Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleSmall-molecule fluorescent probes based on covalent assembly strategy for chemoselective bioimaging
Xingwei Chen†
a,
Zhongxi Huang†a,
Lihua Huanga,
Qian Shena,
Nai-Di Yang a,
Chibin Pu*d,
Jinjun Shao
a,
Chibin Pu*d,
Jinjun Shao *a,
Lin Li
*a,
Lin Li a,
Changmin Yu
a,
Changmin Yu *ab and
Wei Huangac
*ab and
Wei Huangac
aKey Laboratory of Flexible Electronics (KLOFE) & Institute of Advanced Materials (IAM), Nanjing Tech University (Nanjing Tech), 30 South Puzhu Road, Nanjing, 211816, P. R. China. E-mail: bochibin@126.com; iamjjshao@njtech.edu.cn; iamcmyu@njtech.edu.cn
bState Key Laboratory of Coordination Chemistry, Nanjing University, Nanjing, Jiangsu 210023, China
cShaanxi Institute of Flexible Electronics (SIFE), Northwestern Polytechnical University (NPU), 127 West Youyi Road, Xi'an 710072, P. R. China
dDepartment of Gastroenterology, Zhongda Hospital, School of Medicine, Southeast University, 87 Dingjiaqiao Road, Nanjing, 210009, P. R. China
First published on 7th January 2022
Abstract
Fluorescent probes have been widely studied and applied in environment and health analysis, where among them small molecular “covalent assembly” probes are a novel type of reaction probes with many advantages, including no background interference, remarkable colorimetric change, rapid response, high sensitivity, and strong fluorescent signal. During the past decade, significant contributions have been made globally to both the application and mechanism of covalent assembly probes. In this review, we summarize the recent development of covalent assembly probes, classifying them based on different analytes, such as anions, metal ions, small biological molecules, reactive oxidative spices (ROS), reactive nitrogen species (RNS), nerve agent mimics, and enzymes, and introduce their detection mechanism in detail. Furthermore, the perspective on the next generation of covalent-assembly probes toward biomolecules imaging is presented.
1. Introduction
Fluorescent probes are molecular agents that interact with a target analyte and show spectroscopical fluorescence changes simultaneously. Based on the specific stimulus–response interaction and resulting output change, the analyte substrate can be ascertained. Because small molecular fluorescent probes possess a well-defined structure and their spectral properties can be tuned based on their physical and optical characteristics, they have been widely applied in several fields such as chemical analysis, bioassay, and disease diagnosis.1 The recognition principles of most probes are based on the cleavage or formation of covalent bonds or coordination bonds, which can achieve fluorescent signals “turn-on” or “turn-off”. Due to their high sensitivity and detection ability in complicated systems, small molecular fluorescent probes have attracted increasing attention in several fields, especially in the biological and medical fields.However, with the continuous development of social science and technology, the requirements for the performance of small molecule probes are also increasing. To achieve accurate and real-time detection results in a complex detection environment, the research route of improving molecular sensitivity and selectivity and reducing the interference from background signals through new action mechanisms is an important direction for the development of molecular probes.
In 2005, Anslyn et al. designed a specific palladium ion detection probe through the design idea of covalent assembly.2 Through a palladium-catalysed Heck reaction, olefin compounds are coupled, an intramolecular cyclization reaction occurs, and then the fluorescence signal is generated, and the goal of detection is realized. This detection method is a new method for heavy metal analysis by catalytic signal amplification. The signal amplification scheme relies on exogenous inhibitors to deliberately inactivate the organometallic reaction that catalyzes the generation of fluorophores. However, the slow initiation of the Heck catalyst limits the sensitivity of the probe.
Subsequently, in 2014, Yang et al. first reported a novel mechanism based on the principle of “covalent assembly”.3 This mechanism is mainly triggered by the substrate to be tested. Through an intramolecular covalent cascade reaction, two fragments are combined to form fluorophores achieving the detection effect. In principle, the covalent assembly process results in a new electronic “push–pull” backbone and a rigidified bridge,4,5 which can cause a significant change in the fluorescence emission of small molecular probes. In comparison with other types of probes, covalent assembly probes have many outstanding advantages, such as a more remarkable colorimetric change, more rapid response, higher sensitivity, and stronger fluorescent signal. Significantly, they have no background interference due to the novel mechanism of the “covalent assembly” reaction with specific analytes. Therefore, they have been widely investigated in the field of fluorescent probes.
2. Rational design of covalent assembly-based fluorescent probes
Over the past decade, many groups, especially Yang's group4 and Romieu's group,5 have made extraordinary contributions to the development of this novel mechanism and improving its sensitivity for in vitro and in vivo detection. These probes have been widely applied for the detection of various ions, small biological molecules, reactive oxygen species (ROS), reactive nitrogen species (RNS), and enzymes. Herein, this review focuses on the rational design and recent development of small molecular probes based on the covalent assembly principle for fluorescent detection and multi-functional bioimaging, as well as the potential challenges and future directions in this field.2.1 Probes for anions
Fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) is a common luminescence phenomenon. It refers to the phenomenon that the excitation of a donor fluorescence molecule can induce the receptor molecule to emit fluorescence, and the fluorescence intensity of the donor fluorescence molecule itself decays. Nowadays, this type of luminescence phenomenon is widely used in the field of biosensors, including the detection of F− in vivo. However, the conditions of this phenomenon are harsh, where the fluorescence spectrum of the donor molecule must overlap the excitation spectrum of the receptor molecule and the distance between the donor and receptor must be close.
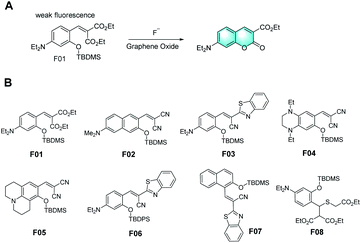
In 2003, several fluorescent F− probes were first designed by Swager et al., where their response mechanism involved the formation of iminocoumarin derivatives through covalent-assembly (Fig. 1A).6 Compared to most semiconductor polymer sensor schemes, which depend on the variation in emission intensity, this sensor system utilizes a new fluorescent signal. The direct electrical connection between the indicator and the band structure of polymers is a promising alternative to FRET. Subsequently, many groups reported various probes using tert-butyldimethylsilyl (TBDMS) or tert-butyldiphenylsilyl (TBDPS) as the recognition groups in accordance with the same mechanism, making full utilization of the high affinity of silicon for fluoride ions (Fig. 1B).7–14 Besides, alkyl-amine groups or strong electron-donating groups (EDG) were introduced into the probes to achieve better fluorescence performances. Subsequently, some of them were modified, exhibiting a more remarkable Stokes shift, higher sensitivity, and better organelle targeting performance. Furthermore, these probes could even detect other ions simultaneously for application as molecular logic gates.15
 | ||
| Fig. 1 (A) Response mechanism of a covalent assembly probe for F−. (Adapted with permission from ref. 6 copyright 2003, Wiley). (B) Molecular structures of representative probes. | ||
As is known, the common phenomenon named aggregation concentration quenching (ACQ) is exhibited by most organic luminescent materials, which tends to weaken or even disappear completely in high-concentration solution or when these materials are in the aggregation state because of the formation of intermolecular aggregation. Different from the traditional ACQ principle, aggregation-induced luminescence (AIE) is a new luminescence mechanism reported by Tang's group. According to this mechanism, the intramolecular rotation of this type of molecule is limited and the non-radiative energy decays as a result of the limited space. The excited molecules can only return to the ground state by radiative transition, and consequently the fluorescence is significantly enhanced. This type of molecular mechanism overcomes the problem of fluorescence quenching and fluorescence concentration reduction in the aggregation state of traditional molecules and has good application prospect. Taking advantage of AIE, in 2019, a probe containing 4-(tertbutyldimethylsilyloxy) benzyl as the recognition group with AIE activity was developed for the detection of fluoride ions (F−) via the covalent assembly mechanism.16 This fluorophore, which shows aggregation in water and emits strong yellow-orange fluorescence, exhibited significant AIE properties. Moreover, by improving the structure of the naphthalene ring, a fluorescent probe for the real-time monitoring of fluorine ions based on two-photon fluorescence covalent assembly was developed.7 However, because of the prominent hydration effect of fluoride in aqueous environments, the performance of most of these probes is affected by the presence of a large number of organic solvents.1 Because of the inevitable hydration of fluorine ions and the limitation of low concentration for chemical dosimeters, the long response time of a large number of probes used for the detection of fluorine ions is unsatisfactory. In addition, the shortcomings of many organic fluorophores used for detection, such as poor water solubility, weak cell penetration, and poor photostability and chemical stability, are also urgent problems to be solved.
Thus, to overcome these problems, Wang et al. concluded that the interaction between the fluorescent chemical dosimeter and target analyte is essentially an organic chemical reaction.9 Accordingly, improving the reaction efficiency will be beneficial to the performance of fluorescent chemical dosimeters. They attempted to offer a solution, where the self-assembly of fluorescent chemo-dosimeter molecules on the surface of graphene oxide (GO) can avoid the above-mentioned problems by taking advantage of the excellent chemical catalysis and nanocarrier functions of GO (Fig. 2). In the cell imaging experiment, the fluorescence response of the graphene oxide-loaded probe to fluorine ions was weaker than that of the non-loaded probe. Nevertheless, the loaded graphene oxide could give the probe the function of reducing its own background, short response time and response to more analytes. This was the first attempt to design a fluorescent probe by combining GO for sensing and bioimaging application. Thus, this simple design approach can help develop more effective fluorescent probes for other analytes through the combination of different nanomaterials.
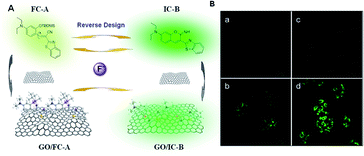 | ||
| Fig. 2 (A) Response process design of fluorescent chemodosimeter FC-A and GO-based fluorescent nanodosimeter GO/FC-A to fluorine ions. (B) Fluorescent confocal images of the graphene oxide-loaded probe to fluorine ions in living cells. (Adapted with permission from ref. 9 copyright 2014, the American Chemical Society). | ||
Many sensors for toxic CN− have been developed based on the strong nucleophilicity of cyanide to metal ions or carbonyl carbon atoms. These sensors showed an adequate limit of detection (LOD) for cyanide, but the LOD for analyte was reduced in the case of an excessive amount of cyanide. Thus, to solve this problem, Kim H. et al. reported a fluorescence probe, CN1, based on 2-hydroxy cinnamate for the detection of cyanide (CN−).17 They introduced an α,β-unsaturated carbonyl moiety in the latent fluorophore, where the 2-hydroxycinnamate group was employed as the fluorogenic unit and the α,β-unsaturated carbonyl group as the reaction unit with cyanide (Fig. 3A). Different from the previous work, cinnamate underwent a rapid cyanide-catalyzed reaction to form a stable coumarin product based on covalent assembly. Characterized by a limit of detection (LOD) of 1.3 μM, this probe also displayed a highly selective and sensitive fluorogenic response to cyanide in the presence of other anions with a micromolar limit for fluorometric detection (Fig. 3B). Kim's work presents an efficient way for developing probes capable of sensing cyanides at a catalytic level.
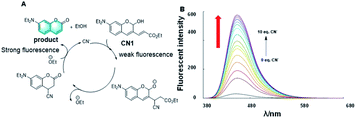 | ||
| Fig. 3 (A) Response mechanism of a covalent assembly probe for CN−. (B) Fluorescence responses of CN1 toward CN− in different eq. CN−. (Adapted with permission from ref. 17 copyright 2016, Elsevier). | ||
The Griess assay is a common method for the quantitative detection of nitrite ions.18 It involves the mechanism of covalent assembly to cause p-amino benzenesulfonic acid to react with analytes to form diazonium ions in an acidic environment, and then produce azo dyes through intermolecular electrophilic substitution reaction with naphthylamine, and its absorption intensity is detected by UV-vis spectroscopy to achieve the detection effect. Nevertheless, due to the toxicity of the materials employed for detection using traditional methods, it is worth improving or developing new and effective methods for the quantitative detection of nitrite ions.
Based on this, Unob et al. proposed a new strategy to optimize the Griess analysis.19 In this strategy, cellulose thread was modified by p-aminobenzoyl, and chromotropic acid was used to replace the toxic aromatic amine n-(1-naphthyl) ethylenediamine (NED), and thus in an acidic environment, the thread acts as a reaction platform for nitrite ions, p-aminobenzoyl and NED. Diazotization reaction and covalent assembly were carried out successively to form azo dyes to form color bands. The effect of the quantitative analysis of nitrite ion concentration was realized according to the dyed length of the thread. This method is convenient and intuitive. Furthermore, the concentration of each reagent and the sample volume were optimized. The proposed method allowed the detection of nitrite in the concentration range of 50–1000 μM. Unob's work further optimized the Griess assay, which realized the accurate quantitative detection of nitrite in a more intuitive and convenient way, exhibiting potential as a detection method.
For detection methods for disease diagnosis, high sensitivity, short response time and efficient and accurate detection effects are the standards to measure their quality. In recent years, fluorescent probes have been developed for the detection of nitrite ions.20–26 However, most of these probes have limited have been developed practical application due to their low sensitivity, high background fluorescence and long response time. In contrast, a novel fluorescent sensor for the quantification of nitrite was designed based on the ‘‘covalent assembly’’ principle by Yu in 2021.27 The response mechanism is actually an intramolecular azo coupling mechanism. In strong acidic medium (pH = 0–1), as is shown in Fig. 4, once the diazotization between nitrite and the aromatic amine part of the probe AAC is completed, the newly formed aryldiazo and the coumarin part of AAC undergo electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction, intramolecular cyclization and protonation, finally forming dye molecules with strong fluorescence. It is worth mentioning that this mechanism utilizes the strategy of covalent assembly. The experimental data showed that the quantum yield of the probe AAC in acidified medium is zero, which shows the characteristics of zero fluorescence background. In addition, its emission spectrum reaches the near-infrared window, which also indicates that it is suitable for practical detection. In addition, this probe also showed some other excellent properties, such as excellent sensitivity and high selectivity. It is worth mentioning that the detection limit is 6.7 nM, which means that the probe is also suitable for low-concentration nitrite environmental monitoring. Consequently, Yu's experiments revealed that their probe is a potential detection tool for practical disease detection.
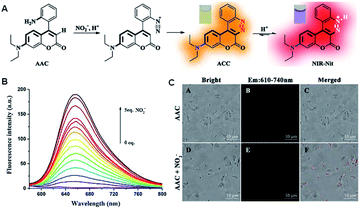 | ||
| Fig. 4 (A) Response mechanism of the covalent assembly probe AAC for NO2−. (B) Fluorescence responses of AAC toward NO2−. (C) Fluorescent confocal microscopy images of E. coli stained with 10 μM AAC for 10 min in the presence of nitrite (5 mM). (Adapted with permission from ref. 27 copyright 2021, Elsevier). | ||
2.2 Probes for metal ions
Accordingly, the question arises, what group can specially respond to gold ions? In 2004, Richard et al. reported the process of the gold-catalysed activation of a C–C multiple bond in alkyne.28 Impressively, in the presence of Au3+, the alkyne was coordinated by the Au3+ in a gold–alkyne complex to realize hydro-arylation, and then underwent intramolecular electrophilic aromatic substitution with a Michael receptor, which indicates that the alkyne group can be used in the design of probes that respond to Au3+.
In 2010, Yoon et al. reported a probe for Au3+ based on the mechanism of gold-catalyzed hydro-arylation, followed by intramolecular electrophilic aromatic substitution with a Michael acceptor (Fig. 5A).29 Through the special response of Au3+, the probe completed the hydro-arylation reaction to afford a coumarin structure, presenting strong fluorescence by covalent-assembly. It is a highly selective and sensitive fluorescence “turn-on” probe for Au3+ ions in protic solvents, which could even realize the bioimaging of Au3+ in live cells.
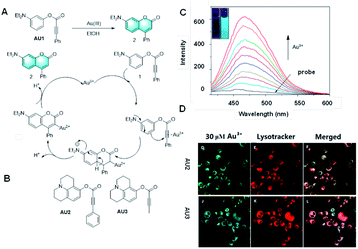 | ||
| Fig. 5 (A) Response mechanism of a covalent assembly probe for Au3+. (B) Structures of covalent assembly probes to Au3+. (C) Response of the probe Au2 towards different concentrations of Au3+. (D) Fluorescent images of Au3+ in HaCaT cells. (Adapted with permission from ref. 42 copyright 2016, Elsevier). | ||
Subsequently, many probes based on the cascade reaction between gold and alkynyl have been developed.30–41 Their luminescence mechanisms are rich and diverse and have excellent performance, but they cannot be strictly classes as the covalent assembly mechanism. It is worth mentioning that two new colorimetric and fluorescent probes were developed for the rapid and highly selective detection of Au3+ (Fig. 3B).42 Acetylene compounds were utilized as probes to rearrange potential fluorophores into fluorescent coumarin derivatives, which could realize the detection and recognition of Au3+ via a gold ion-mediated hydro-arylation reaction. The experimental results showed that these two probes have good selectivity and sensitivity for the detection of gold ions, and their detection limit was as low as 0.1 nM. More importantly, due to their good biocompatibility and cell membrane permeability, these two probes could also be applied for the fluorescence imaging of MCF-cells. They are detection tools with great practical application potential and are expected to bring some practical application value to practical clinical detection. The application of potential fluorophores in the screening of effective catalysts is also an ongoing research topic.
In 2004, Anslyn et al. first reported a highly sensitive probe via thew Heck reaction, which showed high selectivity for Cu2+.43 The recognition mechanism also involved covalent assembly. However, although this probe demonstrated a good detection limit of 30 nM, it also suffered from the drawback that its detection time is nearly 1.5 h.
In recent years, through the same mechanism of N![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N isomerization, many probes for Cu2+ detection have been reported (Fig. 6C).44–54 These probes demonstrated better water solubility, better selectivity, better biocompatibility, higher sensitivity through structural modification, and were applied in cell imaging or paper-based detection devices.
N isomerization, many probes for Cu2+ detection have been reported (Fig. 6C).44–54 These probes demonstrated better water solubility, better selectivity, better biocompatibility, higher sensitivity through structural modification, and were applied in cell imaging or paper-based detection devices.
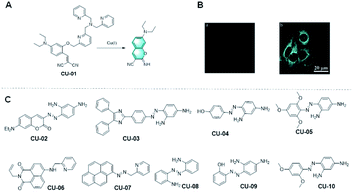 | ||
Fig. 6 (A) Response mechanism of a covalent assembly probe for Cu2+ and (B) fluorescent images of Cu+ in HepG2 cells. (Adapted with permission from ref. 55 copyright 2016, Elsevier). (C) Structures of the probes for Cu2+ detection based on the mechanism of N![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N isomerization. N isomerization. | ||
As the dominant oxidation state in the physiological reducing conditions, recently, Cu+ has been a focus, and thus several synthetic probes have been developed for realizing its detection in biological systems. Among them, many probes contain tris[(2-pyridyl)-methyl] amine (TPA) as the recognition group for Cu+ detection because of the selective promotion of oxidative cleavage of the benzylic ether bond (C–O) upon binding Cu+.
However, the previous designs of TPA-based probes for Cu+ are limited by their dependence on fluorophore scaffolds containing phenolic groups. It is worth mentioning that Hu et al. found that the use of TPA in probes can also be extended to the fluorophore precursors containing hydroxyl groups. According to their strategy, TPA was used in a probe and connected with the phenylphenol group of the fluorophore precursor (Fig. 6A).55 Through the complexation of the analyte cuprous ion, the carbon–oxygen bond is broken, and the fluorophore precursor is covalently assembled through Pinner cyclization to form a fluorophore with strong fluorescence signal. The probe CU-01 made according to this strategy not only showed excellent solubility in aqueous solution and living cells, but also had a low fluorescence background and rapid response to analytes in living cells, which are worthy of recognition. In conclusion, Hu's work solved the limitation of using the TPA group as a cuprous ion recognition group, broadened the detection method of cuprous ions, and provided a good idea for the further preparation of fluorescent probes for the detection for Cu+ with more sensitive performances and more significant detection effects.
A class of probes for the detection of Hg2+ based on vinyl ethers as the reaction unit was reported.56–59 The mechanism of these probes is that the Hg2+-promoted hydrolysis of the vinyl ether group results in a hydroxy-ester intermediate, which undergoes a fast cyclization reaction to afford a fluorescent coumarin structure. Extending coumarin derivatives with electron-donating substituents, such as amino and dimethylamino groups, can improve their photophysical properties. For example, as shown in Fig. 7C–E, upon the addition of Hg2+ in pure aqueous medium, the Hg2+-mediated hydrolysis of vinyl ether and subsequent cyclization reactions converted the probe HGb2 into the corresponding iminocoumarin dye, which is strongly fluorescent and can also be applied for imaging Hg2+ in living cells. The probe HGb4 has a remarkable fluorescence enhancement at 625 nm, a large Stokes shift and low limit of detection (7.1 nM) when 1,4-diethyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroquinoxaline is present instead of a benzene ring in its structure. This probe exhibited a good performance for the detection of Hg2+ in vivo and in vitro.
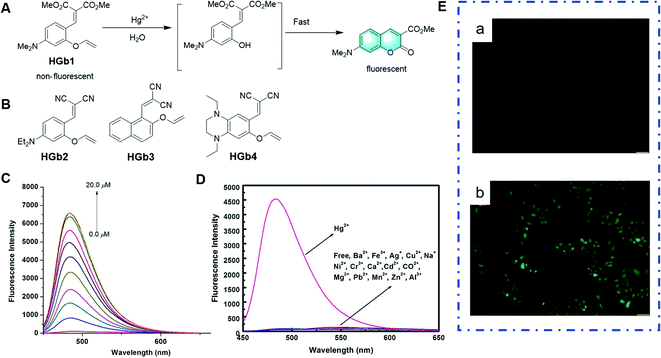 | ||
| Fig. 7 (A) Response mechanism of the probe HGb1 to Hg2+. (B) Structures of probes for Hg2+ based on the same mechanism. (C) Fluorescence responses of HGb2 toward different concentrations of Hg2+ and (D) different metal ions. (E) Images of HeLa cells: (a) fluorescent images of HeLa cells incubated with HGb2 (10 μm) and (b) fluorescent images of HeLa cells treated with HGb2 (10 μm) for 30 min, and then incubated with 30 μm Hg2+ for another 30 min. (Adapted with permission from ref. 57 copyright 2014, Wiley). | ||
The effects of mercury exposure on the nervous system are mainly attributed to the organic form of mercury, methylmercury (MeHg+), which acts physiologically by binding with the sulfhydryl groups in proteins or cysteine, forming water-soluble complexes in tissues, accumulating in the food chain and crossing the human brain blood–brain barrier. However, it is a laborious task to develop molecular probes for the selective detection of MeHg+ in the presence of Hg2+. In 2014, Yang et al. reported Hg2+-promoted desulfurization, with ring-opening of 1,3-dithiolane, and subsequent covalent-assembly with the amino group on the benzene ring owing to the strong nucleophilicity of the amino group.60 As shown in Fig. 8A and B, in the probe HGc1, the conjugated structure of the product generated by detection was expanded, which greatly enhanced the fluorescence. Based on this mechanism, other probes, HGc2 and HGc3, also used 1,3-dithiolane as the reaction unit to achieve the same covalent assembly strategy.61,62 Among them, it is worth mentioning that the probe HGc3 exhibited high sensitivity and selectivity towards Hg2+ and MeHg+, which emitted strong fluorescence. Moreover, it was successfully applied for the quantitative detection of Hg2+ in real environmental samples and imaging of Hg2+ in HeLa cells.
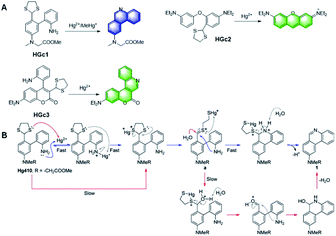 | ||
| Fig. 8 (A) Structures of probes HGc1, HGc2, and HGc3 and their response to Hg2+. (B) Proposed mechanism of the probe HGc1 to Hg2+. (Adapted with permission from ref. 60 copyright 2014, the American Chemical Society). | ||
Over the last few years, considerable efforts have been focused on the exploration of novel palladium ion fluorescent probes based on the coordination action of Pd2+ with heteroatomic ligands, ring-opening reactions, oxidative cyclization reactions, as well as demercuration and deallylation reactions catalyzed by palladium. However, many of them still have limitations, such as working only in organic solvents and/or water organic cosolvents, requiring additional reagents, laborious synthetic processes using expensive chemicals, interference from other coexisting metal ions, and long response time. In addition, among the few available Pd2+ chemical dosimeters reported, most of them use the pH-sensitive fluorescein or rhodamine as fluorophores, and their pH dependence may cause detection errors. Hence, for practical applications, it is necessary to develop new simple and specific fluorochemical dosimeters to detect Pd2+.
In 2005, Anslyn et al. designed a specific palladium ion detection probe via the ‘covalent assembly principle’.2 Through palladium-catalysed Heck reaction, an intramolecular cyclization reaction occurs, which can turn the fluorescence signal on and realize the detection. However, the slow initiation of the Heck catalyst limits the sensitivity of this probe (Fig. 9A).
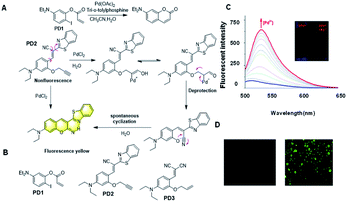 | ||
| Fig. 9 (A) Response mechanism of the probes PD1 and PD2 for Pd2+ detection. (B) Structures of probes for Pd3+. (C) Fluorescence responses of PD2 toward Pd2+ and (D) The fluorescent images of Pd2+ in living cells. (Adapted with permission from ref. 80. Copyright 2016, Elsevier). | ||
It has been reported that through a palladium-catalyzed hydrolysis reaction, the terminal propargyl ether can be cleaved to form the corresponding free hydroxyl group.63–65 Based on the Tsuji Trost reaction, the palladium ion is reduced to palladium(0) by triphenylphosphine in the corresponding process, and then the allyl group in the molecular probe is oxidized with palladium(0) to release a hydroxyl intermediate, which spontaneously forms coumarin derivatives with high fluorescence intensity. The strong fluorescence change before and after the response is also an intuitive manifestation of the effective and sensitive detection of palladium ions. In 2016, Han et al. reported the probe PD2 based on this mechanism (Fig. 9A).66 The free hydroxyl group combined with the cyano-group can form a coumarin structure, which significantly changes its fluorescence. It was successfully utilized for the visualization of Pd2+ in vitro and in living cells (Fig. 9C and D). Later, Yang et al. reported another probe PD3 for the detection of Pd2+ with a simple structure based on the terminal propargyl ether, which was easy to prepare and had a lower detection limit of 1.65 nM in an aqueous solution.67 Because of the non-radiative energy consumption caused by intramolecular rotation, the probe did not show fluorescence in solution. As an effective tool for detecting Pd2+, it can effectively recognize Pd2+, and thereby emit an obvious fluorescent “turn-on” response. Moreover, it exhibited outstanding properties, such as rapid response (within 3 min), good linearity (R2 = 0.9945), specific selectivity, and superior recovery, demonstrating its extraordinary potential for the analysis of real samples.
2.3 Probes for small molecules
In 2015, Phillips and the co-workers used 2,4-dinitrobenzesulfonyl (nosyl) as the reaction unit for detecting thiols in a polymeric monomer.68 As shown in Fig. 10, the nosyl group of the probe BT1 cleaved selectively in response to the added thiol and the free phenol cyclized into a thioester, releasing one equivalent of ethanethiol, while forming an equivalent of fluorescent 7-alkoxycoumarin by the covalent assembly strategy simultaneously. Phillips' work described a responsive polymer membrane realizing the trace level detection of specific molecular signals (thiol), and subsequently triggering a self-propagating reaction in the material to transform the non-fluorescent film into a global fluorescent film. More importantly, according to these findings, it is obvious that the self-propagating reaction in synthetic materials is a promising strategy. In the process of synthesizing materials, due to the self-propagating reaction, the materials can realize self-transformation in response to a trace level of a specific application signal in an autonomous and complete way, realizing the new biomimetic amplification reaction.
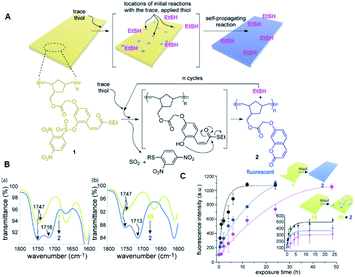 | ||
| Fig. 10 (A) Illustration of the polymeric film response to thiol. (B) Change in IR signature in the carbonyl region when film 1 (a) or 10 (b) is exposed to 10 mM thiol. (C) Fluorescence kinetics when 0.1 mM (pink data), 1 mM (blue data), and 10 mM (black data) solutions of L-cysteine were exposed to films of polymers 1 and 10 at 23 °C. (Adapted with permission from ref. 82 copyright 2015, the American Chemical Society). | ||
For a long time, due to the similarity of GSH, Hcy and Cys, it was a challenge to develop a specific probe for the recognition of Cys in the presence of GSH, Hcy and Cys. Thus, to solve this problem, in 2016, Song et al. designed a probe BT2 using acrylate as the recognition group for the detection of cysteine (Fig. 11).69 In the presence of Cys, GSH and Hcy, probe BT2 formed thioether due to a nucleophilic addition reaction. The difference is that after cysteine treatment, the thioether formed by the probe can further undergo intramolecular cyclization to form an imino coumarin dye and emit strong red fluorescence. However, the addition reaction of Hcy and GSH with the probe could not further cyclize to form imino coumarin dyes, and thus the specific recognition effect of Cys in the presence of biothiols with similar structures was achieved. Consequently, this probe had an excellent performance, displaying a low detection limit of 6.6 nM and a pronounced Stokes shift of 148 nm. It could also be applied for cell imaging because of its permeability and biocompatibility.
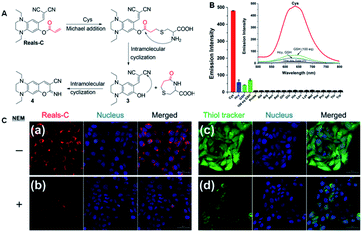 | ||
| Fig. 11 (A) Proposed mechanism of Reals-C with Cys. (B) Emission intensity of Reals-C (10 μm) with 10 equiv. of canonical amino acids and biothiols. (C) Confocal fluorescence images of HaCaT cells incubated with Reals-C (a) and 20 μm thiol tracker (c) for 30 min. Cells were pre-treated with NEM (1 mm) for 30 min, followed by incubation with 10 μm of Reals-C (b) and 20 μm thiol tracker (d) for 30 min. (Adapted with permission from ref. 69 copyright 2016, Elsevier). | ||
Using the same structure, Churchill et al. applied the probe Reals-C in HaCaT human keratinocytes and mice liver.70 Thus, a new preeminent fluorescent probe featuring a red emission, large Stokes shift of cysteine and water-based detection was prepared. The probe detected analytes through the complex interaction established by its leaving group to distinguish and form a red emission analyte sensing platform (λex = 471 nm and λem = 637 nm) via a chemical cascade reaction. Furthermore, the responsive performance of the probe was proven by in vitro and in vivo experiments. Compared with a sensitive commercial thiol probe, this probe could successfully detect endogenous cysteine in human keratinocytes. Reals-C showed preeminent in vivo cysteine detection in a drug-induced liver injury model. The considerable results suggest that this type of Cys-recognizing fluorescent probe can be extended in the future to serve as a promising tool for exploring microbiological systems, such as intracellular organelles related to Cys.
The use of the benzyl azide group as a recognition unit for H2S has been widely reported.71–73 The mechanism is that benzylazide group can be reduced to a benzylamine intermediate in the presence of H2S. The resulting benzylamine fraction is unstable, and thus subsequently self-eliminated by 1,6-disulfide to release a hydroxyl group. Then it will undergo intramolecular cyclization to produce imino coumarin molecules. As shown in Fig. 12A, different probes based on this reaction mechanism via structure modification have been developed. It is gratifying that most of these probes showed superior performances in biological imaging, such as high sensitivity, rapid response time, and good water solubility.
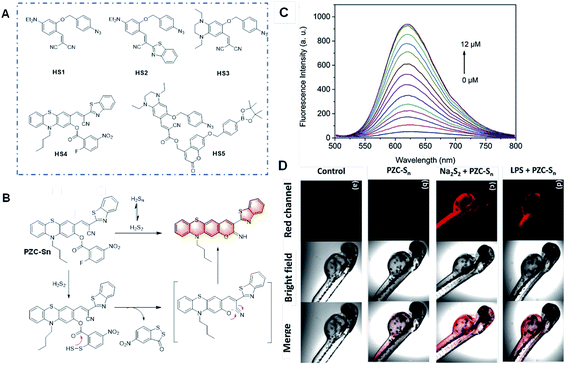 | ||
| Fig. 12 (A) Structures of the probes for H2Sn based on the benzyl azide group as the recognition unit. (B) Structure and response mechanism of PZC-Sn to H2Sn. (C) Fluorescence responses and (D) images of PZC-S in vitro and in zebrafish. (a) Zebrafish without any treatment; (b) zebrafish stained with PZC-Sn; (c) zebrafish treated with 12 μM Na2S2 followed by the staining with PZC-Sn; and (d) zebrafish treated with LPS for 12 h followed by the staining with PZC-Sn. (Adapted with permission from ref. 74 copyright 2010, The Royal Society of Chemistry). | ||
In 2019, Zhao et al. reported an outstanding probe, PZC-Sn, based on a phenothiazine coumarin dye for the detection of H2Sn via covalent assembly (Fig. 12B).74 H2Sn can react with the recognition group (2-fluoro-5-nitrobenzoate moiety) by replacing the F atom to produce an intermediate with an –SSH group and induce cyclization between the ester group and –SSH group. Remarkably, this probe emitted red emission with a massive Stokes shift and showed high sensitivity to H2Sn with a fluorescence turn-on response and low cytotoxicity to cells. The bio-imaging analysis of exogenous and endogenous H2Sn in living RAW264.7 cells and zebrafish was performed, which showed superior results without autofluorescence.
In recent years, many small molecule fluorescent probes have been developed for the detection of thiophenol, but most of them have long response times, relatively small fluorescence enhancement ratio and high detection limit. Thereby, it is challenging to prepare sensitive, rapid response and low detection limit probes for practical biological detection. Based on the mechanism of thiophenol-induced cleavage of the 2,4-dinitrophenolate moiety and a subsequent cyclization reaction, some novel probes have been reported for the detection of thiophenol.75–77 For example, Song et al. developed a probe for the detection of thiophenol.76 As shown in Fig. 13, TP1 was essentially nonfluorescent due to the mechanism of the photo-induced electron transfer (PET) process. In the presence of thiophenol, the 2,4-dinitrophenolate moiety in TP1 would be selectively cleaved and a subsequent cyclization reaction would produce an imino-coumarin dye. The probe TP1 displayed a rapid response (within seconds) and a massive Stokes shift (129 nm). Furthermore, this probe emitted in the red or near infrared (NIR) regions, and thus it can penetrate the cell membrane and allow the visualization of intracellular thiophenol in living cells.
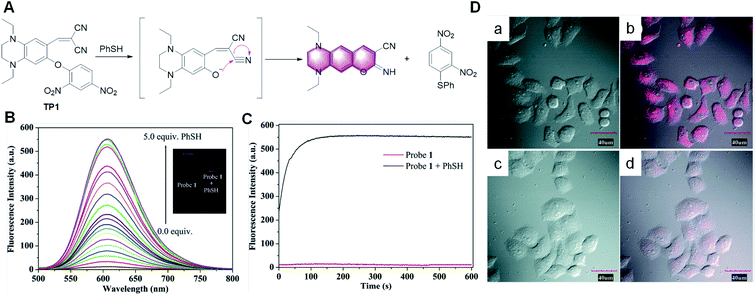 | ||
| Fig. 13 (A) Proposed sensing process of probe TP1 for thiophenol. (B) Fluorescence spectra of TP1 (10.0 μM) upon the addition of thiophenol. (C) Kinetics of the fluorescence enhancement in the absence (red line) and the presence (black line) of thiophenol. (D) Fluorescence (left), bright field (middle) and merged (right) images of living HeLa cells. Top row: cells pre-treated with thiophenol (50.0 μM), and then incubated with TP1 (10.0 μM) for 30 min at 37 °C (a and b). Bottom row: cells incubated with TP1 (10.0 μM) for 30 min at 37 °C (c and d). (Adapted with permission from ref. 76 copyright 2010, The Royal Society of Chemistry). | ||
In 2014, Yang et al. developed a novel probe, NA1, to detect sarin via a Vilsmeier–Haack reaction employing the covalent assembly strategy (Fig. 14A).3 The highly electron deficient phosphorus centers of the nerve agents, their mimics, and precursors were capable of activating the 4-diethylaminobenzaldehyde in NA1 toward nucleophilic attack. After the reaction, the probe emitted strong yellow-orange fluorescence, thus realizing the detection of the sarin. Overall, this is the first case of using the covalent assembly strategy to prepare a small molecule fluorescent probe. Yang's work combined the advantages of the proposed covalent-assembly principle and existing chemistry for the recognition of a nerve agent. Subsequently, the application of the covalent assembly fluorescence response strategy in the sensing field was further expanded. In 2016, Goswami et al. reported a probe, NA2, which could detect F− and the nerve-agent mimic diethyl cyano-phosphonate in mixed aqueous media (Fig. 14A).86 This probe could discriminate diethyl cyanophosphonate (DCNP) and diethyl chlorophosphate (DCP) via cyclization-induced fluorescence enhancement. After the addition of fluoride, the probe NA2 formed a green fluorescent intermediate, NA2F, through a specific intramolecular cyclization reaction triggered by the affinity of fluoride to silicon. Subsequently, in the presence of DCNP, the lone pair electrons on the imino group of NA2F first attacks DCNP to release CN−, which attacks the double bond of the imino-coumarin moiety. Accordingly, the six-membered ring product is formed by the resonance of the imino-coumarin to the benzothiazole nitrogen through the ICT mechanism, which also has strong fluorescent on a different channel to distinguish F− and DNCP. In contrast, in the presence of DCP, the lone pair electron attack of the imino nitrogen of the intermediate NA2F caused a slight fluorescence enhancement, thus achieving the effect of distinguishing DCNP from DCP. This probe was fabricated on test strips, making the test more rapid and convenient. Moreover, the unique “off–on–on” fluorescence response mechanism also provides a reference for the specific detection of fluoride based on the covalent assembly mechanism.
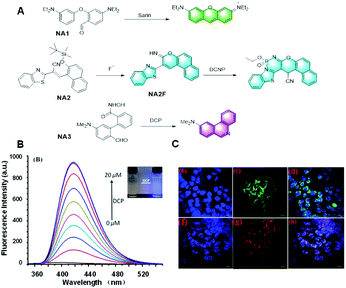 | ||
| Fig. 14 (A) Response mechanism of the probes NA1/2/3 to nerve-agents. (B) Fluorescence responses of probe NA3 toward DCP and (C) fluorescent images of DCP in live cells. (Adapted with permission from ref. 87 copyright 2019, the American Chemical Society). | ||
In addition, Yang et al. reported a probe, NA3, for the detection of DCP based on the Lossen rearrangement (Fig. 14A).87 The hydroxamic acid group in probe NA3 was combined with DCP, and the newly formed phosphoryl intermediate was rapidly rearranged to provide the corresponding isocyanate, which tended to further react with water to release an NH2 group. This probe had many advantages, such as low detection limit (10.4 nM), sensitive response (100 s), and outstanding linearity (R2 = 0.9993) in the range of 2 to 16 μM. More importantly, the successful detection of DCP in the gas state in this paper also proved the practicability of the probe. It is believed that this probe will be a useful tool for sensing nerve agents.
2.4 Probes for ROS/RNS
The “light-up” probe CL1 for the detection of ClO− based on 2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidine-1-oxyl (TEMPO) oxidation was reported in 2019 for the first time (Fig. 15A).88 During the reaction process, the primary alcohols in the probe CL1 are first oxidized to aldehydes by the active intermediates generated by ClO− and TEMPO. The new generated formyl groups are captured swiftly by the adjacent NH2 groups initially, resulting in the spontaneous formation of phenanthridine compounds with strong fluorescence emission. Further research showed that this probe had excellent performance, such as fast response (within 2 min), low detection limit (63.7 nM), and good linearity (R2 = 0.9863). It was also applied for the analysis of everyday samples, such as swimming pool water and tap water. In general, it is a useful strategy for the special detection of ClO−.
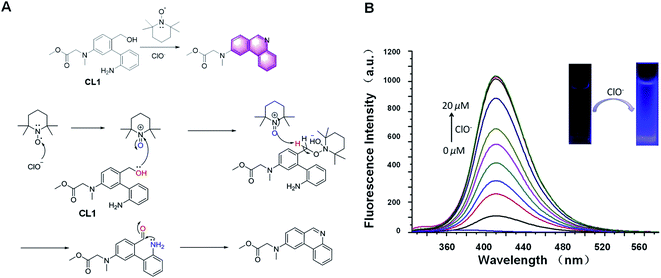 | ||
| Fig. 15 (A) Response mechanism of the probe CL1 to HOCl. (B) Proposed mechanism for the reaction of CL1 with HOCl. (B) Fluorescence responses of probe CL1 toward HOCl (adapted with permission from ref. 88 copyright 2017, The Royal Society of Chemistry). | ||
In recent years, numerous fluorescent probes have been reported for the detection of H2O2. The use of an aromatic boronic ester as a detecting unit for H2O2 has been widely studied for a long time.89 In 2012, Phillips et al. designed several fluorescent H2O2 probes, in which the response mechanism was based on covalent assembly to form imino-coumarin derivatives.90 The initial results demonstrated that appropriate reagent design enabled rapid down-selection before quantitative fluorescence assays were conducted. This strategy should facilitate the time-consuming process of performing quantitative assays in resource-limited environments.
Aromatic boronic esters are the preferred scaffolds for designing fluorescent probes with fluorophores characterized by the red/near-infrared emission and large Stokes shift. This is because long wavelength light can penetrate deep into tissues under low background interference, while a large Stokes shift can minimize self-absorption to improve the detection sensitivity. However, to date, fluorescent probes capable of H2O2 detection with both a red/near-infrared emission and a large Stokes shifts are rare. To better visualize H2O2 detection for bio-imaging, in 2018, Song et al. showed a highly sensitive and selective fluorescence probe for the detection of H2O2 based on the same mechanism (Fig. 16).91 During the detection process, Probe 1 was non-fluorescent initially. Once treated with H2O2, H2O2 caused the cleavage of the boronic ester moiety and the quinone derivative would leave quickly, subsequently resulting in an interference ability in aqueous media, which can also be applied to detect intracellular H2O2 in HeLa cells.
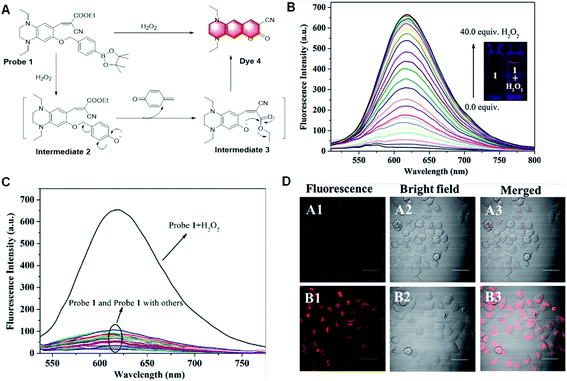 | ||
| Fig. 16 (A) Proposed response mechanism and (B) fluorescence responses of probe 1 toward H2O2. (C) Fluorescence response of probe 1 toward relevant testing species. (D) Images of HeLa cell. A1–A3: cells incubated with probe 1. B1–B3: cells pre-treated with H2O2, and subsequently incubated with probe 1. (Adapted with permission from ref. 91 copyright 2018, Elsevier). | ||
In 2012, Yang et al. first reported a peroxynitrite probe based on a green-emitting coumarin derivative (Fig. 17A).92 The amino group on the coumarin moiety was oxidized by peroxynitrite, which transformed the molecule into a red-emitting resorufin derivative via an orange-emitting intermediate by expanding the conjugated structure. This probe showed three-channel signals, which could distinguish peroxynitrite from other ROS and RNS. Moreover, because of its membrane permeability and low cytotoxicity, it could also be utilized in a cell imaging (Fig. 17B) intramolecular cyclization reaction to form a dye emitting intense fluorescence. The probe had high selectivity and anti-interference ability in aqueous media, which could also be applied to detect intracellular H2O2 in HeLa cells.
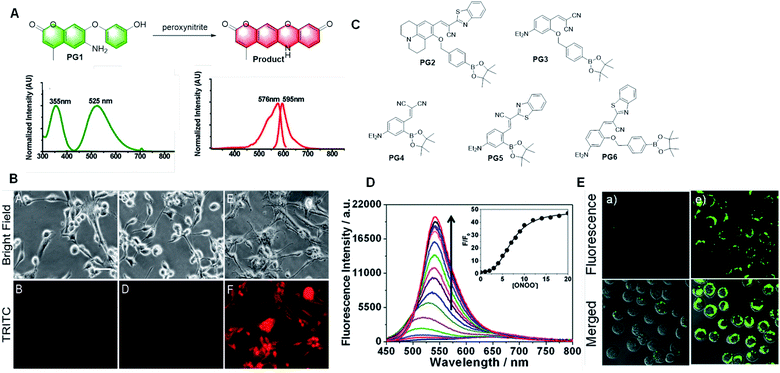 | ||
| Fig. 17 (A) Response and absorption and emission spectra of peroxynitrite probe PG1 based on a green-emitting coumarin derivative to peroxynitrite. (B) Fluorescent images of this probe for peroxynitrite imaging in living cells. (C) Structures of the probes based on aromatic boronic ester to peroxynitrite. (D) Fluorescence response of PG2 toward relevant testing species. (E) Fluorescent images of the probe PG2 for peroxynitrite imaging in living cells. (Adapted with permission from ref. 92 copyright 2018, Elsevier). | ||
Compared with H2O2, aromatic boronic esters react with peroxynitrite nearly a million times faster.93 Consequently, a series of probes containing aromatic boronic esters have been developed to detect peroxynitrite in recent years.94–98 The hydroxyl group obtained by the cleavage of aromatic boronic esters reacts with the cyano group. Finally, these probes form imino-coumarin or coumarin derivatives with strong fluorescence by cyclization (Fig. 17C). These probes have many advantages, such as fast response, excellent selectivity, and sensitivity, and they were used to detect peroxynitrite in cell imaging. However, all these probes displayed low hydrophilicity and the test solvent contained 10% or more organic solvent, such as ethanol, acetonitrile, or DMSO. Thus, there are still some limitations in the application of this type of probe, and consequently more research is needed to solve these problems for its further application.
In the early years, Nagano et al. first reported a diamino-fluorescein as an NO indicator.99 Different form the traditional structure of fluorescein, amino fluorescein shows quenched fluorescence due to the strong electron donor group of amino. Upon interaction with NO, the amino group in the probe is transformed into a relatively weak amide electron donor group, its electronic structure changes and the fluorescence recovers, thus realizing the detection of NO. It is worth mentioning that the triazole product has strong green fluorescence, with the fluorescence quantum yield increasing by more than 100 times. It also had a low detection limit of 5 nM. Many groups followed this mechanism for the design of other probes by changing the fluorophore to achieve better optical performances or modifying the structure to optimize the performance.100–107 However, this type of probe still has a limitation, that is, the probe will be disturbed by endogenous o-dicarbonyl compounds such as deoxyascorbic acid and methylglyoxal, which will distort the probe signal.
In 2010, Anslyn et al. reported an NO fluorescent probe, NO1, based on the formation of a diazo ring (Fig. 18A).108 The electrophilic aromatic substitution on the electron-deficient nitrosamine yielded a hydroxyhydrazine derivative. Elimination of a molecule of water led to the formation of a diazo ring by covalent assembly. The expanded conjugation of the molecule led to a substantial increase in fluorescence. It also possessed many advantages, such as rapid and linear response, excellent selectivity, and low pH dependence.
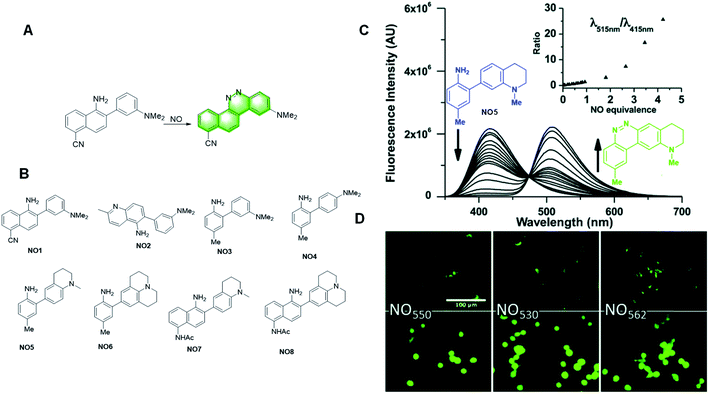 | ||
| Fig. 18 (A) Response mechanism of probe NO1 to NO. (B) Structures of the covalent assembly probes reported for NO detection. (C) Fluorescence responses of probe NO5. (D) 40× magnification, pseudo-colored FITC-filtered images of NIH-3T3 cells without NO dosing (B), and with 320 mM NO added (C) for NO5 (NO550), NO7 (NO530), and NO8 (NO562). (Adapted with permission from ref. 109 copyright 2018, Elsevier). | ||
Subsequently, they developed a series of probes based on the same mechanism. In 2020, Yang et al. summarized the probes they studied for the quantitative detection of NO. They developed probes with various structures based on the design idea of covalent assembly (Fig. 18B) and selected the probes more suitable for clinical detection by comparing their performances (Fig. 18B).109 Among the probes, NO7 acts as a promising material for live cell imaging. Due to its greater response to stimuli, higher selectivity for NO, and the ability to image both the reacted and unreacted probe, NO7 provides an attractive option as a nitric oxide probe and a potentially valuable alternative to the commercial dye DAF-FM in various applications.
After analysing the capacity of the probes they studied, they found that attaching electron-donating groups, primarily dialkyl amines, on the nucleophilic aryl group, and avoiding the conjugation of electron-withdrawing groups to the 2-amino group, render the probes sufficiently nucleophilic to readily scavenge NO in cellular media. Furthermore, fusion of the aminoalkyl groups to the nucleophilic aryl group increased both the fluorescence wavelength and the fluorescence quantum yield of the cinnoline product.
In 2017, Yang et al. reported a probe, OR570, based on the covalent assembly principle, which could detect oxidative radicals (Fig. 19).110 The methine linked with secondary benzylic is the hydrogen atom donor. The presence of the ethoxy group keeps the free radicals stable, thus enhancing the performance of the probe. The main advantage of the assembled probe is the zero-background fluorescence signal, which makes this probe capable of detecting analytes at a trace level with high sensitivity. However, due to its low hydrophilicity, it can only be used in organic solvents.
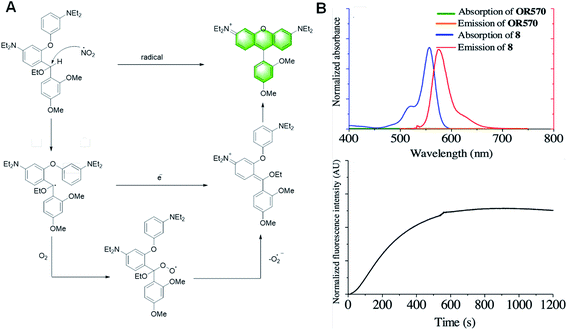 | ||
| Fig. 19 (A) Tentative detection mechanism of OR570 toward highly oxidative radicals. (B) (Top) absorption (black) and emission (red) spectra of OR570 and compound 8. (Bottom) kinetic curve of the formation of OR570 upon the addition of oxidative radicals. (Adapted with permission from ref. 110 copyright 2019, The Royal Society of Chemistry). | ||
Moreover, the main structure of the probe reported by Yang Y. in this paper is the same as that of the probe previously reported for neurotransmitters and mercury ions, and the reaction mechanism is similar. Both of them follow the mechanism of covalent assembly. Once they are activated with the participation of the analytical substrate, intramolecular electrophilic aromatic substitution occurs, and then eliminated to obtain the xanthene dye with strong fluorescence. This means that the main structure of the probe has a good prospect, and it has unlimited possibilities in the detection of other specific substances.
2.5 Probes for enzymes
However, due to the high background fluorescence and detection error of water-soluble hydrolysates secreted by cells, the performance of these probes is restricted. At present, the commercial ELF-97 probe produces water-insoluble hydrolysate after enzymatic hydrolysis. However, under the irradiation of a 488 nm long wavelength Ar ion laser, the excitation effect of the probe is not good, which is the excitation wavelength commonly used by confocal laser scanning microscopes and flow cytometry. Therefore, new fluorescent probes are needed for the detection of ALP, which must be compatible with physiological conditions, have a high signal-to-noise ratio and can be excited on the 488 nm line of the AR laser.
Early on, Kim et al. reported a strategy for the detection of ALP using covalent assembly probes containing an imino-coumarin benzothiazole structure (Fig. 20).114 The probes ALP-1 and ALP-2 reacted with ALP to make the phosphate leave and generate hydroxyl. Combined with the cyano group, the free hydroxyl group can form an imino-coumarin structure with strong fluorescence. They were also applied for imaging endogenous ALP activity in living cells.
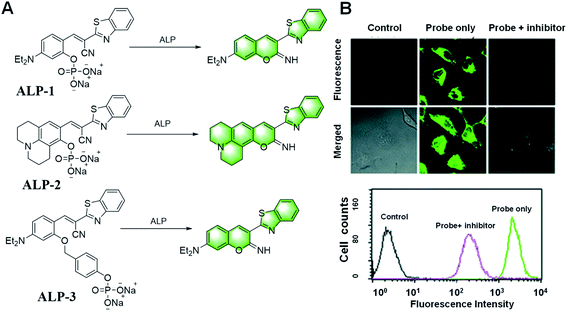 | ||
| Fig. 20 (A) Illustration of the iminocoumarin-benzothiazole-based probes ALP-1/2/3 for the detection of ALP. (B) Representative confocal fluorescence images of HeLa cells incubated with probe ALP-1 for 2 min. (Adapted with permission from ref. 114 copyright 2011, The Royal Society of Chemistry). | ||
Two years later, they introduced a benzyl group between the fluorophore and the phosphate to improve the probes, resulting in ALP-3 with a faster response, and achieved real-time quantitative analysis (Fig. 20).115 In addition, the potential utility of the probe in the screening of ALP inhibitors was demonstrated with levamisole. This work demonstrated the utility of self-immolated linkers in the design of fluorogenic substrates for enzymes possessing comparatively difficult access to the active catalytic site, which opens the possibility to improve existing fluorogenic substrates for various enzymes.
In the early years, Sames et al. reported a probe, MAO1, based on intramolecular cyclization to generate an indole derivative by covalent assembly.116 As shown in Fig. 21, enzymatic oxidation of the ethyl-amino group in probe MAO1 affords an aldehyde intermediate, which subsequently undergoes spontaneous intramolecular condensation with the aniline amino group, furnishing an indole moiety in an irreversible fashion. This overall chemical process results in a profound electronic change in the system, which in turn should alter its fluorescence profile. In 2012, Kim et al. reported a two-photon absorption probe, MAO2, based on imino-coumarin derivatives (Fig. 21).117 The aminopropyl and N-methylaminopropyl as the reactive groups could transform into iminium ions by catalysis with MAOs. The probe following the reaction of hydrolysis and b-elimination generated a hydroxyl group, which could condense with one of the nitrile groups to produce the final product with two-photon fluorescence. In 2019, Li et al. reported novel probes containing amino-propyl as the recognition group, which can detect MAO-B.118 They chose coumarin as the dye group, while decorating the 3-aminopropoxy group for the detection of MAO-B. Once the enzymatic oxidation by MAO-B was triggered, intramolecular cyclization occurred and the fluorescence signal of coumarin was turned on. To date, these two probes, MAO3 and MAO4, not only have excellent selectivity, which can distinguish MAO-B from MAO-A concisely (Fig. 22B), but also have a low detection limit and can be applied in human astrocyte (U87) imaging. Consequently, MAO-B can be selectively detected by the tandem reaction probe at a reasonable pH value (pH = 7.4) and mild temperature (37 °C). The signal enhancement in these two probes was obvious, showing the selectivity between MAO-B and MAO-A. Importantly, the novel design strategy of establishing fluorophores by targeting enzymes in the reaction process is significant in the future.
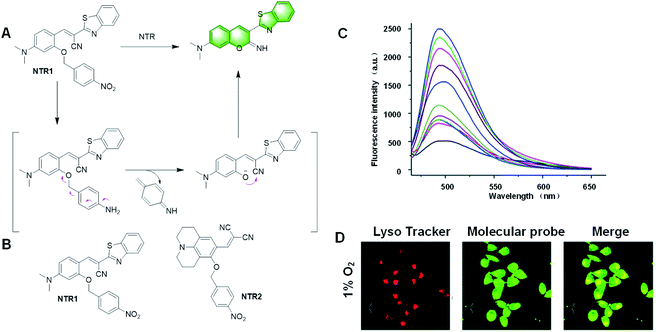 | ||
| Fig. 22 (A) Response mechanism of the probe NTR1 to NTR. (B) Structures of the covalent assembly probes reported for the detection of NTR. (C) Fluorescence response of NTR1 toward different concentrations of NTR. (D) Confocal fluorescence images of MGC-803 cells treated with the probe under 1% O2 conditions for 12 h. (Adapted with permission from ref. 119 copyright 2018, Elsevier). | ||
In 2018, Gu et al. described a probe, NTR1, based on imino-coumarin derivatives, which could detect NTR in the presence of NADH.119 The 4-nitrobenzyl is the reactive group that can leave by NTR catalysis (Fig. 22A). The intramolecular nucleophilic attack of the phenolic oxygen to the nitrile group resulted in the cyclized imino-coumarin-benzothiazole. This probe had a fast fluorescence response in the presence of NADH within only 20 min. NTR1 showed high sensitivity and good selectivity to NTR and a LOD of 11 ng mL−1. It could be applied in the imaging of endogenous NTR in HepG2 cells and tumor tissues under hypoxia conditions. Thus, NTR1 has great potential to monitor NTR in the biological system (Fig. 22C and D).
In recent years, many fluorescent probes for detecting NTR have been developed, but most of them can only achieve single photon excitation, causing great damage to cells and poor permeability. In 2019, Liu et al. realized a two-photon fluorescent probe, NTR2, for the detection of NTR under hypoxic condition.120 The julolidine structure, instead of the imino-coumarin derivative, had two-photon activity (Fig. 23A). The reaction mechanism is as follows: under anoxic condition, nitrating enzyme reduces the nitro group to the corresponding amino group, and then releases iminocoumarin. The NTR detection limit of the probe was 48 ng mL−1. This probe could be applied to monitor the hypoxic status of MGC-803 cells, MCF-7 cells, and 3D tumour spheres by detecting endogenous NTR.
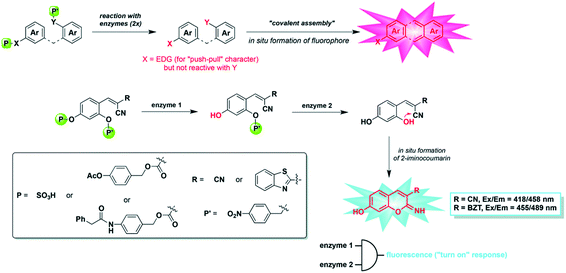 | ||
| Fig. 23 Dual-enzyme sensing strategy explored in this work: (top) “covalent assembly” principle applied to the simultaneous detection of two distinct enzymes (X = NH or O, EDG = electron-donating group) and (bottom) in situ synthesis of 3-substituted-7-hydroxy-2-iminocoumarin scaffolds from a non-fluorescent caged precursor and through domino reactions triggered by the two different enzymes. (Adapted with permission from ref. 125 copyright 2015, The Royal Society of Chemistry). | ||
In recent years, characterized by the simple structure and low cost of PGA, a series of probes was reported with the development of the design principle of the “covalent assembly” based on PGA probe examples.121–124 Recently, it was found that protease (i.e., PGA and ALP) can initiate biocompatible cyclization/aromatization reaction from the mixed cage precursor of diarylether and construct anthracene-based fluorophores. The principal mechanisms of activation are based on the pyronin assembly triggered by the enzyme itself.
However, from a kinetic point of view, there is a problem that needs to be overcome, where the formation of pyronin takes over 10 h, which is too slow to achieve a significant fluorescence level for considering the implementation of this “covalent assembly” probe in diagnostic bioassays or in vivo fluorescence imaging of disease-related enzymes.
To realize a more suitable probe capable of detecting PGA, Romieu et al. reported a dual-reactive probe for the detection of PGA or pig liver esterase (PLE) as well as NTR simultaneously by covalent assembly (Fig. 23).125 The probe was activated via the hydrolysis of an amide (or ester) bond and reduction of a nitro group, followed by domino 1,6-elimination/cyclization to produce 7-hydroxy-(2-imino) coumarin with strong fluorescence. Combined with the reaction/quenching groups of two different analytes, the dual active coumarin precursor in this work can be easily decorated to form a “double-lock” structure, where a dramatic fluorescence signal only occurs when the two analytes exist simultaneously. It is well known that the overproduction of a specific analyte may be more than one pathological feature, and there may be false-positive signals in healthy tissues. Thus, the concept of ‘double-gating’ structure enables the analysis of pathology more accurately by detecting another characteristic analyte.126 Romieu's work provided a good strategy for the preparation of high-precision probes, especially those related to effectively distinguishing molecules with similar chemical reactivity (such as biothiols).
2.6 Probes for DNA
Nucleic acids play an important role in physiological genetics, and thus are a research hotspot. The traditional DNA double helix structure is the most abundant DNA structure in the human body. However, with the discovery from research and the progress of physiological regulation, DNA also contains other secondary structures. Among them, single chain hairpin structure, G-quadruplex structure, double chain cross structure and bimolecular G-quadruplex structure all play an important role in transcriptional regulation mechanism, but their specific physiological mechanism still needs to be studied. Therefore, it is necessary to further understand DNA sequence detection and the physiological mechanism of the DNA structure.In recent years, with the development of small molecule fluorescent probes, many DNA fluorescent probes have been developed. Among them, a new covalent assembly method is attractive. This method uses DNA/RNA template strand recognition to shorten the distance with the substrate and induce the covalent assembly of the substrate to form dyes, effectively improving the effective concentration and reaction rate and realizing the detection of specific sequence of DNA/RNA fragments.
Initially recognized by Huang et al. in 2008 for its application, the DNA-template reaction of trimethylindole catalyzed by diamine with benzaldehyde was developed to finally produce hemicyanine-like dyes via the formation of a Schiff base, methylene indoline, proton transfer and carbon–carbon bond coupling.127 As shown in Fig. 24A, through the DNA-template reaction, probe DNA1 was studied and its spectroscopic performance (λex = 550 nm and λem = 590 nm) showed its potential application in the detection of DNA.
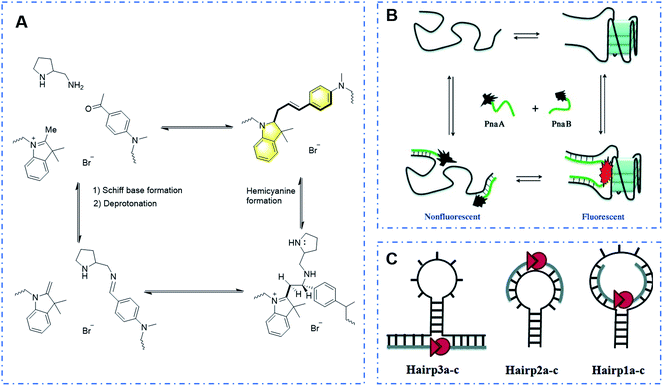 | ||
| Fig. 24 (A) Response mechanism of a covalent assembly probe to DNA. (B) Novel strategy to examine the G-quadruplex structure via covalent assembly and (C) different ways of combination with hairpin structures to realize the detection of hairpin structures. (Adapted with permission from ref. 129 and 130 copyright 2010, the American Chemical Society, copyright 2010, Wiley). | ||
Subsequently, Ladame's research group used the template chain reaction strategy to develop a series of high-performance probes for detecting the DNA sequence and DNA secondary structures.128–130 This strategy makes use of the characteristics of “DNA sequence + structure”. Through sequence combination, the DNA chain structure changes, and thus two parts of the dye structures connected at the head and end can be covalently assembled to form a hemicyanine dye due to structural changes, achieving the detection effect (Fig. 24B and C). Unlike other conventional DNA template reactions, its system has the following significant advantages: (i) its emission spectrum reaches the near-infrared window, and its excellent performance of strong permeability and high resolution makes it suitable for in vivo imaging and (ii) the template reaction does not require a heavy metal catalyst and has good biocompatibility.
It should be noted that this method is similar to the covalent assembly strategy mentioned above. Also, it is believed that this novel strategy can inspire us in the development of small molecular probes to overcome the problems shown in the previous works and design more prominent probes for application in daily life.
3. Conclusion
This review summarized the small molecular fluorescent probes based on covalent assembly for detecting and imaging various ions (anions and cations), small biological molecules, reactive oxygen species (ROS), reactive nitrogen species (RNS), nerve agent mimics, enzymes and DNA. Compared with the traditional small molecular probes, the detection product exhibits a strong signal with pronounced red-shift of the absorption and emission bands; simultaneously, it also has the same advantages as the small molecular fluorescent probe, such as easy preparation and tunability. These probes generally contain common fluorophores such as coumarin, fluorescein, and naphthalene imide, which have the advantages of low cost, easy structural tuning, and excellent fluorescence performance. However, this approach also faces some limitations, such as a relatively narrow range of applicable substrates, which need to be further studied to meet the actual requirement.Briefly, covalently assembled reactive probes are a type of probe materials that change the molecular structure of dyes to respond and produce changes in fluorescence signals. They induce the dye to assemble in situ into dye groups with strong fluorescence through the substrate. The specific methods involve: (1) decorating a push–pull electron group, (2) changing the conjugation degree of the push–pull electron backbone, and (3) changing the rigidity degree of the main chain.
Actually, since the concept of covalent assembly was proposed by Yang et al., only a few covalent assembly reactive probes have been reported. Different from the general mechanism, i.e., photo-induced electron transfer (PET) and fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET), covalent assembly probes involve the assembly of two dye fragments originally fixed by a linker into the corresponding dyes in situ in response to an analyte, ensuring that the fluorescence background of this type of reaction probe is very low, even up to zero background, while the other luminescence mechanisms mentioned above are to inhibit the self-fluorescence of the molecular probe through the modified group, and then react with the analyte to cause the departure of the group or increase the molecular spacing, and finally maintain the “on” state of the probe dye.
In recent years, many probes based on covalent assembly have been developed for better performance with two-photon fluorescence emission and near-infrared emission, which are more suitable for in vivo imaging with low background, high signal-to-noise ratio, and deep penetration depth. These probes tend to focus on detecting small biological molecules and enzymes, which are related to many diseases and physiological/pathological processes. Notably, increasing attention has been paid to explore novel mechanisms with the features of improved sensitivity, selectivity, low toxicity, water solubility, and biocompatibility. Thus, it is a bright future to develop and improve the performance of these probes in various systems.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by National Key R&D Project (2020YFA0709900), Key University Science Research Project of Jiangsu Province (19KJA520005), National Natural Science Foundation of China (81672508, 61601218), Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK20200092) and Natural Science Basic Research Program of Shaanxi (Program No. 2019JM-016).Notes and references
- X. Li, X. Gao, W. Shi and H. Ma, Design strategies for water-soluble small molecular chromogenic and fluorogenic probes, Chem. Rev., 2014, 114, 590–659 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Q. Wu and E. V. Anslyn, Heavy metal analysis using a Heck-catalyzed cyclization to create coumarin, J. Mater. Chem., 2005, 15, 2815–2819 RSC.
- Z. Lei and Y. Yang, A concise colorimetric and fluorometric probe for sarin related threats designed via the “covalent-assembly” approach, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2014, 136, 6594–6597 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Luo, L. Gu, X. Qian and Y. Yang, Molecular probe design via the “covalent-assembly” principle, Chem. Commun., 2020, 56, 9067–9078 RSC.
- K. Renault, S. Debieu, J. Richard and A. Romieu, Deeper insight into protease-sensitive “covalent assembly” fluorescent probes for practical biosensing applications, Org. Biomol. Chem., 2019, 17, 8918–8932 RSC.
- T. Kim and T. Swager, A Fluorescent self-amplifying wavelength-responsive sensory polymer for fluoride ions, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2003, 42, 4803–4806 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. Kim, S. Singha, T. Wang, E. Seo, J. H. Lee, S. Lee, K. H. Kim and K. H. Ahn, In vivo two-photon fluorescent imaging of fluoride with a desilylation-based reactive probe, Chem. Commun., 2012, 48, 10243–10245 RSC.
- Y. Peng, Y. Dong, M. Dong and Y. Wang, A selective, sensitive, colorimetric, and fluorescence probe for relay recognition of fluoride and Cu(II) ions with “off–on–off” switching in ethanol–water solution, J. Org. Chem., 2012, 77, 9072–9080 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. Wang, S. Yang, M. Yi, C. Liu, Y. Wang, J. Li, Y. Li and R. Yang, Graphene oxide assisted fluorescent chemodosimeter for high-performance sensing and bioimaging of fluoride ions, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2014, 6, 9768–9775 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. Hou, S. Chen, H. Wang, J. Wang, K. Voitchovsky and X. Song, An aqueous red emitting fluorescent fluoride sensing probe exhibiting a large Stokes shift and its application in cell imaging, Chem. Commun., 2014, 50, 320–322 RSC.
- S. Zhang, J. Fan, S. Zhang, J. Wang, X. Wang, J. Du and X. Peng, Lighting up fluoride ions in cellular mitochondria using a highly selective and sensitive fluorescent probe, Chem. Commun., 2014, 50, 14021–14024 RSC.
- J. Yeh, P. Venkatesan and S. Wu, A highly selective turn-on fluorescent sensor for fluoride and its application in imaging of living cells, New J. Chem., 2014, 38, 6198–6204 RSC.
- A. K. Das, S. Goswami, C. K. Quah and H. Fun, Relay recognition of F− and a nerve-agent mimic diethyl cyano-phosphonate in mixed aqueous media: discrimination of diethyl cyanophosphonate and diethyl chlorophosphate by cyclization induced fluorescence enhancement, RSC Adv., 2016, 6, 18711–18717 RSC.
- J. Hu, T. Liu, H. Gao, S. Lu, K. Uvdal and Z. Hu, Selective detections of Hg2+ and F− by using tailor-made fluorogenic probes, Sens. Actuators, B, 2018, 269, 368–376 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Romieu, “AND” luminescent “reactive” molecular logic gates: a gateway to multi-analyte bioimaging and biosensing, Org. Biomol. Chem., 2015, 13, 1294–1306 RSC.
- V. Quesneau, B. Roubinet, P. Renard and A. Romieu, Reinvestigation of the synthesis of “covalent-assembly” type probes for fluoride ion detection. Identification of novel 7-(diethylamino) coumarins with aggregation-induced emission properties, Tetrahedron Lett., 2019, 60, 151279 CrossRef CAS.
- D. Kim, S. Na and H. Kim, A fluorescence turn-on probe for a catalytic amount of cyanides through the cyanide-mediated cinnamate-to-coumarin transformation, Sens. Actuators, B, 2016, 226, 227–231 CrossRef CAS.
- A. C. Bratton and E. K. Marshall, A new coupling component for sulfanil-amide determination, J. Bio. Chem., 1939, 128, 537–550 CAS.
- P. Singhaphan and F. Unob, Thread-based platform for nitrite detection based on a modified Griess assay, Sens. Actuators, B, 2021, 327, 128938 CrossRef CAS.
- F. Z. hang, X. Zhu, Z. Jiao, X. Liu and H. Zhang, Sensitive naked eye detection and quantification assay for nitrite by a fluorescence probe in various water resources, Spectrochim. Acta, Part A, 2018, 200, 275–280 CrossRef PubMed.
- D. Tsikas, Analysis of nitrite and nitrate in biological fluids by assays based on the Griess reaction: appraisal of the Griess reaction in the L-arginine/nitric oxide area of research, J. Chromatogr. B: Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci., 2007, 851, 51–70 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Shen, Q. Zhang, X. Qian and Y. Yang, Practical assay for nitrite and nitrosothiol as an alternative to the Griess assay or the 2,3-diaminonaphthalene assay, Anal. Chem., 2015, 87, 1274–1280 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Lu, C. Chen, D. Zhao, F. Yang and X. Yang, A simple and sensitive assay for the determination of nitrite using folic acid as the fluorescent probe, Anal. Methods, 2015, 7, 1543–1548 RSC.
- Q. Wang, H. Huang, B. Ning, M. Li and L. He, A highly sensitive and selective spectrofluorimetric method for the determination of nitrite in food products, Food Anal. Methods, 2016, 9, 1293–1300 CrossRef.
- Y. Zhan, R. Sun, W. Zhu, Y. Xu and J. Ge, An oxazine-based near-infrared fluorescent probe for selective in cellular imaging of exogenous nitrite, Sens. Actuators, B, 2017, 240, 1283–1290 CrossRef CAS.
- Q. Xia, Y. Mao, J. Wu, T. Shu and T. Yi, Two-component organogel for visually detecting nitrite anion, J. Mater. Chem. C, 2014, 2, 1854–1861 RSC.
- K. Yu, S. Pan, K. Li, L. Shi, Y. Liu, S. Chen and X. Yu, A novel near-infrared fluorescent sensor for zero background nitrite detection via the “covalent-assembly” principle, Food Chem., 2021, 341, 128254 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. Yao, X. Zhang and C. L. Richard, AuCl3-catalyzed synthesis of highly substituted furans from 2-(1-alkynyl)-2-alken-1-ones, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2004, 126, 11164–11165 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. H. Do, H. N. Kim, J. Yoon, J. S. Kim and H. Kim, A rationally designed fluorescence turn-on probe for the gold(III) ion, Org. Lett., 2010, 12, 932–934 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. J. Jou, X. Chen, K. M. K. Swamy, H. N. Kim, H. Kim, S. Lee and J. Yoon, Highly selective fluorescent probe for Au3+ based on cyclization of propargylamide, Chem. Commun., 2009, 46, 7218–7220 Search PubMed.
- Y. Yang, S. Lee and J. Tae, A gold(III) ion-selective fluorescent probe and its application to bioimagings, Org. Lett., 2009, 24, 5610–5613 CrossRef PubMed.
- B. Wang, T. Fu, S. Yang, J. Li and Y. Chen, An intramolecular charge transfer (ICT)-based dual emission fluorescent probe for the ratiometric detection of gold ions, Anal. Methods, 2013, 5, 3639–3641 RSC.
- Q. Wang, Y. Feng, J. Jiang, W. Wang, J. Chen, H. Sheng, X. Meng and M. Zhu, A coumarin-based colorimetric and fluorescent probe for the highly selective detection of Au3+ ions, Chin. Chem. Lett., 2016, 27, 1563–1566 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Ucuncu and E. Karakus, A ratiometric fluorescent probe for gold and mercury ions, Chem.–Eur. J., 2015, 21, 13201–13205 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Han, L. Zhao, D. Wang, J. Xu, L. Zhang, M. Yuan, Q. Tu and J. Wang, A TBET-based ratiometric probe for Au3+ and its application in living cells, Analyst, 2016, 141, 1098–1104 RSC.
- M. Ucuncu, E. Karakus and M. Emrullahoglu, A BODIPY-based fluorescent probe for ratiometric detection of gold ions: utilization of Z-enynol as the reactive unit, Chem. Commun., 2016, 52, 8247–8250 RSC.
- X. Cao, W. Lin and Y. Ding, Ratio-Au: a FRET-based fluorescent probe for ratiometric determination of Gold Ions and Nanoparticles, Chem.–Eur. J., 2011, 17, 9066–9069 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Q. Ding, Z. Chen, X. Yu, Y. Peng and J. Wu, Highly efficient electrophilic cyclization of N′-(2-alkynylbenzylidene) hydrazides, Tetradron. Lett., 2009, 50, 340–342 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Emrullahoglu, E. Karakus and M. Ucuncu, A rhodamine based “turn-on” chemodosimeter for monitoring gold ions in synthetic samples and living cells, Analyst, 2013, 138, 3638–3641 RSC.
- C. Cetintas, E. Karakus, M. Ucuncu and M. Emrullahoglu, A fluorescein-based chemodosimeter for selective gold(III) ion monitoring in aqueous media and living systems, Sens. Actuators, B, 2016, 234, 109–114 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Wechakorn, S. Prabpai, K. Suksen, P. Piyachaturawat and P. Kongsaeree, Rhodol-based fluorescent probe for Au3+ detection and its application in bioimaging, RSC Adv., 2016, 6, 24752–24755 RSC.
- Y. Yang, B. Bai, M. Jin, Z. Xu, J. Zhang, W. Li, W. i. Xu, X. Wang and C. Yin, Fluorescent imaging of Au3+ in living cells with two new high selective Au3+ probes, Biosens. Bioelectron., 2016, 86, 939–943 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Q. Wu and E. V. Anslyn, Catalytic signal amplification using a Heck reaction. An example in the fluorescence sensing of Cu(II), J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2004, 126, 14682–14683 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Jo, H. Y. Lee, W. Liu, A. Olasz, C. Chen and D. Lee, Reactivity-based detection of copper(II) ion in water: oxidative cyclization of azoaromatics as fluorescence turn-on signaling mechanism, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2012, 134, 16000–16007 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Cao, Q. Jin, L. Geng, L. Mu and S. Dong, A ‘‘turn-on’’ fluorescent probe for the detection of Cu2+ in living cells based on a signaling mechanism of N
![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N isomerization, New J. Chem., 2016, 40, 6264–6269 RSC.
N isomerization, New J. Chem., 2016, 40, 6264–6269 RSC. - Y. Wang, S. Liu, H. Chen, Y. Liu and H. Li, A novel “turn-on” fluorescence probe based on azoaniline–arylimidazole dyad for the detection of Cu2+, Dyes Pigm., 2017, 142, 293–299 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Gupta and H. Lee, A dual responsive molecular probe for the efficient and selective detection of nerve agent mimics and copper(II) ions with controllable detection time, Sens. Actuators, B, 2017, 242, 977–982 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Jung, J. Jo and A. Dinescu, Rapid turn-on fluorescence detection of copper(II): aromatic substituent effects on the response rate, Org. Process Res. Dev., 2017, 21, 1689–1693 CrossRef CAS.
- Z. Xu, P. Deng, J. Li and S. Tang, Fluorescent ion-imprinted sensor for selective and sensitive detection of copper (II) ions, Sens. Actuators, B, 2018, 255, 2095–2104 CrossRef CAS.
- E. Falcone, A. Sour, V. Lebrun, G. Ulrich, L. Raibaut and P. Faller, Reversible turn-on fluorescent Cu(II) sensors: rather dream than reality?, Dalton Trans., 2019, 48, 14233–14237 RSC.
- H. Ren, P. Wu, F. Li, L. Jin and D. Lou, Visual colorimetric and fluorescence turn-on probe for Cu(II) ion based on coordination and catalyzed oxidative cyclization of ortho amino azobenzene, Inorg. Chim. Acta, 2019, 487, 234–239 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Jung and J. Jo, Residual copper(II) detection in chemical processes: high-throughput analysis and real-time monitoring with a colorimetric copper probe, Org. Process Res. Dev., 2019, 23, 1257–1261 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Ren, P. Wu, F. Li, S. Yu, L. Jin and D. Lou, Development of a colorimetric and fluorescent Cu2+ ion probe based on 2′-hydroxy-2,4-diaminoazobenzene and its application in real water sample and living cells, Inorg. Chim. Acta, 2020, 507, 119583 CrossRef.
- J. Jung, A. Dinescu and A. Kukrek, Synthesis and comparative kinetic study of reaction-based copper(II) probes to visualize aromatic substituent effects on reactivity, J. Chem. Educ., 2020, 97, 533–537 CrossRef CAS.
- Z. Hu, J. Hu, H. Wang, Q. Zhang, M. Zhao, C. Brommesson, Y. Tian, H. Gao, X. Zhang and K. Uvdal, A TPA-caged precursor of (imino)coumarin for “turn-on” fluorogenic detection of Cu+, Anal. Chim. Acta, 2016, 933, 189–195 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- I. Kim, D. Kim, S. Sambasivan and K. H. Ahn, Synthesis of p-extended coumarins and evaluation of their precursors as reactive fluorescent probes for mercury ions, Asian J. Org. Chem., 2012, 1, 60–64 CrossRef CAS.
- Q. Fang, Q. Liu, X. Song and J. Kang, An aqueous fluorescent probe for Hg2+ detection with high selectivity and sensitivity, Luminescence, 2015, 30, 1280–1284 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Han, C. Yang, K. Wu, Y. Chen, B. Zhou and M. Xia, A facile naphthalene-based fluorescent chemodosimeter for mercury ions in aqueous solution, RSC Adv., 2015, 5, 16723–16726 RSC.
- L. Yang, Y. Su, Y. Geng, H. Xiong, J. Han, Q. Fang and X. Song, A red-emitting fluorescent probe for the detection of Hg2+ in aqueous medium, living cells and organisms with a large Stokes shift, Org. Biomol. Chem., 2018, 16, 5036–5042 RSC.
- Z. Zhang, B. Zhang, X. Qian, Z. Li, Z. Xu and Y. Yang, Simultaneous quantification of Hg2+ and MeHg+ in aqueous media with a single fluorescent probe by multiplexing in the time domain, Anal. Chem., 2014, 86, 11919–11924 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Song, Z. Lei, B. Zhang, Z. Xu, Z. Li and Y. Yang, A zero-background fluorescent probe for Hg2+ designed via the “covalent-assembly” principle, Anal. Methods, 2014, 6, 7597–7600 RSC.
- S. Pan, K. Li, L. Li, M. Li, L. Shi, Y. Liu and X. Yu, A reaction-based ratiometric fluorescent sensor for the detection of Hg(II) ions in both cells and bacteria, Chem. Commun., 2018, 54, 4955–4958 RSC.
- M. Santra, S. Ko, I. Shin and K. H. Ahn, Fluorescent detection of palladium species with an O-propargylated fluorescein, Chem. Commun., 2010, 46, 3964–3966 RSC.
- H. Chen, W. Lin and L. Yuan, Construction of a near-infrared fluorescence turn-on and ratiometric probe for imaging palladium in living cells, Org. Biomol. Chem., 2013, 11, 1938–1941 RSC.
- Y. Chen, M. Zhang, Y. Han and J. Wei, A depropargylation-triggered spontaneous cyclization based fluorescent “turn-on” chemodosimeter for the detection of palladium ions and its application in live-cell imaging, RSC Adv., 2016, 6, 8380–8383 RSC.
- Y. Chen, B. Chen, D. Luo, Y. Cai, Y. Wei and Y. Han, A facile naphthalene-based fluorescent ‘turn-on’ chemodosimeter for palladium ions in aqueous solution, Tetrahedron Lett., 2016, 57, 1192–1195 CrossRef CAS.
- B. Huo, M. Du, A. Gong, M. Li, L. Fang, A. Shen, Y. Lai, X. Bai and Y. Yang, A novel intramolecular cyclization-induced fluorescent “turn-on” probe for detection of Pd2+ based on the Tsuji–Trost reaction, Anal. Methods, 2018, 10, 3475–3480 RSC.
- H. Mohapatra, H. Kim and S. T. Phillips, Stimuli-responsive polymer film that autonomously translates a molecular detection event into a macroscopic change in its optical properties via a continuous, thiol-mediated self-propagating reaction, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2015, 137, 12498–12501 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Liu, D. Yang, W. Chen, L. Yang, F. Qi and X. Song, A red-emitting fluorescent probe for specific detection of cysteine over homocysteine and glutathione with a large Stokes shift, Sens. Actuators, B, 2016, 234, 27–33 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Kim, M. Choi, S. V. Mulay, M. Jang, J. Y. Kim, W. Lee, S. Jon and D. G. Churchill, Aqueous red-emissive probe for the selective fluorescent detection of cysteine by deprotection/cyclization cascade resulting in large stokes' shift, Chem.–Eur. J., 2018, 24, 5623–5629 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. K. Mishra, T. Saha and P. Talukdar, Hydrogen sulfide mediated cascade reaction forming an imino-coumarin: applications in fluorescent probe development and live-cell imaging, Org. Biomol. Chem., 2015, 13, 7430–7436 RSC.
- H. Zhang, Y. Xie, P. Wang, G. Chen, R. Liu, Y. Lam, Y. Hu, Q. Zhu and H. Sun, A imino-coumarin benzothiazole-based fluorescent probe for imaging hydrogen sulfide in living cells, Talanta, 2015, 135, 149–154 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Yang, Y. Su, Z. Sha, Y. Geng, F. Qi and X. Song, A red-emitting fluorescent probe for hydrogen sulfide in living cells with a large Stokes shift, Org. Biomol. Chem., 2018, 16, 1150–1156 RSC.
- W. Li, S. Zhou, L. Zhang, Z. Yang, H. Chen, W. Chen, J. Qin, X. Shen and S. Zhao, A red emitting fluorescent probe for sensitively monitoring hydrogen polysulfides in living cells and zebrafish, Sens. Actuators, B, 2019, 284, 30–35 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Liu, F. Qi, Y. Su, W. Chen, L. Yang and X. Song, A red emitting fluorescent probe for instantaneous sensing of thiophenol in both aqueous medium and living cells with a large Stokes shift, J. Mater. Chem. C, 2016, 4, 4320–4326 RSC.
- W. Chen, X. Yue, W. Li, Y. Hao, L. Zhang, L. Zhu, J. Sheng and X. Song, A phenothiazine coumarin-based red emitting fluorescent probe for nanomolar detection of thiophenol with a large Stokes shift, Sens. Actuators, B, 2017, 245, 702–710 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Yang, Y. Liu, Y. Li, H. Wang, H. Zhang, J. Xu, L. Ji, Q. Wang and G. He, A highly sensitive fluorescence probe for thiophenol in living cells via a substitution-cyclization strategy, Tetrahedron, 2019, 75, 130538 CrossRef CAS.
- L. M. Eubanks, T. J. Dickerson and K. D. Janda, Technological advancements for the detection of and protection against biological and chemical warfare agents, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2007, 36, 458–470 RSC.
- T. Kim, S. B. Maity, J. Bouffard and Y. Kim, Molecular rotors for the detection of chemical warfare agent simulants, Anal. Chem., 2016, 88, 9259–9263 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. S. J. Khan, Y. Wang, M. O. Senge and Y. Peng, Sensitive fluorescence on-off probes for the fast detection of a chemical warfare agent mimic, J. Hazard. Mater., 2018, 342, 10–19 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. R. Sambrook and S. Notman, Supramolecular chemistry and chemical warfare agents: from fundamentals of recognition to catalysis and sensing, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2013, 42, 9251–9267 RSC.
- S. Zhang and T. M. Swager, Fluorescent detection of chemical warfare agents: functional group specific ratiometric chemosensors, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2003, 125, 3420–3421 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Yao, Y. Fu, W. Xu, T. Fan, Y. Gao, Q. He, D. Zhu, H. Cao and J. Cheng, Concise and efficient fluorescent probe via an intromolecular charge transfer for the chemical warfare agent mimic diethyl chlorophosphate vapor detection, Anal. Chem., 2016, 88, 2497–2501 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- L. Chen, D. Wu and J. Yoon, Recent Advances in the development of chromophore-based chemosensors for nerve agents and phosgene, ACS Sens., 2018, 3, 27–43 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Mahapatra, K. Maiti, S. K. Manna, R. Maji, S. Mondal, C. D. Mukhopadhyay, P. Sahoo and D. Mandal, A cyclization-induced emission enhancement (CIEE)-based ratiometric fluorogenic and chromogenic probe for the facile detection of a nerve agent simulant DCP, Chem. Commun., 2015, 51, 9729–9732 RSC.
- A. K. Das, S. Goswami, C. K. Quah and H. Fun, Relay recognition of F− and a nerve-agent mimic diethyl cyano-phosphonate in mixed aqueous media: discrimination of diethyl cyanophosphonate and diethyl chlorophosphate by cyclization induced fluorescence enhancement, RSC Adv., 2016, 6, 18711–18717 RSC.
- B. Huo, M. Du, A. Shen, M. Li, Y. Lai, X. Bai, A. Gong and Y. Yang, “Covalent-assembly”-based fluorescent probe for detection of a nerve-agent mimic (DCP) via Lossen rearrangement, Anal. Chem., 2019, 91, 10979–10983 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- B. Huo, M. Du, A. Shen, M. Li, Y. Lai, X. Bai, A. Gong, L. Fang and Y. Yang, A “light-up” fluorescent probe based on TEMPO-oxidation for the detection of ClO− and application in real samples, Sens. Actuators, B, 2019, 284, 23–29 CrossRef CAS.
- M. C. Y. Chang, A. Pralle, E. Y. Isacoff and C. J. Chang, A selective, cell-permeable optical probe for hydrogen peroxide in living cells, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2004, 126, 15392–15393 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Mohapatra and S. T. Phillips, Using smell to triage samples in point-of-care assays, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2012, 51, 11145–11148 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Liu, L. He, L. Yang, Y. Geng, L. Yang and X. Song, Imino-coumarin-based fluorescence probe for intracellular H2O2 detection with a red emission and a large Stokes shift, Sens. Actuators, B, 2018, 259, 803–808 CrossRef CAS.
- Q. Zhang, Z. Zhu, Y. Zheng, J. Cheng, N. Zhang, Y. Long, J. Zheng, X. Qian and Y. Yang, A three-channel fluorescent probe that distinguishes peroxynitrite from hypochlorite, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2012, 134, 18479–18482 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Zielonka, A. Sikora, M. Hardy, J. Joseph, B. P. Dranka and B. Kalyanaraman, Boronate probes as diagnostic tools for real time monitoring of peroxynitrite and hydroperoxides, Chem. Res. Toxicol., 2012, 25, 1793–1799 Search PubMed.
- J. Kim, J. Park, H. Lee, Y. Choi and Y. Kim, A boronate-based fluorescent probe for the selective detection of cellular peroxynitrite, Chem. Commun., 2014, 50, 9353–9356 RSC.
- J. Zhou, Y. Li, J. Shen, Q. Li, R. Wang, Y. Xu and X. Qian, A ratiometric fluorescent probe for fast and sensitive detection of peroxynitrite: a boronate ester as the receptor to initiate a cascade reaction, RSC Adv., 2014, 4, 51589–51592 RSC.
- J. Zhang, Y. Li and W. Guo, Anarylboronate-based fluorescent probe for peroxynitrite with fast response and high selectivity, Anal. Methods, 2015, 7, 4885–4888 RSC.
- J. Zhang, Y. Li, J. Zhao and W. Guo, Anarylboronate-based fluorescent probe for selective and sensitive detection of peroxynitrite and its applications for fluorescence imaging in living cells, Sens. Actuators, B, 2016, 237, 67–74 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Xia, Y. Tong, L. Li, M. Cui, Y. Gu and P. Wang, A selective fluorescent turn-on probe for imaging peroxynitrite in living cells and drug-damaged liver tissues, Talanta, 2019, 204, 431–437 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Kojima, N. Nakatsubo, K. Kikuchi, S. Kawahara, Y. Kirino, H. Nagoshi, Y. Hirata and T. Nagano, Detection and imaging of nitric oxide with novel fluorescent indicators: diaminofluoresceins, Anal. Chem., 1998, 70, 2446–2453 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Kojima, M. Hirotani, N. Nakatsubo, K. Kikuchi, Y. Urano, T. Higuchi, Y. Hirata and T. Nagano, Bioimaging of nitric oxide with fluorescent indicators based on the rhodamine chromophore, Anal. Chem., 2001, 73, 1967–1973 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Dong, C. H. Heo, S. Chen, H. M. Kim and Z. Liu, Quinoline-based two-photon fluorescent probe for nitric oxide in live cells and tissues, Anal. Chem., 2014, 86, 308–311 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Zhang, J. Chen, X. Guo, H. Wang and H. Zhang, Highly-sensitive low-background fluorescent probes for imaging of nitric oxide in cells and tissues, Anal. Chem., 2014, 86, 3115–3123 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- E. Sasaki, H. Kojima, H. Nishimatsu, Y. Urano, K. Kikuchi, Y. Hirata and T. Nagano, Highly sensitive near-infrared fluorescent probes for nitric oxide and their application to isolated organs, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2005, 127, 3684–3685 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Yu, Y. Xiao and L. Jin, A lysosome-targetable and two-photon fluorescent probe for monitoring endogenous and exogenous nitric oxide in living cells, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2012, 134, 17486–17489 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Sun, J. Liu, H. Zhang, Y. Huo, X. Lv, Y. Shi and W. Guo, A mitochondria-targetable fluorescent probe for dual-channel NO imaging assisted by intracellular cysteine and glutathione, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2014, 136, 12520–12523 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Z. Mao, W. Feng, Z. Li, L. Zeng, W. Lv and Z. Liu, NIR in, far-red out: developing a two-photon fluorescent probe for tracking nitric oxide in deep tissue, Chem. Sci., 2016, 7, 5230–5235 RSC.
- Y. Huo, J. Miao, L. Han, Y. Li, Z. Li, Y. Shi and W. Guo, Selective and sensitive visualization of endogenous nitric oxide in living cells and animals by a Si-rhodamine deoxylactam-based near-infrared fluorescent probe, Chem. Sci., 2017, 8, 6857–6864 RSC.
- Y. Yang, S. K. Seidlits, M. M. Adams, V. M. Lynch, C. E. Schmidt, E. V. Anslyn and J. B. Shear, A highly selective low-background fluorescent imaging agent for nitric oxide, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2010, 132, 13114–13116 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. R. Escamilla, Y. Shen, Q. Zhang, D. S. Hernandez, C. J. Howard, X. Qian, D. Y. Filonov, A. V. Kinev, J. B. Shear, E. V. Anslyn and Y. Yang, 2-Amino-3′-dialkylaminobiphenyl-based fluorescent intracellular probes for nitric oxide surrogate N2O3, Chem. Sci., 2020, 11, 1394–1403 RSC.
- Z. Lei, Z. Zeng, X. Qian and Y. Yang, A novel chromogenic and fluorogenic scaffold for detection of oxidative radicals, Chin. Chem. Lett., 2017, 28, 2001–2004 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Niu, K. Ye, L. Wang, Y. Lin and D. Du, A review on emerging principles and strategies for colorimetric and fluorescent detection of alkaline phosphatase activity, Anal. Chim. Acta, 2019, 1086, 29–45 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Han, J. Chen, Z. Li, H. Chen and H. Qiu, Recent progress and prospects of alkaline phosphatase biosensor based on fluorescence strategy, Biosens. Bioelectron., 2020, 148, 111811 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Zhu and C. Jiang, 8-Quinolyl phosphate as a substrate for the fluorimetric determination of alkaline phosphatase, Clin. Chim. Acta, 2007, 377, 150–153 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. Kim, H. Kim, Y. Choi and Y. Kim, A fluorescent turn-on probe for the detection of alkaline phosphatase activity in living cells, Chem. Commun., 2011, 47, 9825–9827 RSC.
- J. Park and Y. Kim, An improved fluorogenic substrate for the detection of alkaline phosphatase activity, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 2013, 23, 2332–2335 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- G. Chen, D. J. Yee, N. G. Gubernator and D. Sames, Design of optical switches as metabolic indicators: new fluorogenic probes for monoamine oxidases (MAO A and B), J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2005, 127, 4544–4545 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. Kim, S. Sambasivan, H. Nam, K. H. Kim, J. Y. Kim, T. Joo, K. Lee, K. Kim and K. H. Ahn, Reaction-based two-photon probes for in vitro analysis and cellular imaging of monoamine oxidase activity, Chem. Commun., 2012, 48, 6833–6835 RSC.
- H. Qin, L. Li, K. Li and X. Yu, Novel strategy of constructing fluorescent probe for MAO-B via cascade reaction and its application in imaging MAO-B in human astrocyte, Chin. Chem. Lett., 2019, 30, 71–74 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Xia, F. Hu, J. Huang, N. Li, Y. Gu and P. Wang, A fluorescent turn-on probe for nitroreductase imaging in living cells and tissues under hypoxia conditions, Sens. Actuators, B, 2018, 268, 70–76 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Liu, W. Yan, H. Li, H. Peng, X. Suo, Z. Li, H. Liu, J. Zhang, S. Wang and D. Liu, Two-photon fluorescent probe for hypoxic cancer stem cells by responding to endogenous nitroreductase, Anal. Methods, 2019, 11, 421–426 RSC.
- S. Debieu and A. Romieu, In situ formation of pyronin dyes for fluorescence protease sensing, Org. Biomol. Chem., 2017, 15, 2575–2584 RSC.
- S. Debieu and A. Romieu, Kinetics improvement of protease-mediated formation of pyronin dyes, Tetrahedron Lett., 2018, 59, 1940–1944 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Srirangan, V. Orr, L. Akawi, A. Westbrook, M. Moo-Young and C. P. Chou, Biotechnological advances on penicillin G acylase: pharmaceutical implications, unique expression mechanism and production strategies, Biotechnol. Adv., 2013, 31, 1319–1332 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. Li, M. A. A. Mohammed, Y. Zhou, H. Tu, J. Zhang, C. Liu, Z. Chen, R. Burns, D. Hu, J. M. Ruso, Z. Tang and Z. Liu, Recent progress in the development of immobilized penicillin G acylase for chemical and industrial applications: a mini-review, Polym. Adv. Technol., 2020, 31, 368 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Debieu and A. Romieu, Dual enzyme-responsive “turn-on” fluorescence sensing systems based on in situ formation of 7-hydroxy-2-imino-coumarin scaffolds, Org. Biomol. Chem., 2015, 13, 10348–10361 RSC.
- M. Prost and J. Hasserodt, “Double gating” – a concept for enzyme-responsive imaging probes aiming at high tissue specificity, Chem. Commun., 2014, 50, 14896–14899 RSC.
- Y. Huang and J. M. Coull, Diamine catalyzed hemicyanine dye formation from nonfluorescent precursors through DNA programmed chemistry, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2008, 130, 3238–3239 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- G. Koripelly, K. Meguellati and S. Ladame, Dual sensing of hairpin and quadruplex DNA structures using multicolored peptide nucleic acid fluorescent probes, Bioconjugate Chem., 2010, 21, 2103–2109 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. Meguellati, G. Koripelly and S. Ladame, DNA-templated synthesis of trimethine cyanine dyes: a versatile fluorogenic reaction for sensing G-quadruplex formation, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2010, 49, 2738–2742 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. H. Sleiman and S. Ladame, Synthesis of squaraine dyes under mild conditions: applications for labelling and sensing of biomolecules, Chem. Commun., 2014, 50, 5288–5290 RSC.
Footnote |
| † These authors contribute equally to this work. |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2022 |