Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleCreative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported Licence
Cooperative C–H activation of pyridine by PBP complexes of Rh and Ir can lead to bridging 2-pyridyls with different connectivity to the B–M unit†
Yihan Caoa,
Wei-Chun Shiha,
Nattamai Bhuvanesha,
Jia Zhou *b and
Oleg V. Ozerov
*b and
Oleg V. Ozerov *a
*a
aDepartment of Chemistry, Texas A&M University, 3255 TAMU, College Station, Texas 77842, USA. E-mail: ozerov@chem.tamu.edu
bState Key Laboratory of Urban Water Resource and Environment, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin 150090, China. E-mail: jiazhou@hit.edu.cn
First published on 5th October 2021
Abstract
Pyridine and quinoline undergo selective C–H activation in the 2-position with Rh and Ir complexes of a boryl/bis(phosphine) PBP pincer ligand, resulting in a 2-pyridyl bridging the transition metal and the boron center. Examination of this reactivity with Rh and Ir complexes carrying different non-pincer ligands on the transition metal led to the realization of the possible isomerism derived from the 2-pyridyl fragment connecting either via B–N/C–M bonds or via B–C/N–M bonds. This M–C/M–N isomerism was systematically examined for four structural types. Each of these types has a defined set of ligands on Rh/Ir besides 2-pyridyl and PBP. A pair of M–C/M–N isomers for each type was computationally examined for Rh and for Ir, totaling 16 compounds. Several of these compounds were isolated or observed in solution by experimental methods, in addition to a few 2-quinolyl variants. The DFT predictions concerning the thermodynamic preference within each M–C/M–N isomeric match the experimental findings very well. In two cases where DFT predicts <2 kcal mol−1 difference in free energy, both isomers were experimentally observed in solution. Analysis of the structural data, of the relevant Wiberg bond indices, and of the ETS-NOCV partitioning of the interaction of the 2-pyridyl fragment with the rest of the molecule points to the strength of the M–C(pyridyl) bond as the dominant parameter determining the relative M–C/M–N isomer favorability. This M–C bond is always stronger for the analogous Ir vs. Rh compounds, but the nature of the ligand trans to it has a significant influence, as well. DFT calculations were used to evaluate the mechanism of isomerization for one of the molecule types.
Introduction
Selective C–H activation and functionalization of pyridines and other azines presents special challenges, in part because these heterocycles can function as good ligands towards many transition metals.1,2 Selectivity for the 3- (or meta-) position is more common with transition metals,3–5 but studies of selective 2-position functionalization are also known.4,6–12 In many specific cases, the scope may be limited, and a particular substitution pattern on the azine is often required for selectivity.In 2017, we reported a new approach to the directed activation of C–H bonds in pyridine derivatives using an Ir system supported by a boryl/bis(phosphine) PBP13 pincer14,15 ligand.16 The binding of the pyridine (or quinoline) nitrogen to the Lewis acidic boryl site directs Ir to the 2-position in the heterocycle. This approach is distinct from the more classical directed C–H activation, where the directing group donor binds to the same atom (transition metal) which effects C–H cleavage (Fig. 1).17–21 Pyridine derivatives have played a prominent role in the development of classical directed C–H activation,19,20 but they typically direct the metal not to the C–H bonds of the pyridine ring itself, but to the more remote C–H bonds in a substituent, such as in the 2-phenyl group. We reasoned that the (PBP)Ir system preferred the C–H activation of the pyridine ring because of the favorability of the Ir/C/N/B trapezoidal four-membered ring formation.16 Some of the aspects of the mechanism of pyridine activation in our PBP system were recently studied computationally by Ke and coworkers.22 A similar selectivity was observed by Nakao et al. in the C–H activation of pyridines with a Rh complex23 supported by a closely related aluminyl/bis(phosphine) PAlP pincer (Fig. 1).24,25
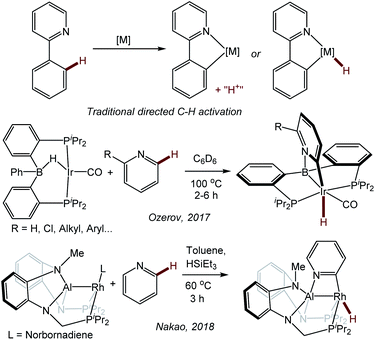 | ||
| Fig. 1 Traditional directed C–H activation of 2-phenylpyridine (top) and boryl- or aluminyl-directed C–H activation of the 2-position of a pyridine ring. | ||
Given Nakao's precedent with Rh, we wished to explore the reactivity with pyridine using the (PBP)Rh system,26,27 as well as the variations of the Rh and Ir systems with and without the carbonyl ligand. While exploring the analogous reactivity with (PBP)Rh, we came across an unexpected finding. As with Ir, C–H activation of pyridine resulted in the formation of a 2-pyridyl that is bridging the B–Rh bond. However, the connectivity was reversed, with C of the pyridyl attached to B and the N atom of the pyridyl attached to Rh. This prompted us to explore this M–C/M–N isomerism in more systematic detail, as it does not appear to have been considered in the literature. This report describes our analysis of the isomeric preference of the 2-pyridyl (or 2-quinolyl) fragment bridging the B–Ir or B–Rh bond in a series of compounds supported by the PBP pincer.
Results and discussion
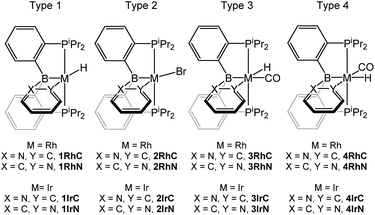
Compounds under consideration and nomenclature
We selected four structural types for analysis (Fig. 2). For each type, we considered M–C/M–N isomerism for the Rh and for the Ir version, resulting in sixteen 2-pyridyl compounds whose structures were optimized computationally. The compound labels (Fig. 2) are derived from the general type (numeral) and the bond present between the metal (Rh or Ir) and C or N. Some of these compounds were isolated or observed experimentally in this (Scheme 1) or the previous report.16 In addition, we synthesized a few 2-quinolyl analogs of the 2-pyridyl compounds (Scheme 1); they are denoted by adding a “q” to the compound label. The type 3 and type 4 compounds are isomeric. We did not attempt the syntheses of the type 4 compounds because DFT calculations indicated that they are considerably higher in energy than the corresponding type 3 isomers (vide infra).Synthesis of Rh and Ir complexes
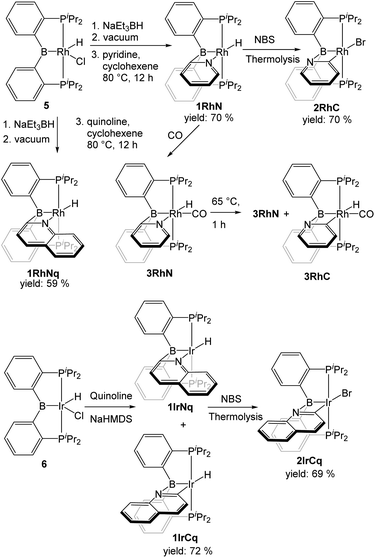
In order to access a Rh species capable of C–H activation, the previously reported 5 was treated with NaBEt3H followed by the removal of volatiles. Although the stoichiometry suggests the formation of “(PBP)RhH2”, we have not established the nature of the resultant species; from the in situ NMR observations, it appears that a mixture of a few complexes forms (Fig. S1†). Nonetheless, thermolysis of this mixture in the presence of cyclohexene and either pyridine or quinoline led to the formation of complexes 1RhN and 1RhNq, with an isolated yield of 70% and 59% respectively. The corresponding type 1 Ir compound 1IrCq was prepared by the treatment of (PBP)IrHCl with NaN(SiMe3)2 in the presence of quinoline. Compound 1IrCq exists in equilibrium with the minor isomer 1IrNq (1.00![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 0.055 ratio at 25 °C and 1.00
0.055 ratio at 25 °C and 1.00![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 0.095 at 65 °C). Attempts to prepare 1IrC in a pure form were not successful. Unlike 1RhN, 1IrC appeared to bind an extra equivalent of pyridine, which resulted in a mixture of products when one equiv. of pyridine was used. Utilization of 3 equiv. of pyridine permitted observation of the pyridine adduct of 1IrC as the dominant product by NMR spectroscopy, but we did not pursue its isolation in a pure solid form (compound 7, Fig. S4†).
0.095 at 65 °C). Attempts to prepare 1IrC in a pure form were not successful. Unlike 1RhN, 1IrC appeared to bind an extra equivalent of pyridine, which resulted in a mixture of products when one equiv. of pyridine was used. Utilization of 3 equiv. of pyridine permitted observation of the pyridine adduct of 1IrC as the dominant product by NMR spectroscopy, but we did not pursue its isolation in a pure solid form (compound 7, Fig. S4†).
The conversion of the hydride complexes 1RhN and 1IrCq to the bromide derivatives 2RhC and 2IrCq was effected by thermolysis with NBS. Good isolated yields (70% and 69% respectively) were obtained after workup. No evidence of the presence of 2RhN or 2IrNq was noted.
The carbonyl adduct 3RhN was prepared by exposure of 1RhN to carbon monoxide and characterized in situ in solution after 10 min. After removing the excess carbon monoxide under vacuum, thermolysis of the solution of 3RhN in C6D6 for 1 h at 65 °C resulted in the formation of a mixture of 3RhN and 3RhC in a 1.0![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 0.08 ratio. Extended thermolysis for 24 h at 65 °C led to the formation of multiple complexes along with 3RhN and 3RhC, but in that mixture 3RhN was still present in a much higher concentration than 3RhC. The synthesis of the analogous Ir complex 3IrC was previously reported. The synthesis involved extended thermolysis at 100 °C and no evidence of the presence of 3IrN was noted.
0.08 ratio. Extended thermolysis for 24 h at 65 °C led to the formation of multiple complexes along with 3RhN and 3RhC, but in that mixture 3RhN was still present in a much higher concentration than 3RhC. The synthesis of the analogous Ir complex 3IrC was previously reported. The synthesis involved extended thermolysis at 100 °C and no evidence of the presence of 3IrN was noted.
Spectroscopic characterization
The compounds explored in this study are rich in NMR active nuclei (1H, 13C, 31P, 11B, and 103Rh) (Table 1). All of the compounds possess Cs-symmetry on the NMR time scale. The M–C/M–N isomers can be distinguished based on the relative 1H NMR chemical shift of the Rh/Ir–H signal. Since N of pyridyl is less trans-influencing than C of 2-pyridyl, a hydride trans to N appears at a more upfield frequency vs. a hydride trans to C. For the Rh compounds 1RhN, 1RhNq, and 3RhN with a hydride trans to N, its 1H NMR chemical shift falls into a narrow range of −15.7 to −17.3 ppm, but for 3RhC, the hydride resonates considerably upfield at δ −11.04 ppm. The contrast is even greater for the Ir pair 1IrCq (δ −0.20 ppm) and 1IrNq (δ −17.10 ppm).The shape of the 13C{1H} NMR resonance corresponding to the boron- or metal-bound carbon of the 2-pyridyl or 2-quinolyl unit is also telling. In compounds 1RhN, 1RhNq, and 3RhN, this carbon is bound to boron and the corresponding 13C NMR resonances in these compounds possess some broadness. In compounds RhBr-C and IrH-Cq, this carbon is bound do the metal and displays coupling to the two equivalent 31P nuclei, as well as to 103Rh in RhBr-C.
| Complexes | Rh/Ir–Ha | 11B{1H} | Ir/Rh–Cb | B–Cc |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| a 1H NMR chemical shift of the metal-bound hydride. b 13C NMR chemical shift of the metal-bound carbon. c 13C NMR chemical shift of the boron-bound carbon in the bridging pyridyl or quinolyl. d Resonance was not observed due to low concentration. e Spectra of 2IrCq were recorded in CDCl3. | ||||
| 1RhN | −17.25 | 3.5 | — | 188.2 |
| 1RhNq | −16.81 | 4.5 | — | 189.5 |
| 1IrCq | −0.20 | −8.5 | 201.3 | — |
| 1IrNq | −17.10 | —d | — | —d |
| 2RhC | — | 1.7 | 178.0 | — |
| 2IrCq | — | −6.8 | 176.9 | — |
| 3RhN | −15.69 | 2 | — | 193.5 |
| 3RhC | −11.04 | —d | —d | — |
| 3IrC | −14.15 | 164.9 | ||
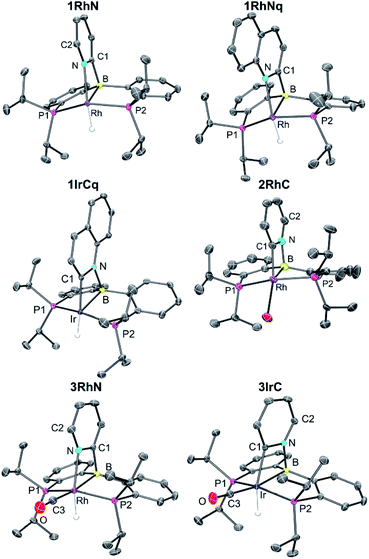
XRD structural characterization
Single crystal X-ray diffractometry permitted the determination of the solid-state structures of 1RhN, 1RhNq, 1IrCq, 2RhC, and 3RhN. The solid-state structure of 3IrC was reported in 2017 (Fig. 3).The Ir–B (2.209(2) and 2.195(2) Å) and the Ir–C distances (2.034(3) and 2.029(3) Å) in the two crystallographically independent molecules of 1IrCq are slightly shorter than the Ir–B distance of 2.285(2) Å and the Ir–C distance of 2.079(2) Å in the previously reported 3IrC. The B–N and N–C distances in these molecules are very similar. Comparing the Rh–B distances in 1RhN (2.229(2) Å) and 3RhN (2.319(1) Å) also shows that the presence of CO is correlated with the elongation of the M–B bond (trans to CO) by almost 0.1 Å. However, the Rh–N distances (2.163(1) Å in 1RhN and 2.158(1) Å in 3RhN) seem to be unaffected by the presence of the CO ligand.
The values for the sum of angles that exclude the pyridyl/quinolyl nitrogen about the boron atom in 1RhN, 1RhNq and 3RhN are in the ca. 339.4°–343.8° range. The range of the corresponding values (excluding the pyridyl/quinolyl carbon) in 1IrCq, 2RhC and 3IrC is ca. 335.6°–341.9°. Likewise, the P–M–P angles in the six structures in Fig. 3 all fall within the ca. 151–161° range. Thus. while there are significant differences in the metrics of the M–C/N–B cycle among the six structures, the conformation of the (PBP)M fragment is close to constant.
The hydride ligand in 1RhN, 1RhNq, 1IrCq, 3RhN, and 3IrC is close to being trans to either C or N of the pyridyl (161°–174° angle range). In the structure of 2RhC, the C–Rh–Br angle deviates from linearity to a greater extent (149.57(11)°) and 2RhC can be viewed as adopting a Y-shaped geometry as opposed to square-pyramidal for the five-coordinate hydride complexes 1RhN, 1RhNq, 1IrCq.28
DFT studies
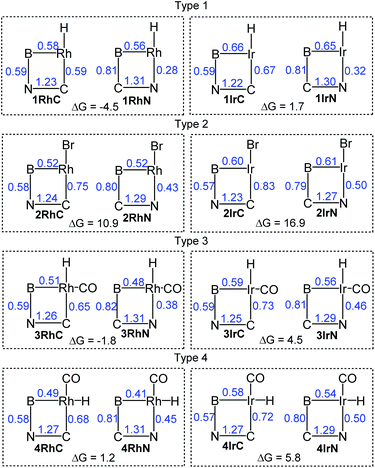
The structures of the 16 molecules shown in Fig. 2 were optimized using the B97D3/LANL2DZ/6-31G(d) method (see details in the ESI†). Fig. 4 summarizes the results of the calculations, showing the Wiberg bond indices (WBI) within the four-membered rings, as well as the calculated free energies of the isomerization from the M–C to the M–N isomer. The metric details of the DFT-optimized geometries matched those from the XRD structures reasonably well.Calculations indicate that the isomers with the carbon bound to the transition metal are more favorable for all Ir complexes and for the Rh complexes of types 2 and 4. For the other Rh complexes, the isomer with the nitrogen bound to Rh is preferred. Across all four types, the relative free energy preference of Ir for the metal–carbon bonded isomer is very consistently 5–7 kcal mol−1 higher than that of Rh.
Overall, the calculated thermodynamic parameters are consistent with the experimental observations we have for the Rh and Ir compounds of types 1–3. Moreover, the calculated free energy preferences for 1IrC (over 1IrN) and for 3RhN (over 3RhC) are <2 kcal mol−1, suggesting that both isomers in these two pairs should be present at observable concentrations. This is precisely what we observed for 1IrCq/1IrNq and for 3RhN/3RhC (vide supra), with the isomer predicted to be more favorable by DFT present in a higher proportion.
Type 3 (CO trans to B) compounds are isomeric to type 4 (H trans to B), and DFT calculations predict that any of the four type 3 compounds (3IrC, 3IrN, 3RhC, 3RhN) is lower in free energy than their corresponding type 4 analog (4IrC, 4IrN, 4RhC, 4RhN, respectively) by 13–19 kcal mol−1. This is consistent with the lack of observation of 4RhC or 4RhN in the thermolysis of the 3RhC/3RhN mixture.
The calculated Wiberg bond indices (WBI) provide a way to analyze the changes in the nature of the bonds in the four-membered cycle for the pairs of isomers. The WBI for the M–B bond in any Ir compound is 0.08–0.13 higher than for the exact Rh analog. Higher WBI values in Ir (vs. Rh) compounds are also notable for the M–C and M–N bonds (by 0.04–0.08). This is in general expected for a 5d metal (Ir) compared to its 4d congener (Rh).
Within each M–C/M–N isomeric pair with the same metal, the M–B bond WBI values differ only by 0.04 or less, except for the 4RhC/4RhN pair (0.08 difference). The WBI vary even less for the C–B bonds (0.79–0.82 range) and for the N–B bonds (0.57–0.59) throughout the whole array of compounds. It can be concluded that the changes in the M–B, C–B, and N–B bonding contribute little to the thermodynamic preferences for the M–C vs. M–N isomers.
The WBI values for the CN bond vary within a range of 1.22–1.31 for all 16 compounds. Within every M–C/M–N isomeric pair, this value is higher for the N–M bound isomer, by 0.02–0.08, suggesting that coordination to Ir or Rh strengthens the C–N bond slightly, but to a similar degree across all four types of compounds.
Considering the M–C bonds, there appears to be a surprisingly linear correlation (Fig. 5) between the WBI values and the thermodynamic isomeric preference, that covers both the Rh and the Ir examples. Higher M–C WBI corresponds to higher preference for the M–C isomer, with ergoneutrality of the isomerization predicted at ca. 0.65 M–C WBI. The WBI values of the M–N bonds trend in the same direction. However, the correlation is more diffuse and not as steep, likely reflecting the intrinsically weaker nature of the M–N bond and its lesser dependence on the environment about the metal center (see Fig. S5†).
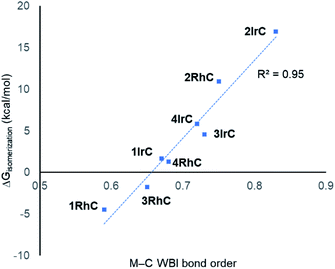 | ||
| Fig. 5 Correlation between the free energy of isomerization and the M–C WBI values for compounds under study. | ||
These observations lead us to conclude that the main factor controlling the thermodynamics of the M–C/M–N isomerization is the quality of the M–C bond, or in other words, the capacity of the metal site for making the strongest M–C bond. This capacity is always greater for Ir than for Rh, but it is also strongly influenced by the nature of the ligand trans to C. A hydride trans to C (types 1 and 3) is a maximal trans-influence conflict, leading to the weakest M–C bonds. A bromide trans to C (type 2) is much less trans-influencing than a hydride, leading to the strongest M–C bonds. A carbonyl ligand trans to C (type 4) represents an intermediate situation. Type 3 can be viewed as type 1 with additional CO ligand coordinated; apparently, CO coordination increases the M–C bond strength and therefore the preference for the M–C bound isomer. Notably, the WBI for the Rh–C bond in 2RhC is higher than the WBI values for all the Ir complexes except 2IrC, meaning that the weak trans-influence of Br (vs. H or CO) can strengthen the M–C bond trans to it to a degree that can overcome the 4d/5d metal handicap.
We have also analyzed the bonding using the extended-transition-state natural orbitals for chemical valence (ETS-NOCV) partitioning of the interaction of the closed shell 2-pyridyl anionic fragment with the formally cationic (PBP)Ir framework (see details in the ESI†). The findings dovetailed the WBI analysis: greater energy of interaction was calculated for (1) Ir vs. Rh, (2) M–C vs. M–N isomers, and (3) for type 2 vs. the other types.
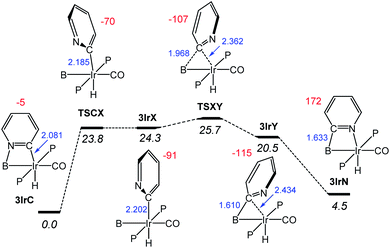
Next, we examined the mechanism29 of the interconversion between 3IrC and 3IrN as a representative example (Fig. 6). From 3IrC, the reaction proceeds via dissociation of the pyridine N from B with concomitant ca. 90° rotation about the Ir–C bond, resulting in 3IrX. The structure of the intermediate 3IrX evinces no bonding interactions between the pyridyl fragment and B, but a full-fledged Ir–C bond. The transition state connecting it with 3IrC (TSCX) possesses both a similar energy and geometry, with an incomplete rotation. The migration of the pyridyl from Ir in 3IrX to B in intermediate 3IrY proceeds viaTSXY. In 3IrY, the pyridyl C is connected to the B by means of well-developed C–B bond, which is even 0.023 Å shorter than the calculated C–B distance in 3IrN. The pyridyl C in 3IrY can also be viewed as weakly interacting with Ir. We did not locate a transition state for the conversion of 3IrY into 3IrN; this process is also simply a rotation of the pyridyl with coordination to Ir. It is clear that most of the barrier for the interconversion between 3IrC and 3IrN is owing to the dissociation of N from B/Ir, corresponding to the rotation of N away from B/Ir. Once the pyridyl N is free, the barrier for the migration of the C-pyridyl between B and Ir is only a few kcal mol−1. This likely also applies to the other types presented in this paper.
Conclusion
In summary, we have examined an unusual isomerization of a bridging 2-pyridyl unit in an array of Rh and Ir complexes supported by a PBP pincer ligand. The main factor governing the thermodynamic preference appears to be the strength of the M–C bond in the M–C bonded isomer. It was observed that the thermodynamic preference for the M–N vs. M–C bond depends both on the nature of the metal center and on the nature of the ligand trans to the M–N/M–C bond. The M–C isomer is favored for the 5d metal Ir vs. Rh and by the presence of a more weakly trans-influencing ligand trans to the M–N/M–C bond. For some of the complexes, both isomers were observed experimentally, in close agreement with theoretical analysis. The interconversion between isomers of similar thermodynamic stability appears to be easily accessible on the experimental timescale, consistent with the computational analysis of a representative system. These findings suggest that the possibility of M–C/M–N isomerization of 2-pyridyl and other closely related fragments should be taken into account when investigating C–H bond activation in azines using a combination of a late transition metal and an embedded main group Lewis acid.Data availability
Crystallographic information associated with this publication has been deposited and is available from https://www.ccdc.cam.ac.uk/ under CCDC 2014200, 2014201, 2014203–2014205.Author contributions
Y. C., J. Z., and O. V. O. conceived of the project, Y. C. and W.-C. S. performed the synthetic and spectroscopic characterization work, Y. C. and N. B. carried out the X-ray diffractions studies, J. Z. performed the DFT calculations, Y. C. and O. V. O. performed the bulk of the manuscript writing with input from the other co-authors, and J. Z. and O. V. O. supervised the overall direction of the work.Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.Acknowledgements
We are grateful for the support of this work by the US National Science Foundation (grant CHE-2102095). This work was also supported by Open Project of State Key Laboratory of Urban Water Resource and Environment, Harbin Institute of Technology (No. QA202009). Computer time made available by the National Supercomputing Center of China in Shenzhen (Shenzhen Cloud Computing Center) is gratefully acknowledged. We thank R. A. Gholson for assistance with manuscript formatting.Notes and references
- Y. Nakao, Synthesis, 2011, 2011, 3209–3219 CrossRef.
- K. Murakami, S. Yamada, T. Kaneda and K. Itami, Chem. Rev., 2017, 117, 9302–9332 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. C. Lewis, R. G. Bergman and J. A. Ellman, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2007, 129, 5332–5333 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- B.-T. Guan and Z. Hou, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2011, 133, 18086–18089 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- G. Tran, K. D. Hesp, V. Mascitti and J. A. Ellman, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2017, 56, 5899 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H.-Q. Do and O. Daugulis, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2011, 133, 13577–13586 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. M. Berman, J. C. Lewis, R. G. Bergman and J. A. Ellman, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2008, 130, 14926–14927 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Li and R. Hua, Tetrahedron Lett., 2009, 50, 1478–1481 CrossRef CAS.
- I. B. Seiple, S. Su, R. A. Rodriguez, R. Gianatassio, Y. Fujiwara, A. L. Sobel and P. S. Baran, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2010, 132, 13194–13196 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Wen, S. Qin, L.-F. Ma, L. Dong, J. Zhang, S.-S. Liu, Y.-S. Duan, S.-Y. Chen, C.-W. Hu and X.-Q. Yu, Org. Lett., 2010, 12, 2694–2697 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Tobisu, I. Hyodo and N. Chatani, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2009, 131, 12070–12071 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Yin, K. Zhong, W. Li, X. Yang, R. Sun, C. Zhang, X. Zheng, M. Yuan, R. Li, Y. Lan, H. Fu and H. Chen, Adv. Synth. Catal., 2018, 360, 3990–3998 CrossRef CAS.
- For the reports on other boryl-centered pincer complexes, see: (a) Y. Segawa, M. Yamashita and K. Nozaki, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2009, 131, 9201–9203 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (b) T.-P. Lin and J. C. Peters, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2014, 136, 13672–13683 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (c) A. F. Hill and C. M. A. McQueen, Organometallics, 2014, 33, 1977–1985 CrossRef CAS; (d) E. H. Kwan, Y. J. Kawai, S. Kamakura and M. Yamashita, Dalton Trans., 2016, 45, 15931–15941 RSC; (e) A. M. Spokoyny, M. G. Reuter, C. L. Stern, M. A. Ratner, T. Seideman and C. A. Mirkin, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2009, 131, 9482–9483 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (f) M. E. El-Zaria, H. Arii and H. Nakamura, Inorg. Chem., 2011, 50, 4149–4161 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (g) B. J. Eleazer, M. D. Smith, A. A. Popov and D. V. Peryshkov, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2016, 138, 10531–10538 CrossRef CAS PubMed; (h) D. Schuhknecht, F. Ritter and M. E. Tauchert, Chem. Commun., 2016, 52, 11823–11826 RSC.
- Organometallic Pincer Chemistry, ed. G. Van Koten, and D. Milstein. Springer, Heidelberg, 2013 Search PubMed.
- E. Peris and R. H. Crabtree, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2018, 47, 1959–1968 RSC.
- W.-C. Shih and O. V. Ozerov, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2017, 139, 17297–17300 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- V. Snieckus, Chem. Rev., 1990, 90, 879–933 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Murai, F. Kakiuchi, S. Sekine, Y. Tanaka, A. Kamatani, M. Sonoda and N. Chatani, Nature, 1993, 366, 529–531 CrossRef CAS.
- T. W. Lyons and M. S. Sanford, Chem. Rev., 2010, 110, 1147–1169 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Zhang, Y. Zhang, X. Jie, H. Zhao, G. Li and W. Su, Org. Chem. Front., 2014, 1, 843–895 RSC.
- J. He, M. Wasa, K. S. L. Chan, Q. Shao and J.-Q. Yu, Chem. Rev., 2017, 117, 8754–8786 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Liu, Y. Li, J. Jiang, Y. Liu and Z. Ke, ACS Catal., 2021, 11, 6186–6192 CrossRef CAS.
- N. Hara, T. Saito, K. Semba, N. Kuroakose, H. Zheng, S. Sakaki and Y. Nakao, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2018, 140, 7070–7073 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- I. Fujii, K. Semba, Q.-Z. Li, S. Sakaki and Y. Nakao, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2020, 142, 11647–11652 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Q.-Z. Li, N. Hara and S. Sakaki, Inorg. Chem., 2020, 59, 15862–15876 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- W.-C. Shih, W. Gu, M. C. MacInnis, S. D. Timpa, N. Bhuvanesh, J. Zhou and O. V. Ozerov, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2016, 138, 2086–2089 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- W.-C. Shih, W. Gu, M. C. MacInnis, D. E. Herbert and O. V. Ozerov, Organometallics, 2017, 36, 1718–1726 CrossRef CAS.
- J.-F. Riehl, Y. Jean, O. Eisenstein and M. Pelissier, Organometallics, 1992, 11, 729–737 CrossRef CAS.
- A part of the sequence presented in Fig. 6 was also calculated by Ke et al. (ref. 22), while considering other processes. The sequence 3IrC–TSCX–3IrX–TSXY–3IrY in Fig. 6 corresponds to PC-TS6-B-IM5-B-TS5-B-IM4-B in the paper by Ke et al. They did not consider 3IrN. The calculations by Ke et al. resulted in lower barriers relative to Ir3C; this is likely owing to a combination of a different chosen functional and basis set, continuum model solvation and a different isopropyl group conformation chosen in the work by Ke et al..
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available: Experimental details and pictorial NMR spectra, details of the computational studies and the DFT coordinate files. CCDC 2014200, 2014201 and 2014203–2014205. For ESI and crystallographic data in CIF or other electronic format see DOI: 10.1039/d1sc01850g |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2021 |