019, 43, 17941–17945 RSC.
- Y. Wang, W. Jiang and C. Huo, J. Org. Chem., 2017, 82, 10628–10634 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Ahmadi, A. Hosseinian, P. D. Kheirollahi Nezhad, A. Monfared and E. Vessally, Iran. J. Chem. Chem. Eng., 2019, 38, 1–19 CAS.
- E. Vessally, S. Mohammadi, M. Abdoli, A. Hosseinian and P. Ojaghloo, Iran. J. Chem. Chem. Eng., 2020, 39, 11–19 CAS.
- M. Zou, Y. Qi, R. Qu, G. Al-Basher, X. Pan, Z. Wang and F. Zhu, Sci. Total Environ., 2021, 771, 144743 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Gupta, V. Dangi, M. Baral and B. Kanungo, Iran. J. Chem. Chem. Eng., 2019, 38, 141–156 CAS.
- H. Zhang, W. Guan, L. Zhang, X. Guan and S. Wang, ACS Omega, 2020, 5, 18007–18012 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Ahmadizadegan, Iran. J. Chem. Chem. Eng., 2020, 39, 33–47 Search PubMed.
- M. Jamil, N. Sultana, M. Sarfraz, M. N. Tahir and M. I. Tariq, Iran. J. Chem. Chem. Eng., 2020, 39, 45–57 CAS.
- Y. Yang, H. Chen, X. Zou, X. Shi, W. Liu, L. Feng and Z. Chen, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2020, 12, 24845–24854 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2021 |