Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleCreative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported Licence
Kinetic analysis to describe Co-operative redox enhancement effects exhibited by bimetallic Au–Pd systems in aerobic oxidation†
Isaac T.
Daniel
 a,
Liang
Zhao
a,
Liang
Zhao
 a,
Donald
Bethell
a,
Mark
Douthwaite
*a,
Samuel
Pattisson
a,
Richard J.
Lewis
a,
Donald
Bethell
a,
Mark
Douthwaite
*a,
Samuel
Pattisson
a,
Richard J.
Lewis
 a,
Ouardia
Akdim
a,
David J.
Morgan
a,
Ouardia
Akdim
a,
David J.
Morgan
 a,
Steven
McIntosh
a,
Steven
McIntosh
 b and
Graham J.
Hutchings
b and
Graham J.
Hutchings
 *a
*a
aMax Planck-Cardiff Centre on the Fundamentals of Heterogeneous Catalysis FUNCAT, Cardiff Catalysis Institute, School of Chemistry, Cardiff University, Main Building, Park Place, Cardiff, CF10 3AT, UK. E-mail: douthwaitejm@cardiff.ac.uk; hutch@cardiff.ac.uk
bDepartment of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, Lehigh University, Bethlehem, PA, USA
First published on 10th November 2022
Abstract
Recent work has demonstrated that for bimetallic Au–Pd systems, the rate of catalytic alcohol and formyl dehydrogenation (DH) is intrinsically linked to the rate of oxygen reduction (ORR) within the same system. Herein, the rate enhancement as a result of the coupling between these two processes is assessed via kinetic analysis for the oxidative dehydrogenation of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural. The influence of the Au and Pd molar ratio is explored for a physical mixture of carbon-supported catalysts by changing the mass of each 1 wt% catalyst. Importantly, the activity of the bimetallic system exceeds the sum of the monometallic analogues, at all molar ratios. It is shown that by considering the coupling between two individual reactions (DH and ORR), the kinetic analysis of the system predicts where the maxima in monometallic and bimetallic activity will be observed. The accuracy of the model provides further evidence and understanding of cooperative redox enhancement (CORE) effects observed in bimetallic, heterogeneous catalytic systems.
1. Introduction
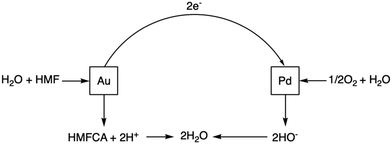
The combination of Au and Pd to produce supported bimetallic catalysts has led to significant performance enhancements in a variety of important reactions including the oxidative dehydrogenation (ODH) of alcohols and formyls1–4 and the direct synthesis of H2O2.5–8 Understanding the origin and scope of these enhancement effects is crucial to ensure bimetallic systems are employed in the most effective way. The heightened catalytic efficiency relative to the analogous monometallic systems is often attributed to synergistic effects between the two metals. These can arise from the changing of several different factors, such as coordination number and surface electronic states, and can result in preferable activity and selectivity.9–11Recently, Huang et al.12 developed an alternative approach to explain rate enhancements observed over bimetallic Au–Pd catalytic systems. The authors utilized both thermo- and electro-catalytic methods to study the rate enhancements that arise when Au and Pd are combined in supported, heterogeneous catalytic systems, with 5-hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF) used as their primary model substrate. HMF is an ideal model to study such reactions, as it possesses both alcohol and formyl functionalities. Crucially, it was determined that by spatially separating the metallic sites, either by using a physical mixture (PM) of monometallic catalysts or through the synthesis of a Janus-type structure, the enhancement exceeded that exhibited by an analogous Au–Pd alloy catalyst.
Heightened performance was observed for both PM and Janus-type systems for the ODH of a range of alcohols and through linear-sweep voltammetry (LSV) experiments, the separation of sites is shown to be essential in maximising the rate of dehydrogenation (DH). It was demonstrated that Au and Pd nanoparticles are individually catalysing distinct half-cell reactions, namely DH and the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR). The activity enhancement for all the ‘non-alloyed’ bimetallic systems was attributed to the intrinsic coupling of DH occurring over Au sites and the consumption of produced electrons via ORR at Pd sites. Pd is known to be much more effective at ORR than Au, with the inverse true for DH, hence it is consistent that the half-cell reactions should predominately take place in this way.13,14
The transfer of electrons generated by DH through a conductive support was found to be a significant part of the system and the rate enhancement is diminished with the use of semi-conducting materials. Overall, this cooperative redox enhancement (CORE) effect observed between Au and Pd is a new observation and differs from the traditionally discussed “synergy” as the individual metallic properties, such as redox potential, are importantly unaltered, as is their individual ability to catalyse each half-cell reaction.
Clearly, this analysis means that the rate of ORR is vital during alcohol and formyl DH and needs to be considered. It was demonstrated that within the CORE system, by increasing the amount of Pd catalyst present, and therefore increasing the rate of ORR, the rate of DH is proportionally (yet indirectly) increased.12 Using monometallic Au and Pd catalytic systems, Davis et al.15 extensively investigated the importance of ORR during selective alcohol oxidation. It is demonstrated that at high pH, hydroxide ions are the source of the inserted oxygen atom. This suggests that O2 plays an important but indirect role within the catalytic cycle; to be the source of hydroxide ions through its reduction prior to dissociation. This work supports our recent discovery,12 making clear the importance of efficient electron consumption, in this case through oxygen reduction, that leads to CORE effects.
ORR is a comprehensively researched reaction due to its important role in fuel cells.16–19 The exceptional strength of the O![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O double bond (498 kJ mol−1) means the presence of a catalyst is required to avoid excessive energy input.20 In alkaline media, oxygen reduction can occur via a four electron or two sequential two electron processes (eqn (1)–(3)).21 Due to the high pH, the initial two electron process will produce an unstable peroxide intermediate of the form HO2−, which will undergo rapid reduction to hydroxide ions.22,23
O double bond (498 kJ mol−1) means the presence of a catalyst is required to avoid excessive energy input.20 In alkaline media, oxygen reduction can occur via a four electron or two sequential two electron processes (eqn (1)–(3)).21 Due to the high pH, the initial two electron process will produce an unstable peroxide intermediate of the form HO2−, which will undergo rapid reduction to hydroxide ions.22,23
O2(g) + 2H2O(aq) + 4e− → 4OH−(l) # E0 = +0.401![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) V V | (1) |
O2(g) + H2O(aq) + 2e− → HO2−(l) + OH−(l) # E0 = −0.065![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) V V | (2) |
HO2−(l) + H2O(l) + 2e− → 3OH−(aq) # E0 = +0.87![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) V V | (3) |
The experimental work presented by Huang et al.12 focused on the use of HMF as a substrate, hence the important valorisation of HMF will also be the focus of this work. HMF can be obtained from renewable biomass resources through the dehydration of fructose and glucose and is a pivotal platform chemical.26,27 Through a multistep process, the full ODH of HMF produces 2,5-furandicarboxylic acid (FDCA), which is an important platform chemical in itself and was named as one of the top 12 value-added chemicals derived from biomass by the U.S. Department of Energy.28 For example, it has the potential to replace terephthalic acid – the starting monomer in the production of polyethylene terephthalate (PET).29
The bimetallic PM catalytic system investigated here will use a constant HMF: total metal (mol![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) mol) ratio; the Au
mol) ratio; the Au![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) Pd molar ratio will be varied by varying the mass of each catalyst used, whilst keeping the total metal moles constant. Previously, CORE effects have only been reported using a fixed molar ratio (4
Pd molar ratio will be varied by varying the mass of each catalyst used, whilst keeping the total metal moles constant. Previously, CORE effects have only been reported using a fixed molar ratio (4![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 (Au
1 (Au![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) Pd)),12 hence it is essential to explore where the maxima in rate enhancement is for the combination of these specific catalysts. The sum of the analogous monometallic systems will be used as an activity baseline, with CORE effects responsible for any activity above this. The monometallic systems will be firstly assessed as to whether catalytic activity has a linear (or otherwise) dependency on metal moles. Given that ORR must be occurring even in monometallic situations, the dependency will elucidate if any CORE enhancement is present here due to the single metal performing two catalytic roles (i.e., DH and ORR).
Pd)),12 hence it is essential to explore where the maxima in rate enhancement is for the combination of these specific catalysts. The sum of the analogous monometallic systems will be used as an activity baseline, with CORE effects responsible for any activity above this. The monometallic systems will be firstly assessed as to whether catalytic activity has a linear (or otherwise) dependency on metal moles. Given that ORR must be occurring even in monometallic situations, the dependency will elucidate if any CORE enhancement is present here due to the single metal performing two catalytic roles (i.e., DH and ORR).
To build a deeper understanding of CORE effects in Au and Pd catalysis,12 it is important to consider the kinetics of the system. The full DH of HMF can proceed via two routes (Scheme 1) with either the alcohol or formyl oxidation occurring first. We have observed that the alcohol oxidation occurs first almost exclusively when using Au and Pd catalysts,12 therefore the initial oxidation of HMF to HMFCA will herein be used as the basis from which to build a kinetic understanding. Assumptions made during the kinetic analysis presented are formulated from current understanding of CORE effects in a Au and Pd system. A kinetic model that accurately correlates with the experimental data will further support the proposed system for bimetallic activity enhancement.
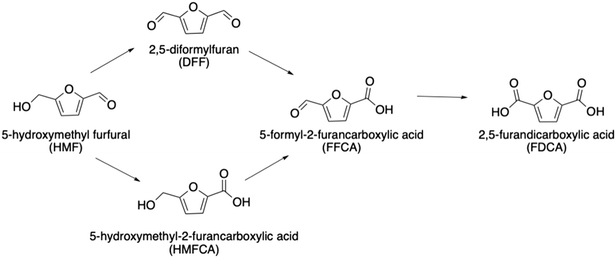 | ||
| Scheme 1 The oxidative dehydrogenation of HMF can proceed via the oxidation of either the alcohol or formyl group first. | ||
2. Experimental
2.1. Chemicals
Chloroauric acid (HAuCl4·3H2O, Strem Chemicals, 99.8%); distilled water (Millipore, 18.2![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) MΩ
MΩ![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) cm at 25
cm at 25![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) °C); 5-hydroxymethylfurfural (Sigma-Aldrich, >99%); palladium chloride (PdCl2, Sigma-Aldrich, >99.9%); polyvinyl alcohol (PVA, Sigma-Aldrich, 80% hydrolysed); sodium borohydride (NaBH4, Sigma-Aldrich, 99.99%); sodium hydrogen carbonate (Fisher Scientific, >99.5%); Vulcan XC72R (Cabot).
°C); 5-hydroxymethylfurfural (Sigma-Aldrich, >99%); palladium chloride (PdCl2, Sigma-Aldrich, >99.9%); polyvinyl alcohol (PVA, Sigma-Aldrich, 80% hydrolysed); sodium borohydride (NaBH4, Sigma-Aldrich, 99.99%); sodium hydrogen carbonate (Fisher Scientific, >99.5%); Vulcan XC72R (Cabot).
2.2. Catalyst preparation – sol immobilisation
The following method was used to synthesise 0.5 g of 1 wt% Au/C and 1 wt% Pd/C catalysts. Aqueous precursor solution (HAuCl4, 11 mgAu mL−1 or PdCl2, 5.5 mgPd mL−1) and PVA (10 mg mL−1, PVA mass![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) metal mass = 1
metal mass = 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) were added to vigorously stirred DI water (140 mL) in a 600 mL glass beaker. After 15 minutes of mixing, freshly prepared NaBH4 (0.15 M, mol
1) were added to vigorously stirred DI water (140 mL) in a 600 mL glass beaker. After 15 minutes of mixing, freshly prepared NaBH4 (0.15 M, mol![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) metal mol = 4
metal mol = 4![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1) was rapidly added and the resulting sol stirred for a further 30 minutes. The support material (Carbon Black, Vulcan XC72R, 0.495 g) was added to the colloidal solution and stirred for a further 30 minutes enabling immobilisation. The resulting catalyst was filtered, washed (DI water, 1 L g−1) to remove inorganic ions and dried under static air (110 °C, 16 h).
1) was rapidly added and the resulting sol stirred for a further 30 minutes. The support material (Carbon Black, Vulcan XC72R, 0.495 g) was added to the colloidal solution and stirred for a further 30 minutes enabling immobilisation. The resulting catalyst was filtered, washed (DI water, 1 L g−1) to remove inorganic ions and dried under static air (110 °C, 16 h).
2.3. HMF oxidative dehydrogenation
A glass Colaver reactor (50 mL) was charged with an aqueous solution (16 mL) of HMF (0.1 M) and NaHCO3 (0.4 M). Under constant stirring (1000 rpm), the solution was allowed to stabilise (10 minutes) at 80 °C before the addition of the catalyst in the requisite amounts. The Colaver was purged 5 times with O2 before pressure was maintained at 3 bar with O2 constantly fed into the system. The molar ratio of Au![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) Pd was varied by varying the mass of the 1 wt% catalysts used. In bimetallic reactions, the HMF
Pd was varied by varying the mass of the 1 wt% catalysts used. In bimetallic reactions, the HMF![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) metal molar ratio was kept constant (200
metal molar ratio was kept constant (200![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1). Typical reaction time was either 30 or 120 minutes, with samples taken at regular intervals.
1). Typical reaction time was either 30 or 120 minutes, with samples taken at regular intervals.
Sample analysis was carried out using high-performance liquid chromatography (Agilent Technologies 1200 series) equipped with a diode array detector and a Hi-Plex H (300 × 7.7 mm) column. The mobile phase consisted of 5.5 mM H2SO4 solution at a flow rate of 0.7 mL min−1. Molar quantification, HMF conversion and product selectivity was obtained by pre-determined response factors based on calibrations with known concentrations of HMFCA, FFCA and FDCA. Turnover activity is calculated from molar quantities of the intermediates and products using the equation below.
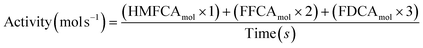 | (4) |
2.4. Catalyst analysis
Inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectroscopy (ICP-AES) was used to determine metal loading. Catalyst samples were initially digested by microwave radiation before analysis. An Agilent 7900 ICP-MS with I-AS autosampler was used to analyse the digested catalysts for specific metal content. All samples were diluted by a factor of 10 and made up with 500 μL of sample into class A volumetric flasks with DI-H2O (which included 1% HNO3 and 0.5% HCl matrix). For interference reduction, Nickel Sampling and Skimmer cones were used with He mode on the ORS4 Octopol. Certified Reference material from Perkin Elmer (1000/100/10/10/blank μg L−1) was used for five-point calibration, with an Agilent certified internal standard.Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) was conducted on a JEOL 2100-JEM operating at 200 kV. Catalyst samples were analysed as a solid dispersed on holey carbon films on 300 mesh copper grids. At least 100 particles were measured for each catalyst to produce a particle size distribution.
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) was performed on a Thermo Fisher Scientific K-alpha+ spectrometer. Samples were analysed using a micro-focused monochromatic Al X-ray source (72 W) using the “400-micron spot” mode, which provides an analysis defining elliptical X-ray spot of ca. 400 × 600 microns. Data was recorded at pass energies of 150 eV for survey scans and 40 eV for high resolution scan with 1 eV and 0.1 eV step sizes respectively. Charge neutralisation of the sample was achieved using a combination of both low energy electrons and argon ions.
Data analysis was performed in CasaXPS v2.3.25 (ref. 30) after calibrating the data to the C(1s) peak maximum at 284.5 eV which is characteristic of the sp2 component of the activated carbon. Quantification was made using a Shirley type background and Scofield cross sections, with an electron energy dependence corresponding to the TPP-2 M method.31
3. Results and discussion
3.1. Kinetic model development
Within the proposed bimetallic CORE system, the initial DH of HMF occurs over Au sites, with ORR subsequently occurring over Pd sites. Electrons that are produced during the DH reaction are consumed in the latter ORR reaction. The overall process can be simply described by Scheme 2 and the accompanying equations (eqn (5) and (6)), with the associated rate constants detailed in Table 1.| Rate constant | Equation | Descriptor |
|---|---|---|
| k A1/kP1/k−1 | 5 | Reversible formation of activated intermediate state over Au (A) or Pd (P) sites |
| k A2/kP2 | 6 | Oxygen reduction occurring over Au or Pd sites |
In electrochemical experiments, the electron transfer occurs through an external circuit. Under thermocatalytic conditions however, electron transfer is considered to be mediated by the carbon support. This electron transport between metallic sites will be facile and far more rapid that any chemical reaction taking place. Therefore, we will assume that there is no barrier between the Au and Pd activated states. The measurement of electron transfer barriers would subsequently not improve the model's ability to predict experimental behaviour.
| HMF + H2O ⇌ HMFCA + 2H+ + 2e− | (5) |
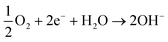 | (6) |
 | (7) |
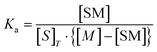 | (8) |
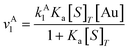 | (9) |
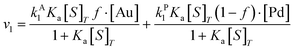 | (10) |
| v1 = [M]·{kA1·f + kP1·(1 − f)} | (11) |
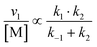 | (12) |
Overall, with the individual values of k1 and k2 assumed to remain constant, it is still the changing of the molar ratio between Au and Pd (i.e., the value of f) along with the oxygen reduction pathway that will affect the rate of HMFCA production. This presents several possible scenarios that can be compared to the experimental data to reveal further insights into the CORE system. Given what we know about the system already,12 here we will most prominently consider the following: for monometallic Au, DH coupled with 2e− ORR (eqn (14)); and for the bimetallic system, DH occurring on Au coupled with 4e− ORR occurring on Pd (eqn (15)). In the case of the latter, it is important to note that these roles could be reversed, but this is not under consideration here.
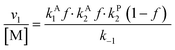 | (13) |
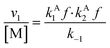 | (14) |
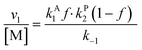 | (15) |
3.2. Catalyst characterisation
To begin our experimental investigation, two carbon supported Au and Pd catalysts were prepared via sol-immobilisation to a target loading of 1 wt%. Microwave digestion of the solid catalysts followed by ICP-AES analysis confirmed both Au/C and Pd/C had an accurate loading of 1.0 wt% (Table S1†). The carbon support used – Vulcan XC72R – is important due to its high conductivity,32 which is necessary to facilitate electron transport.Within our previous work on CORE effects,12 the Au and Pd catalysts used had a metal loading of 1.75 wt% and 0.25 wt%, respectively. As they were used in a 4![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 molar ratio, the catalysts were synthesised with differing metal loadings to ensure a relatively consistent amount of carbon was used for each catalyst (in a typical experiment, 72 mg and 71 mg of Au/C and Pd/C were used, respectively). However, subsequent experiments have shown that the addition of blank carbon support to a catalytic system (either monometallic or bimetallic) has no effect on the activity or enhancement (Fig. S1†). Therefore, throughout the experimental work, a consistent loading of 1 wt% is used for both Au/C and Pd/C catalysts. This is to ensure that physical characteristics, such as metal dispersion, are consistent allowing for us to better probe the influence of the Au
1 molar ratio, the catalysts were synthesised with differing metal loadings to ensure a relatively consistent amount of carbon was used for each catalyst (in a typical experiment, 72 mg and 71 mg of Au/C and Pd/C were used, respectively). However, subsequent experiments have shown that the addition of blank carbon support to a catalytic system (either monometallic or bimetallic) has no effect on the activity or enhancement (Fig. S1†). Therefore, throughout the experimental work, a consistent loading of 1 wt% is used for both Au/C and Pd/C catalysts. This is to ensure that physical characteristics, such as metal dispersion, are consistent allowing for us to better probe the influence of the Au![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) Pd ratio.
Pd ratio.
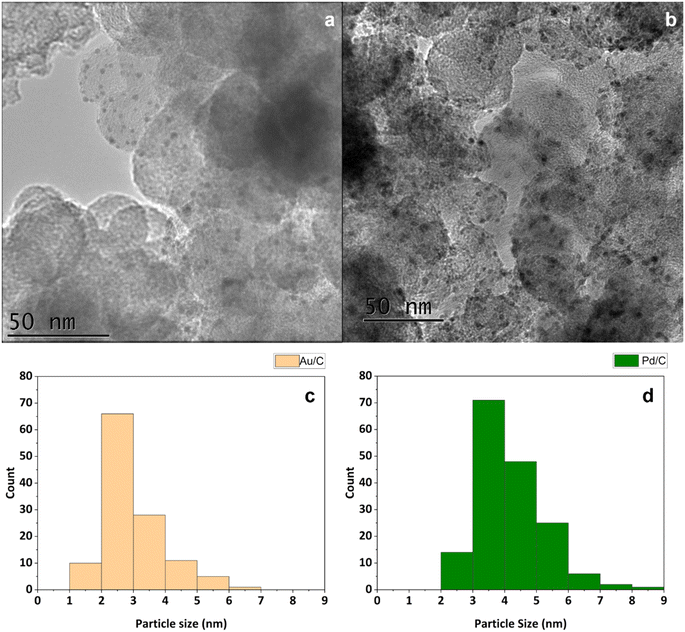
After synthesis of these materials, they were probed by transition electron microscopy (TEM) to determine the supported metal particle sizes. For this, analysis was conducted on multiple areas of each catalyst. The TEM experiments confirmed that the sol-immobilisation method had been effective, as each catalyst exhibited narrow particle size distributions. Mean particle diameters of 3.0 nm and 4.2 nm were determined for the Au/C and Pd/C catalysts, respectively (Fig. 1). Achieving a small particle size within a tight range is vital to ensure the high activity of supported Au and Pd catalysts, as particle size effects can influence catalytic performance of both DH and ORR.33–35
XPS analysis of the Au4f region and Pd3d region was conducted over the respective catalysts (Fig. S2†), which confirms the metallic nature of the Au present. For the fresh Pd/C catalyst, a small proportion of Pd2+ is observed with a Pd0/Pd2+ at% ratio of 6.33. The Pd2+ species are likely to arise through passivation, which is unsurprising given the reduced Pd/C catalyst is dried at 110 °C in air. Given that electron transfer between Au and Pd is not considered to be limiting, it is not anticipated that the proportion of Pd2+ present in the fresh Pd/C catalyst will influence the rate of reaction.
3.3. HMF oxidative dehydrogenation
The Au/C and Pd/C catalysts were subsequently used for the thermocatalytic conversion of HMF. The experimental data (Fig. 2 and 3) discussed here is taken at 30 minutes where initial rates are still valid and the consumption of HMF can be considered a true measure of reaction rate. Initially, both catalysts were reacted separately in monometallic systems and the quantity of each catalyst used was varied to establish how this influenced the activity. Au/C and Pd/C were then used in a physical mixture where the total metal moles was kept constant (HMF: metal = 200![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 (mol
1 (mol![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) mol)) and the molar ratio between Au and Pd was varied. Throughout these experiments, the molar ratio between Au and Pd was controlled by varying the mass of each 1 wt% catalyst, as opposed to keeping mass constant and altering the weight percent during synthesis. Although this changes the amount of carbon support present, it eliminates any variables that may arise from preparing catalysts with different weight loadings. For this section, results are displayed in terms of activity turnover (eqn (4)) as it accounts for consecutive surface reactions that occur from reaction intermediates. Though, it is important to note that, for both catalysts, the trends exhibited by these activity measurements are mirrored in the analogous conversion data (Fig. S3†).
mol)) and the molar ratio between Au and Pd was varied. Throughout these experiments, the molar ratio between Au and Pd was controlled by varying the mass of each 1 wt% catalyst, as opposed to keeping mass constant and altering the weight percent during synthesis. Although this changes the amount of carbon support present, it eliminates any variables that may arise from preparing catalysts with different weight loadings. For this section, results are displayed in terms of activity turnover (eqn (4)) as it accounts for consecutive surface reactions that occur from reaction intermediates. Though, it is important to note that, for both catalysts, the trends exhibited by these activity measurements are mirrored in the analogous conversion data (Fig. S3†).
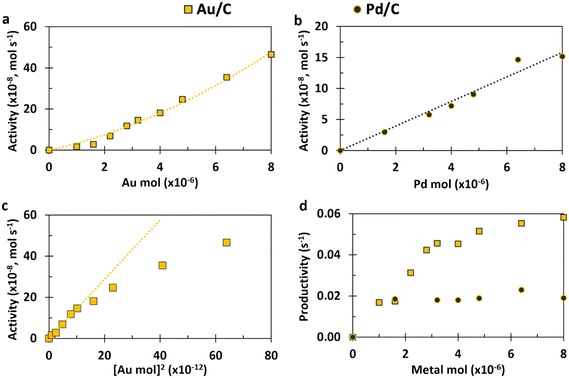
Eqn (14) concerns a situation where monometallic Au catalyses both DH and 2e− ORR and gives a scenario where the rate of HMFCA production is proportional to the square of the Au content (f2). This would give a maximum rate at f = 1 and a parabolic relationship between the quantity of Au present and activity. Fig. 2(a) and (c) show how the experimental activity of the Au system correlates with the moles of Au and the square of moles of Au, respectively. Not unexpectedly, the maximum rate is seen at the highest Au content. Somewhat more surprisingly and in line with the kinetic model prediction, there is a clear parabolic relationship. A linear correlation between activity and the square of Au moles is evident at low masses of Au, but this begins to plateau at higher masses. In line with the model, this suggests that CORE is present at low masses in this monometallic system, and that Au does indeed catalyse both DH and ORR, simultaneously. At high moles (>3.2 × 10−6), the relationship tends to be more linear (Fig. 2(a)), indicating that the kinetic model no longer holds and that one of the half-cell reactions becomes limiting.
Considering the Pd system (Fig. 2(b)), there is a clear linear relationship, demonstrating that the activity is always limited by the rate of the one of the half-cell reactions (likely DH as Pd is a very effective ORR catalyst) and cooperation between the DH and ORR is not enhancing the activity. Fig. 2(d) supports both conclusions for Au and Pd as it can be seen that the productivity of Au increases as the total amount of catalyst increases (until a plateau at high masses). That is to say that the more Au there is present, the more effective each Au site is, which is not the case for Pd. In summary, the Au monometallic system conforms to the kinetic model at low Au masses, showing evidence for coupling between DH and ORR half-cells, which leads to an above-linear enhancement. At high masses of catalyst and throughout the Pd data set, the relationship between activity and metal moles is linear.
Next, the rate of HMF oxidation over physical mixtures of Au/C and Pd/C was investigated. The stability of the Au/C and Pd/C catalysts, when employed as physical mixtures, is an important consideration that should be addressed.36,37 Previous studies have demonstrated that Pd can be transferred to Au particles over physical mixtures of supported monometallic Au and Pd catalysts in an organic medium, thus influencing their activity over time. However, the catalyst synthesis and testing conditions used herein align with those used in our previous work,12 where a variety of techniques were used to assess this. Collectively these experiments demonstrated that no Au or Pd migration occurred, suggesting that under basic aqueous conditions the Au/C and Pd/C catalysts are stable.
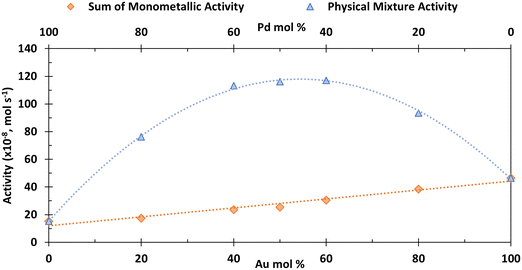
Fig. 3 shows that at all molar ratios there is a significant and symmetrical enhancement in activity compared to the sum of the analogous monometallic systems (similar enhancement is seen for HMF conversion (Fig. S4†)). For example, the activity for HMF conversion (× 10−8) of a monometallic Au catalyst at 4 × 10−6 mol (50 mol.%) is 18.1 mol s−1; the analogous activity for the same amount of Pd moles in a monometallic system is 7.2 mol s−1. In a physical mixture, when combining these two quantities of catalyst, the activity is 116 mol s−1, which is far in excess of the sum of the two monometallic systems (25.3 mol s−1), hence demonstrating the significant enhancement which is governed by the CORE effect.12
The kinetic model formulated based on the CORE effect predicts that the rate of HMFCA production (or the activity as presented here) of the physical mixture will be proportional to f(1 − f) (eqn (15)), which is based the scenario that Au catalysed DH is coupled with Pd catalysed 4e− oxygen reduction. A typical graph of the form y = f(1 − f) is a symmetrical curve with a maxima at f = 0.5. From Fig. 3 we can see that the experimental data correlates exceptionally well with this, showing symmetrical enhancements across the molar ratios. Although very close, the activity at 50 mol% is not actually the true maxima, but small derivations are to be expected due to competing ORR pathways always being present. Overall, it can be concluded that kinetic analysis presented here accurately describes the physical mixture system in the case of Au and Pd.
From both Fig. 2 and 3, it is clearly shown that the kinetic model presented, specifically eqn (14) and (15), predict certain experimental activity. The dependence on the molar quantity of Au and/or Pd is varied depending on the catalytic system. However, the coupling between DH and ORR is consistently evident, supporting the assumptions made during the derivation.
4. Conclusion
The kinetic model presented in this work was based upon the novel CORE effect observed in alcohol oxidation reactions.12 It explains the significant activity enhancement seen when using a Au and Pd bimetallic catalytic system by demonstrating coupling between DH and ORR reactions on separate catalytic sites. Herein, a kinetic model is presented that correctly predicts the relative activity (i.e., the trend and the maxima) of a monometallic Au system, as a correlation was observed between activity and squared metal moles. This is to say that rate of HMFCA production if proportional to f2. In a bimetallic system, containing a physical mixture of Au and Pd catalysts, the shape and maxima of activity values when the molar ratio is varied is equivalent to that modelled by the kinetic analysis, which predicted a shape proportional to f(1 − f). This provides further evidence in support of the CORE system and emphasises how the rate of ORR is vital in the overall rate of DH of alcohols and formyls. Building from this there are other scenarios (e.g., eqn (13)) that could potentially exist for various bimetallic combinations, where maximum enhancement, if any, is seen at a different molar ratio.Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest to declare.Acknowledgements
XPS data collection was performed at the EPSRC National Facility for XPS (‘HarwellXPS’), operated by Cardiff University and UCL, under contract No. PR16195. All authors would like to thank the CCI-Electron Microscopy Facility which has been part-funded by the European Regional Development Fund through the Welsh Government (Grant Number: 82126), and the Wolfson Foundation (Grant Number: 360G-wolfson-20882). Liang Zhao would like to thank the Chinese Scholarship Council for funding.References
- S. Han and C. B. Mullins, Acc. Chem. Res., 2021, 54, 379–387 CrossRef PubMed
.
- N. Dimitratos, J. A. Lopez-Sanchez, D. Morgan, A. F. Carley, R. Tiruvalam, C. J. Kiely, D. Bethell and G. J. Hutchings, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2009, 11, 5142–5153 RSC
.
- A. Villa, M. Schiavoni, S. Campisi, G. M. Veith and L. Prati, ChemSusChem, 2013, 6, 609–612 CrossRef
.
- J. Pritchard, L. Kesavan, M. Piccinini, Q. He, R. Tiruvalam, N. Dimitratos, J. A. Lopez-Sanchez, A. F. Carley, J. K. Edwards, C. J. Kiely and G. J. Hutchings, Langmuir, 2010, 26, 16568–16577 CrossRef
.
- N. Agarwal, L. Thomas, A. Nasrallah, M. A. Sainna, S. J. Freakley, J. K. Edwards, C. R. A. Catlow, G. J. Hutchings, S. H. Taylor and D. J. Willock, Catal. Today, 2021, 381, 76–85 CrossRef
.
- J. K. Edwards, B. E. Solsona, P. Landon, A. F. Carley, A. Herzing, C. J. Kiely and G. J. Hutchings, J. Catal., 2005, 236, 69–79 CrossRef CAS
.
- Y. Yi, L. Wang, G. Li and H. Guo, Catal. Sci. Technol., 2016, 6, 1593–1610 RSC
.
- J. K. Edwards, E. N. Ntainjua, A. F. Carley, A. A. Herzing, C. J. Kiely and G. J. Hutchings, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2009, 48, 8512–8515 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- A. Groß, Top. Catal., 2006, 37(1), 29–39 CrossRef
.
- H. C. Ham, G. S. Hwang, J. Han, S. W. Nam and T. H. Lim, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2010, 114, 14922–14928 CrossRef CAS
.
- A. K. Singh and Q. Xu, ChemCatChem, 2013, 5, 652–676 CrossRef CAS
.
- X. Huang, O. Akdim, M. Douthwaite, K. Wang, L. Zhao, R. J. Lewis, S. Pattisson, I. T. Daniel, P. J. Miedziak, G. Shaw, D. J. Morgan, S. M. Althahban, T. E. Davies, Q. He, F. Wang, J. Fu, D. Bethell, S. McIntosh, C. J. Kiely and G. J. Hutchings, Nature, 2022, 603, 271–275 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- A. Kulkarni, S. Siahrostami, A. Patel and J. K. Nørskov, Chem. Rev., 2018, 118, 2302–2312 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- J. K. Nørskov, J. Rossmeisl, A. A. Logadottir, L. Lindqvist, J. R. Kitchin, T. Bligaard and H. Jónsson, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2004, 108, 17886–17892 CrossRef
.
- B. N. Zope, D. D. Hibbitts, M. Neurock and R. J. Davis, Science, 2010, 330, 74–78 CrossRef CAS
.
- S. Sui, X. Wang, X. Zhou, Y. Su, S. Riffat and C. J. Liu, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2017, 5, 1808–1825 RSC
.
- F. D. Sanij, P. Balakrishnan, P. Leung, A. Shah, H. Su and Q. Xu, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2021, 46, 14596–14627 CrossRef
.
- S. Zaman, L. Huang, A. I. Douka, H. Yang, B. You and B. Y. Xia, Am. Ethnol., 2021, 133, 17976–17996 Search PubMed
.
- F. Jaouen, E. Proietti, M. Lefèvre, R. Chenitz, J. P. Dodelet, G. Wu, H. T. Chung, C. M. Johnston and P. Zelenay, Energy Environ. Sci., 2010, 4, 114–130 RSC
.
- R. Ma, G. Lin, Y. Zhou, Q. Liu, T. Zhang, G. Shan, M. Yang and J. Wang, npj Comput. Mater., 2019, 5(1), 1–15 CrossRef
.
- K. G. C. Senarathna, H. M. S. P. Randiligama and R. M. G. Rajapakse, RSC Adv., 2016, 6, 112853–112863 RSC
.
- Z. Qiang, J. H. Chang and C. P. Huang, Water Res., 2002, 36, 85–94 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- X. Zhang, X. Zhao, P. Zhu, Z. Adler, Z.-Y. Wu, Y. Liu and H. Wang, Nat. Commun., 2022, 13(1), 1–11 CrossRef CAS
.
- P. Sabatier, Ber. Dtsch. Chem. Ges., 1911, 44, 1984–2001 CrossRef CAS
.
- A. J. Medford, A. Vojvodic, J. S. Hummelshøj, J. Voss, F. Abild-Pedersen, F. Studt, T. Bligaard, A. Nilsson and J. K. Nørskov, J. Catal., 2015, 328, 36–42 CrossRef CAS
.
- J. N. Chheda, Y. Román-Leshkov and J. A. Dumesic, Green Chem., 2007, 9, 342–350 RSC
.
- S. E. Davis, L. R. Houk, E. C. Tamargo, A. K. Datye and R. J. Davis, Catal. Today, 2011, 160, 55–60 CrossRef CAS
.
-
T. Werpy and G. Petersen, Top Value Added Chemicals from Biomass Volume I-Results of Screening for Potential Candidates from Sugars and Synthesis Gas, 2004 Search PubMed
.
- A. Gandini, A. J. D. Silvestre, C. P. Neto, A. F. Sousa and M. Gomes, J. Polym. Sci., Part A: Polym. Chem., 2009, 47, 295–298 CrossRef
.
- N. Fairley, V. Fernandez, M. Richard-Plouet, C. Guillot-Deudon, J. Walton, E. Smith, D. Flahaut, M. Greiner, M. Biesinger, S. Tougaard, D. Morgan and J. Baltrusaitis, Applied Surface Science Advances, 2021, 5, 100112 CrossRef
.
- S. Tanuma, C. J. Powell and D. R. Penn, Surf. Interface Anal., 1994, 21, 165–176 CrossRef
.
-
S. Pérez-Rodríguez, E. Pastor and M. J. Lázaro, Electrochemical behavior of the carbon black Vulcan XC-72R: influence of the surface chemistry, 2018 Search PubMed
.
- N. Dimitratos, J. A. Lopez-Sanchez, D. Lennon, F. Porta, L. Prati and A. Villa, Catal. Lett., 2006, 108(3), 147–153 CrossRef
.
- C. Megías-Sayago, A. Lolli, D. Bonincontro, A. Penkova, S. Albonetti, F. Cavani, J. A. Odriozola and S. Ivanova, ChemCatChem, 2020, 12, 1177–1183 CrossRef
.
- O. Schade, P. Dolcet, A. Nefedov, X. Huang, E. Saraçi, C. Wöll and J.-D. Grunwaldt, Catalysts, 2020, 10, 342 CrossRef CAS
.
- C. M. Olmos, L. E. Chinchilla, A. Villa, J. J. Delgado, A. B. Hungría, G. Blanco, L. Prati, J. J. Calvino and X. Chen, J. Catal., 2019, 375, 44–55 CrossRef CAS
.
- D. Wang, A. Villa, P. Spontoni, D. S. Su and L. Prati, Chem. – Eur. J., 2010, 16, 10007–10013 CrossRef CAS
.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available. See DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/d2cy01474b |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2023 |