Fast switching of spontaneous polarization in a microporous molecular rotor ferroelectric†
Le-Ping
Miao‡
 a,
Ning
Ding‡
b,
Na
Wang
a,
Heng-Yun
Ye
a,
Ning
Ding‡
b,
Na
Wang
a,
Heng-Yun
Ye
 a,
Chao
Shi
a,
Chao
Shi
 *a and
Shuai
Dong
*a and
Shuai
Dong
 *b
*b
aChaotic Matter Science Research Center, Jiangxi Provincial Key Laboratory of Functional Molecular Materials Chemistry, Jiangxi University of Science and Technology, Ganzhou 341000, China
bSchool of Physics, Southeast University, Nanjing 211189, China. E-mail: sdong@seu.edu.cn
First published on 8th November 2022
Abstract
The fast switching feature of spontaneous polarization (Ps) is one of the basis for ferroelectric applications in the field of data storage. However, most molecular ferroelectrics exhibit low operating performance in polarization switching. Herein, we report fast switching Ps (25 kHz, 293 K) and low coercive field (0.55 kV cm−1, 353 K) for a microporous structural molecular rotor ferroelectric [CdL4]2+[NO3−]2 (L = β-alanine). In particular, the high switching frequency of Ps remains steady with high operational cycles (4.66 × 107). Single-crystal structures analysis and density functional theory (DFT) calculations reveal the fast switching of Ps originating from the fast static–rotating–static process of NO3−. This molecular rotor-type ferroelectric material provides more possibilities to develop next-generation non-volatile memory devices.
Introduction
Switching spontaneous polarization (Ps) is a representative characteristic property of ferroelectric materials. The switching feature makes these materials widely applicable in data storage, photoelectric devices, sensors, etc.1–3 In these fields, ferroelectric random access memory (FeRAM) has been the focus of research for the advantages of low-energy consumption, short write-access times, etc.4,5 It is well known that a ferroelectric memory device is directly correlated with polarization reversal properties.1 The time of polarization switching is one of the key properties determined by energy barrier, applied electric field, temperature, and critical volume. At present, inorganic ferroelectrics, such as BaTiO3 and (PbLa)(ZrTi)O3,6,7 dominate the market due to their outstanding performances. However, this type of ferroelectric materials is constrained by difficulties including the preparation of thin films. Simultaneously, they cause environmental concerns as they contain toxic lead and/or rare heavy metal elements.8,9Over the past years, organic–inorganic hybrid molecular ferroelectrics have become an important complement of inorganic ferroelectrics in the ferroelectric research field. It is because of their features such as easily derived structures, low density, softness, especially low toxicity, and environment friendliness.10,11 Some of them even exhibit exceptional performances, which are almost equal to those exhibited by inorganic oxide ceramics, such as BaTiO3.12 However, most of the hybrid molecular ferroelectrics demonstrate quite low operating frequencies on polarization switching, for example, organic salt diisopropylammonium bromide at 25 Hz,13 [C(NH2)3]Cl2SO4 at 50 Hz,14 organic co-crystal phenazine chloranilic/bromanilic acid at 1 Hz,15 organic–inorganic hybrid Ca–(NO3)2(15-crown-5) at 25 Hz16 and (H2dabco)Cu(H2O)6–(SeO4)2 at 400 Hz.17 Currently, few hybrid molecular ferroelectrics display a well-defined electric hysteresis loop (P–E) at high frequencies because almost all the polarization switching of molecular ferroelectrics originate from the reorientation of dipoles with steric difficulties (high energy barriers).18 Molecular rotors exhibit an inherent feature, i.e., the periodically arrayed motional rotors can rotate in the space room offered by the relative static stators.19 The intrinsic molecular motion in these amphidynamic crystals is the origin of structural phase transitions, which are accompanied by ferroelectricity or switching properties.20,21 Thus, a suitable stator–rotor system with a rotor rotating fast may display fast switching properties, such as a microporous structural system. This kind of structural system commonly shows weak intermolecular interactions between the host frameworks and guests.22–25 According to the definition of molecular rotors, rotors in a microporous structural system can achieve the goal of fast rotation. Because when rotors are located in the cavities of stators, weak intermolecular interactions result in low rotating energy barriers. Therefore, the microporous structural type molecular rotors may provide a feasible avenue to solve the above-mentioned issue of high energy barriers of dipole redirection.
Herein, we report a hybrid microporous structural molecular rotor ferroelectric 1 ([CdL4]2+[NO3−]2 (L = β-alanine)) containing butterfly-like host cations β-alanine cadmium complexes and planar nitrate guest anions with 356/357 K TC. The host–guest microporous compound 1 exhibits fast switching Ps at 25 kHz, possessing excellent fatigue resistance that remains steady with high operational cycles (4.66 × 107). The ferroelectric mechanism was obtained by variable temperature single-crystal XRD analysis and density functional theory (DFT) calculations. The NO3− anionic guest rotor is located in the diamond channel built by a butterfly-like cationic host stator. The ferroelectric mechanism originates from the reorientation of the NO3− rotor after fast rotation. This study may provide a new research platform and strategy for designing fast-switching Ps ferroelectric materials.
Results and discussion
Structural phase transition
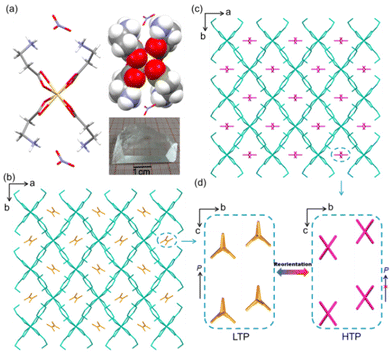
Block crystals of 1 were directly obtained in aqueous solution containing β-alanine and cadmium nitrate salt. It was easy to obtain a large block of the colorless single-crystal of 1 through this method (Fig. S1†). The purity of the polycrystalline samples of 1 was analyzed by the powder X-ray diffraction (PXRD) (Fig. S2†) technique. The differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) measurement (Fig. S3†) shows a pair of endo/exothermic peaks at 353/357 K. This result indicates that 1 undergoes a structural phase transition (SPT).According to the DSC result, we analyzed the crystal structures of 1 at 293 and 373 K. Crystal 1 contains a butterfly-like shaped [CdL4] (Cd(II), L = β-alanine) cation and two uncombined anions (NO3−), demonstrating a typical microporous structure. In the low-temperature phase (LTP), 1 crystallizes in the mm2 polar point group and orthogonal space group Fdd2 with unit cell parameters, a = 18.8987(5) Å, b = 23.8991(5) Å, c = 10.5306(2) Å, V = 4756.27(18) Å3 and Z = 8 (Table S1†). The asymmetric unit contains half of the cationic host framework and one complete anion guest. It can be noticed that its cationic hosts form a diamond-shaped channel along the c axis and afford free space for anionic guests. The guests adopt polar arrangements in the channel (Fig. 1a and b).
When in the HTP, the symmetry of 1 rises to the space group Fddd. The asymmetric unit changes to a quarter of the cationic host and half of the anion guest (Table S1†). Besides, the cationic host frameworks have a slight twist, retaining the continuous channel (Fig. S4†), and the dihedral angles of the host change from 75.40° and 26.34° to 75.2° and 23.99°, respectively (Fig. S5†). More importantly, the anionic guests NO3− change their orientation and position along the a axis with a centrosymmetric arrangement (Fig. 1c and d). Interestingly, this kind of movement is distinguished from the classical type of order–disorder or displacement.26 Hirshfeld surface analysis27,28 shows the weak hydrogen bonding of the cationic hosts and anionic guests almost with no difference in the LTP and HTP (Fig. S6†). This indicates that the molecular interactions remain basically unchanged in the SPT process. Therefore, the anionic guests perhaps undergo a fast motion and then go back to a static state process, which requires a low energy barrier.
According to the changes in the symmetry during the phase transition process, the transition of 1 may be a ferroelectric transition with Aizu notion mmmFmm2.29 For convenience, the phase below TC is labeled as FP (ferroelectric phase), and the phase above TC is PP (paraelectric phase). The FP space group Fdd2 is one of the maximal non-isomorphic subgroups of the PP space group Fddd. This transition leads to halving the symmetry elements of the corresponding point groups (from 8 to 4). Such transition has the order of 8/4 = 2 and satisfies the symmetry-breaking requirement of the Landau theorem for continuous ferroelectric transition. This is proved by the continuity of various physical properties.
Proof of ferroelectricity
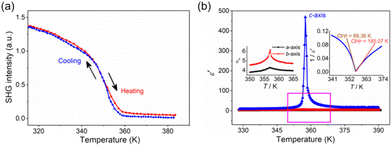
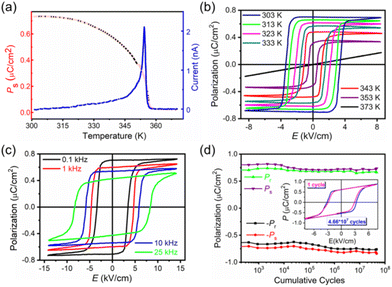
To prove the ferroelectric transition, the measurements of the temperature-dependent SHG (second harmonic generation) and dielectric constant were conducted. The SHG signal intensity of crystalline particles drops to zero at around TC, unambiguously supporting the structural transition from the polar phase to the centrosymmetric phase. The SHG intensity is 1.5 times as strong as that of KDP with the same particle size (Fig. 2a), revealing its application potential. The easy availability of large crystals is another advantage of 1 for SHG applications. Ferroelectricity is evident from the significant dielectric anomalies of both the polycrystalline and single-crystal samples at around TC (Fig. S7 and S8†). As shown in Fig. 2b, the dielectric constant along the c axis upon temperature dependences is different from others. The changes in ε′a and ε′b are not significant, while ε′c has a significant pronounced anomaly in the vicinity of TC (where ε′a, ε′b and ε′c represent the dielectric constants along the a, b and c axes, respectively). Around TC, ε′c follows the Curie–Weiss law,30ε′c = CPP/(T − T0) (T > TC) or CFP/(T′0 − T) (T < TC). The fitted Curie constants are CPP = 185.1 K and CFP = 89.4 K, and the Weiss temperature T0 ≈ T′0 = 357.4 ± 0.2 K.Further, the polarization properties of 1 were investigated meticulously using the thin monocrystal. We first determined Ps by integrating the pyroelectric current. Ps determined at room temperature is 0.72 μC cm−2. The evolution of Ps is same as that of the SHG intensity (Fig. 3a), following that expected for a ferroelectric material with the centrosymmetric paraelectric phase (χ(2) ≈ 6ε0βP, where β is a material-dependent coefficient and almost independent of temperature).31 The determined Ps is close to that determined from the P–E (polarization–electric field) hysteresis loops. As shown in Fig. 3b, the linear P–E dependence in the PP at 373 K reveals that 1 is a linear lossless dielectric. Thus the observed remanent polarization (Pr) in FP is due to Ps. The loops are characterized by high rectangularity and low coercive field (Ec), which is important for repeated reversal operations. At 303 K and 50 Hz, Ec is about 3.2 kV cm−1, and 0.55 kV cm−1 at 353 K and Pr (≈Ps) is close to 0.70 μC cm−2. Compared to some classical ferroelectrics, the Ec of 1 is lower (Table 1).32
| PZT | BTO | HfO2 | P(VDF–TrFE) | TGS | This work | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E c (kV cm−1) | 21–76 | 10 | 1000–2000 | 500 | 0.9 | 0.55 |
The excellent performance of polarization reversal is also demonstrated in high-frequency response. As shown in Fig. 3c, the P–E hysteresis loop retains high rectangularity even at 25 kHz (293 K). Such high performance in polarization switching for metal–organic ferroelectrics is scarce.18 Moreover, a preliminary study on the ferroelectric fatigue properties shows that after 4.66 × 107 switching operation cycles, Ps remains almost unchanged and the finally examined loops have the same Ps and high rectangularity as those of the initial state (Fig. 3d). This reveals the great potential of 1 in device applications based on polarization reversal.
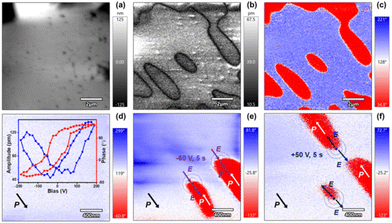
The polarization switch property was finally investigated using piezoresponse force microscopy (PFM). We recorded the domain structure on a thin film of 1. The vertical topology images of the thin film are shown in Fig. 4a. The domain walls can be clearly observed in the amplitude image and correspond well with the phase image (Fig. 4b and c), which is a direct sign of ferroelectricity for 1. To show polarization reversal, we recorded the amplitude and phase as the function of the applied field on a selected point. The typical hysteresis of the phase and butterfly loops of the amplitude reveals that it is easy to control the domain structure by an applied field (Fig. 4d). Moreover, the reverse of the domain was carried out through a biased PFM tip. We first choose the homogeneous signal of the PFM amplitude and phase of an area. Then we applied a negative bias of −60 V and 5 s on the region marked in the PFM phase image, and the domain reversal was observed in the amplitude and phase images. Furthermore, the positive bias of +50 V and 5 s on the marked region resulted in the domain back (up) and reverse (down) in the PFM phase and amplitude images (Fig. 4e, f and Fig. S9†). The domain reversal reveals the ferroelectric polarization switching nature.
Origin of ferroelectricity
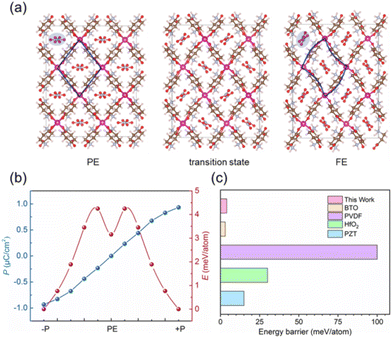
The ferroelectric origin of 1 is associated with the reorientation of NO3− guests and the distortion of [CdL4]2+ hosts according to the above experimental evidence. This can be determined from the single-crystal structures and DFT calculations. In LTP, the NO3− guests take a Y-type array in the channel, which induces polarization at the view of a axial, and the [CdL4]2+ hosts are non-centrosymmetric. When in HTP, guests change to face-to-face arrangement in the channel and with no polar. Meanwhile, the host frameworks also exhibit centrosymmetric. Thus, compound 1 has no spontaneous polarization any more (Fig. 1d and 5a). Thus, the symmetry broken is closely related to the movement of the guests and hosts. It should be noted that anions undergo a static–rotation–static process. This type of ferroelectric origin is different from the common order–disorder/displacement mechanism based on the structure transformation.26The polarization in this system as estimated by the Berry phase method is about 0.93 μC cm−2, which is close to the experimental data. Moreover, the energy barrier of the ferroelectric flip is an important parameter for the ferroelectric property, which can be simulated by the NEB method quantitatively. As shown in Fig. 5a, the phase transformation from FE (ferroelectric phase) to PE (paraelectric phase) originates from the rotation of NO3− and the twist of [CdL4]2+ along the c axis (SI_video†). Polarization increases linearly with the decrease in the rotation of NO3− and the twist of [CdL4]2+, as depicted in Fig. 5b. Further, the energy barrier of two degenerate ferroelectric states (±P) is about 4.25 meV per atom with a double peak shape. Moreover, this energy barrier is small enough to be comparable to the classic inorganic ceramic ferroelectrics, such as the BTO with excellent data storage performance (Fig. 5c).33–36 This result matches the bulk phase fast reversal of polarization in the experiment.
In addition, to distinguish the contribution of NO3− and [CdL4]2+ to polarization, we restricted the motion of one, and then calculated the changes in the polarization and barrier energy of the other one. As shown in Fig. S10a,† the NO3− guests are fixed in the Y-type array and the [CdL4]2+ hosts are twisted gradually. Further, polarization is ∼2.41 μC cm−2 in the case when the NO3− guests take a Y-type array in the channel, which is larger than 0.93 μC cm−2 in the FE state, and the [CdL4]2+ hosts adopt a centrosymmetric array. However, polarization decreases with the twist of [CdL4]2+. Thus, this indicates that the contribution of [CdL4]2+ to polarization is negative. In contrast, when the [CdL4]2+ hosts are fixed and the NO3− guests are rotated gradually (Fig. S10b†), as can be seen, the polarization increases with the rotation of NO3−, which hints that the contribution of NO3− to polarization is positive. In short, DFT calculations reveal the distortion of the [CdL4]2+ frame and rotation of NO3−, contributing to the ferroelectric polarization together. Moreover, the fast reversal of polarization is determined by the fast static–rotation–static process of the NO3− anions.
Conclusions
In summary, the fast static–rotation–static process of the rotor-induced ferroelectric phase transition and fast switching of polarization is proved by experimental results and DFT calculations. This kind of ferroelectric molecular mechanism distinguishes from the common order–disorder or displacement mechanism. This study presents a good case to understand the role of the motion of the rotor on ferroelectric phase transition and switching properties. This may open a new avenue to realize the fast switching polarization of ferroelectric materials for applications in data storage.Author contributions
C. S. and S. D. conceived the project. C. S. designed the experiments. S. D. proposed the theoretical mechanisms. L. P. M. prepared the samples and performed the DSC, dielectric, and P–E hysteresis loops measurements. N. D. performed the DFT calculations guided by S. D. N. W. contributed to PFM measurements and analysis. H. Y. Y. contributed to single crystal measurement and analysis. C. S. and L. P. M. wrote the manuscript with inputs from all other authors. L. P. M. and N. D. contributed equally.Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest to declare.Acknowledgements
We thank Prof. Yi Zhang for his kind help on the P–E hysteresis loops analysis. S. D. acknowledges the support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 11834002). C. S. acknowledges the support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 22175079). L.-P. M. acknowledges the support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 22205087) and Jiangxi Provincial Key Laboratory of Functional Molecular Materials Chemistry (Grant No. 20212BCD42018). H.-Y. Y. acknowledges the support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 21875093) and the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangxi Province (Grant No. 20204BCJ22015 and 20202ACBL203001). We thank the Big Data Center of Southeast University for providing the facility support on the numerical calculations.Notes and references
- J. F. Scott and C. A. Paz de Araujo, Ferroelectric memories, Science, 1989, 246, 1400–1405 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Masuda and M. Echizen, Polarization reversal property of ferroelectric thin film for ferroelectric memories, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys., 2006, 45, 817–821 CrossRef CAS.
- M. E. Lines and A. M. Glass, Principles and applications of ferroelectrics and related materials, Oxford University Press, New York, 2001 Search PubMed.
- Y. Masuda, The polarization-reversal and nonlinear properties of optoelectronic ceramics, Ferroelectrics, 1990, 109, 143–148 CrossRef CAS.
- J. F. Scott, Applications of modern ferroelectrics, Science, 2007, 315, 954–959 CrossRef CAS.
- W. J. Merz, Switching time in ferroelectric BaTiO3 and its dependence on crystal thickness, J. Appl. Phys., 1956, 27, 938–943 CrossRef CAS.
- C. E. Land, P. D. Thacher and G. H. Haertling, Applied solid state science advanced in materials and device research, Academic Press, New York, 1974 Search PubMed.
- S. Horiuchi and Y. Tokura, Organic ferroelectrics, Nat. Mater., 2008, 7, 357–366 CrossRef CAS.
- B. Neese, J. B. Chu, S. G. Lu, Y. Wang, E. Furman and Q. M. Zhang, Large electrocaloric effect in ferroelectric polymers near room temperature, Science, 2008, 321, 821–823 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. S. Tayi, A. K. Shveyd, A. H. Sue, J. M. Szarko, B. S. Rolczynski and S. I. Stupp, Room-temperature ferroelectricity in supramolecular networks of charge-transfer complexes, Nature, 2012, 488, 485–489 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- W. Zhang and R. G. Xiong, Ferroelectric Metal-Organic Frameworks, Chem. Rev., 2012, 112, 1163–1195 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. M. You, W. Q. Liao, D. W. Zhao, H. Y. Ye, Y. Zhang, Q. H. Zhou, X. H. Niu, J. L. Wang, P. F. Li, D. W. Fu, Z. M. Wang, S. Gao, K. L. Yang, J. M. Liu, J. Y. Li, Y. F. Yan and R. G. Xiong, An organic-inorganic perovskite ferroelectric with large piezoelectric response, Science, 2017, 357, 306–309 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Das and S. Ghosh, Supramolecular assemblies by charge-transfer interactions between donor and acceptor chromophores, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2014, 53, 2038–2054 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Szafrański, Ferroelectricity in the guanidinium compound [C(NH2)3]4Cl2SO4: synthesis and characterization, Phys. Rev. B: Condens. Matter Mater. Phys., 2005, 72, 054122 CrossRef.
- S. Horiuchi, R. Kumai, Y. Tokunaga and Y. Tokura, Proton dynamics and room-temperature ferroelectricity in anilate salts with a proton sponge, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2008, 130, 13382–13391 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Y. Ye, Y. Zhang, D. W. Fu and R. G. Xiong, A displacive-type metal crown ether ferroelectric compound: Ca(NO3)2(15-crown-5), Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2014, 53, 6724–6729 CrossRef CAS.
- W. Zhang, L. Z. Chen, R. G. Xiong, T. Nakamura and S. D. Huang, New ferroelectrics based on divalent metal ion alum, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2009, 131, 12544–12545 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Z. H. Sun, X. F. Yi, K. W. Tao, C. M. Ji, X. T. Liu, L. N. Li, S. G. Han, A. M. Zheng, M. C. Hong and J. H. Luo, A molecular ferroelectric showing room-temperature record-fast switching of spontaneous polarization, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2018, 57, 9833–9837 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. S. Vogelsberg and M. A. Garcia-Garibay, Crystalline molecular machines function, phase order, dimensionality, and composition, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2012, 41, 1892–1910 RSC.
- T. Akutagawa, H. Koshinaka, D. Sato, S. Takeda, S. I. Noro, H. Takahashi and T. Nakamura, Ferroelectricity and polarity control in solid-state flip-flop supramolecular rotators, Nat. Mater., 2009, 8, 342–347 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- D. W. Fu, W. Zhang, H. L. Cai, Y. Zhang, J. Z. Ge, R. G. Xiong and S. D. Huang, Supramolecular bola-like ferroelectric: 4-methoxyanilinium tetrafluoroborate-18-crown-6, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2011, 133, 12780–12786 CrossRef PubMed.
- C. S. Vogelsberga, F. J. Uribe-Romob, A. S. Liptonc, S. Yang, K. N. Houk, S. Brown and M. A. Garcia-Garibay, Ultrafast rotation in an amphidynamic crystalline metal organic framework, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2017, 114, 13613–13618 CrossRef.
- B. L. Chen, S. C. Xiang and G. D. Qian, Metal-organic frameworks with functional pores for recognition of small molecules, Acc. Chem. Res., 2010, 43, 1115–1124 CrossRef CAS.
- P. Nugent, T. Pham, K. McLaughlin, P. A. Georgiev, W. Lohstroh, J. P. Embs and J. Eckert, Dramatic effect of pore size reduction on the dynamics of hydrogen adsorbed in metal–organic materials, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2014, 2, 13884–13891 RSC.
- C. Y. Liu, X. R. Chen, H. X. Chen, Z. Niu, H. Hirao, P. Braunstein and J. P. Lang, Ultrafast luminescent light-up guest detection based on the lock of the host molecular vibration., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2020, 142, 6690–6697 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. P. Shi, Y. Y. Tang, P. F. Li, W. Q. Liao, Z. X. Wang, Q. Ye and R. G. Xiong, Symmetry breaking in molecular ferroelectrics, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2016, 45, 3811–3827 RSC.
- M. A. Spackman and J. J. McKinnon, Fingerprinting intermolecular interactions in molecular crystals, CrystEngComm, 2002, 4, 378–392 RSC.
- M. A. Spackman and D. Jayatilaka, Hirshfeld surface analysis, CrystEngComm, 2009, 11, 19–32 RSC.
- K. Aizu, Possible species of “ferroelastic” crystals, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn., 1969, 27, 387–396 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Trainer, Ferroelectrics and the Curie-Weiss law, Eur. J. Phys., 2000, 21, 459–464 CrossRef CAS.
- A. M. Glass, Dielectric, Thermal, and pyroelectric properties of ferroelectric LiTao3, Phys. Rev., 1968, 172, 564–571 CrossRef CAS.
- H. S. Choi, S. N. Li, I. H. Park, W. H. Liew, Z. Zhu, K. C. Kwon and K. P. Loh, Tailoring the coercive field in ferroelectric metalfree perovskites by hydrogen bonding, Nat. Commun., 2022, 13, 794 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. Buchacher, M. Rokosz, R. Dorey, J. Allam and A. Gregory, Electrocaloric induced retarded ferroelectric switching, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2017, 110, 022901 CrossRef.
- Y. W. Chen, S. T. Fan and C. W. Liu, Energy preference of uniform polarization switching for HfO2 by first-principle study, J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys., 2021, 54, 085304 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Tinte, M. G. Stachiotti, M. M. Sepliarsky, R. L. Migoni and C. O. Rodriguez, Atomistic modelling of BaTiO3 based on first-principles calculations, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter, 1999, 11, 9679–9690 CrossRef CAS.
- S. P. Beckman, X. J. Wang, K. M. Rabe and D. Vanderbilt, Ideal barriers to polarization reversal and domain-wall motion in strained ferroelectric thin films, Phys. Rev. B: Condens. Matter Mater. Phys., 2009, 79, 144124 CrossRef.
Footnotes |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available. CCDC 1918863 and 1918864. For ESI and crystallographic data in CIF or other electronic format see DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/d2qi02167f |
| ‡ The authors contributed equally. |
| This journal is © the Partner Organisations 2023 |