Open Access Article
Open Access ArticlePetal-like Mn-doped α-Ni(OH)2 nanosheets for high-performance Li–S cathode material†
Changfeng Zhao *a,
Hanyang Liua,
Jiawei Liub,
Yanhong Shia,
Shuguang Wanga,
Qiwei Tanga,
Xiangbing Zhua,
Huimin Zhanga and
Yan Zhaoa
*a,
Hanyang Liua,
Jiawei Liub,
Yanhong Shia,
Shuguang Wanga,
Qiwei Tanga,
Xiangbing Zhua,
Huimin Zhanga and
Yan Zhaoa
aSchool of Energy and Mechanical Engineering, Dezhou University, DeZhou, Shandong 253023, P. R. China. E-mail: 867713584@qq.com
bCollege of Agriculture, Shihezi University, Shihezi, Xinjiang 832003, P. R. China
First published on 15th March 2023
Abstract
Lithium–sulphur (Li–S) batteries are high-energy-density and cost-effective batteries. Herein, petal-like Ni1−xMnx(OH)2 (x ≈ 0.04) nanosheets were synthesised using a hydrothermal method and the electrical conductivity of Ni(OH)2 was improved by applying the cathode functional materials in Li–S batteries. With up to 5 mg cm−2 of S content in the cathode, the fabricated Ni1−xMnx(OH)2 electrode exhibited specific discharge capacities up to 1375 and 1150 mA h g−1 at 0.2 and 0.5C, and retained this capacity at 813 and 714 mA h g−1 after 200 cycles, respectively. Electrochemical measurement results show that Ni1−xMnx(OH)2 plays a critical role in Li–S batteries as it has a larger specific surface area than Ni(OH)2, which has superior adsorption performance toward lithium polysulphides. Moreover, the conductivity performance of Ni1−xMnx(OH)2 is significantly better than that of Ni(OH)2, which improves the electrochemical reaction kinetics of the Li–S batteries.
1. Introduction
With the rapidly increasing demand for energy applications in various fields, such as stationary storage, military power supplies and transportation facilities, the energy densities of commercial batteries (e.g. Ni–H [80 W h kg−1] and Li-ion [300 W h kg−1] batteries) cannot fulfil the current energy requirements of industries. Therefore, batteries with low costs and high energy densities/specific capacities are in critical demand for energy storage. In this regard, lithium–sulphur (Li–S) batteries have some obvious advantages, such as the low cost of S, high theoretical specific energy (1672 mA h g−1) and environmental friendliness; such characteristics have significantly promoted the high-speed development of Li–S batteries.1–3 However, the following defects have hampered the application of Li–S batteries: (1) the large volume expansion (80%) that occurs in cathodes when the conversion reaction occurs; (2) the shuttle effect of Li polysulphides (LiPSs); and (3) the electrical insulation nature of S and its process products (Li2S2/Li2S).4–6 Commendable progress has been made in the study of both modified separators and cathodes to ameliorate the lifespans and energy density of Li–S batteries.Because of the abundant surface hydroxyl groups of polar metal hydroxides such as Ca(OH)2 (ref. 7) and Ni(OH)2,8,9 polysulphides exhibit strong interactions. For instance, nickel hydroxide nanosheets are important encapsulation materials because of the high chemical adsorption of polysulphides; moreover, the size of the nickel hydroxide nanosheets blocks polysulphides but allows Li+ to pass through.8,9 Ni(OH)2 materials, however, have some disadvantages as well: poor conductivity and less electrochemically active areas that confine the kinetic diffusion to nickel hydroxide materials. Thus, the component and structure of nickel hydroxide requires further optimisation to address these issues. Furthermore, conductive materials with large specific surface areas compounded with Ni(OH)2 materials can enhance band structures and charge transfers, exposing catalytic active sites and avoiding nanosheet aggregation.10,11 Another effective method of promoting the physicochemical property of Ni(OH)2 materials is heterostructure or atomic doping. The conductivity of Ni(OH)2 will significantly improve when cobalt (Co), manganese (Mn), iron (Fe) or aluminium (Al) atomic dopes in Ni(OH)2 materials.12,13
However, different atomic dopes in Ni(OH)2 materials present different layered double hydroxides (LDHs) such as NiCo-LDH and NiMn-LDH.14–17 The thin layer structures of LDHs increase their defects and surface areas, which can change their physicochemical properties and electronic structures. Of these materials, NiMn-LDH is a nontoxic, low-cost and highly active material, and the abovementioned properties make the use of Li–S batteries profitable.
Under this context, we developed a cost-effective and simple method for synthesising Ni1−xMnx(OH)2 (x ≈ 0.04) nanowalls with highly uniform and large areas. With carbon nanotube (CNT), Ni1−xMnx(OH)2 and S (mass ratio of 15![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10
10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 75) content in the cathode, the first discharge specific capacity reached up to 1375 mA h g−1 at 0.2C, and still reached 813 mA h g−1 after 200 cycles. The above-described cell exhibits excellent rate performance. These superior electrochemical properties evidence that the conductivity and electrochemical reaction kinetics of Ni1−xMnx(OH)2 were effectively enhanced after Mn2+ was doped into Ni(OH)2. These enhanced properties of Ni1−xMnx(OH)2 can be ascribed to the following two reasons: first, Ni1−xMnx(OH)2 has an oversized specific surface area and superior adsorption performance for LiPSs, which can inhibit the shuttle effect of soluble LiPSs to a certain extent during discharge. Second, the conductivity performance of Ni1−xMnx(OH)2 is significantly improved, which accelerates the electrochemical reaction kinetics of the charge–discharge process.
75) content in the cathode, the first discharge specific capacity reached up to 1375 mA h g−1 at 0.2C, and still reached 813 mA h g−1 after 200 cycles. The above-described cell exhibits excellent rate performance. These superior electrochemical properties evidence that the conductivity and electrochemical reaction kinetics of Ni1−xMnx(OH)2 were effectively enhanced after Mn2+ was doped into Ni(OH)2. These enhanced properties of Ni1−xMnx(OH)2 can be ascribed to the following two reasons: first, Ni1−xMnx(OH)2 has an oversized specific surface area and superior adsorption performance for LiPSs, which can inhibit the shuttle effect of soluble LiPSs to a certain extent during discharge. Second, the conductivity performance of Ni1−xMnx(OH)2 is significantly improved, which accelerates the electrochemical reaction kinetics of the charge–discharge process.
2. Experimental
2.1 Material synthesis
The Mn-doped Ni(OH)2 material was fabricated quickly via the hydrothermal method. To this end, 50 mg of Mn(NO3)2·4H2O, 1105 mg of Ni(NO3)2·6H2O (Mn![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) Ni atomic ratio of 5
Ni atomic ratio of 5![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 95) and 560 mg of hexamethylenetetramine (HMTA) were dispersed in 40 mL of deionised water. The mixtures were subjected to magnetic stirring for 30 min and then placed in a three-necked flask for hydrothermal treatment at 95 °C for 6 h. Oxygen was removed from the flask using Ar, and both sides of the flask were sealed. Notably, the third bottle mouth was sealed with a balloon to relieve the pressure in the flask during heating. The obtained light green sample was thoroughly washed with deionised water several times. The sample was dried at 60 °C for 12 h in an oven and defined as Ni1−xMnx(OH)2. For comparison, the atomic ratio of Mn
95) and 560 mg of hexamethylenetetramine (HMTA) were dispersed in 40 mL of deionised water. The mixtures were subjected to magnetic stirring for 30 min and then placed in a three-necked flask for hydrothermal treatment at 95 °C for 6 h. Oxygen was removed from the flask using Ar, and both sides of the flask were sealed. Notably, the third bottle mouth was sealed with a balloon to relieve the pressure in the flask during heating. The obtained light green sample was thoroughly washed with deionised water several times. The sample was dried at 60 °C for 12 h in an oven and defined as Ni1−xMnx(OH)2. For comparison, the atomic ratio of Mn![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) Ni was changed to 1
Ni was changed to 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 9, and the sample thus obtained was defined as NiMn-LDH. Ni(OH)2 synthesis was similar to Ni1−xMnx(OH)2 synthesis with the exception that the solution contained no Mn2+. Finally, 1000 mg of Mn(NO3)2·4H2O, and 560 mg of HMTA were reacted in the same manner as that described above.
9, and the sample thus obtained was defined as NiMn-LDH. Ni(OH)2 synthesis was similar to Ni1−xMnx(OH)2 synthesis with the exception that the solution contained no Mn2+. Finally, 1000 mg of Mn(NO3)2·4H2O, and 560 mg of HMTA were reacted in the same manner as that described above.
2.2 Cathode fabrication
The weight ratio of Ni1−xMnx(OH)2 (or Ni(OH)2), S and CNT is 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 75
75![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 15, or the weight ratio of S and CNT is 75
15, or the weight ratio of S and CNT is 75![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 25. Then, the different mixtures were placed in different polytetrafluoroethylene reactors after they were fully ground and then heated at 155 °C for 12 h. The weight ratio of the composite (CNT/S/Ni1−xMnx(OH)2 or CNT/S/Ni(OH)2 or CNT/S) prepared above, super-P (SP), polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) is 80
25. Then, the different mixtures were placed in different polytetrafluoroethylene reactors after they were fully ground and then heated at 155 °C for 12 h. The weight ratio of the composite (CNT/S/Ni1−xMnx(OH)2 or CNT/S/Ni(OH)2 or CNT/S) prepared above, super-P (SP), polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) is 80![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10
10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10, the mixture was milled with N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone (NMP) to form uniform slurries. These slurries were pasted onto an aluminium foil each with a thickness of 300 μm and dried at 60 °C for 12 h in an oven with N2. Next, the dried slurries were cut into 12 mm-diameter samples on each of which about 5 mg cm−2 of S was coated. The sample discs are denoted as CNT/S/Ni1−xMnx(OH)2, CNT/S/Ni(OH)2 and CNT/S, respectively.
10, the mixture was milled with N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone (NMP) to form uniform slurries. These slurries were pasted onto an aluminium foil each with a thickness of 300 μm and dried at 60 °C for 12 h in an oven with N2. Next, the dried slurries were cut into 12 mm-diameter samples on each of which about 5 mg cm−2 of S was coated. The sample discs are denoted as CNT/S/Ni1−xMnx(OH)2, CNT/S/Ni(OH)2 and CNT/S, respectively.
2.3 Symmetric cell testing
For symmetric cell measurements, SP, PVDF and the CNT/Ni1−xMnx(OH)2 (mass ratio of 3![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 2) composites (or CNT/Ni(OH)2, the same mass ratio as above, or CNT) were weighed to the mass ratio of 10
2) composites (or CNT/Ni(OH)2, the same mass ratio as above, or CNT) were weighed to the mass ratio of 10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10
10![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 80. The sample discs were prepared via the cathode method, and the Ni1−xMnx(OH)2 (or Ni(OH)2 or CNT) loading on the disc was approximately 0.5 mg cm−2. The same discs were used as both the anode and cathode to assemble CR2025 cells. Li2S6 (0.2 M, 20 μL) was used as the electrolyte and the Celgard 2400 micromembrane was used as the separator. Cyclic voltammetry (CV) was tested on different symmetric cells configurations with a voltage window of −1.0 to 1.0 V at scanning rate of 3 mV s−1.
80. The sample discs were prepared via the cathode method, and the Ni1−xMnx(OH)2 (or Ni(OH)2 or CNT) loading on the disc was approximately 0.5 mg cm−2. The same discs were used as both the anode and cathode to assemble CR2025 cells. Li2S6 (0.2 M, 20 μL) was used as the electrolyte and the Celgard 2400 micromembrane was used as the separator. Cyclic voltammetry (CV) was tested on different symmetric cells configurations with a voltage window of −1.0 to 1.0 V at scanning rate of 3 mV s−1.
2.4 Li2S nucleation tests
Li metal discs and the prepared sample discs from Section 2.3 were utilised as the anodes and cathodes, respectively. The Celgard 2400 micromembrane was used as a separator. 0.1 M Li2S8 electrolyte (20 μL) was dropped onto the cathode and 1 M lithium bis(trifluoromethane sulphonimide) (LiTFSI) electrolyte without Li2S8 (20 μL) was dripped onto the anode. All prepared coin cells were firstly discharged at 0.112 mA to 2.06 V and then potentiostatic discharge curves were recorded at 2.05 V until the current was below 10−5 A.2.5 Electrochemical measurements
We used the CNT/S/Ni1−xMnx(OH)2, CNT/S/Ni(OH)2 or CNT/S disc as the cathode, the Celgard 2400 micromembrane as the separator, metallic Li as the anode, 1 wt% LiNO3 and 1 M LiTFSI dissolved in DME/DOL (1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1, by volume) as the electrolyte. The obtained coin cell was denoted as Ni1−xMnx(OH)2, (Ni(OH)2 or CNT. Charge–discharge performances for all three were tested on a Neware cell test analyser with a voltage window of 1.6–2.8 V. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) and CV measurements were performed on a CHI760C electrochemical workstation.
1, by volume) as the electrolyte. The obtained coin cell was denoted as Ni1−xMnx(OH)2, (Ni(OH)2 or CNT. Charge–discharge performances for all three were tested on a Neware cell test analyser with a voltage window of 1.6–2.8 V. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) and CV measurements were performed on a CHI760C electrochemical workstation.
2.6 Material characterisation
The prepared samples were examined through scanning electron microscopy and energy dispersive spectrometer (EDS) (SEM, Zeiss G-500), transmission electron microscopy (TEM, JEOL, JEM-1011), selected-area electron diffraction (SAED) and high-resolution TEM (HRTEM, JEOL, JEM2100Plus), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS, ESCALAB 250) and X-ray diffraction (XRD, Bruker D8). Surface areas were calculated using the Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) method. Mass ratios of S and Ni1−xMnx(OH)2 (or Ni(OH)2) in the sample were preprocessed using a HCl solution and thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) (Netzsch, STA 449 F3, 5 °C min−1 in N2).3. Results and discussion
A preparation method of petal-like Ni1−xMnx(OH)2 nanosheets is shown in Fig. 1a.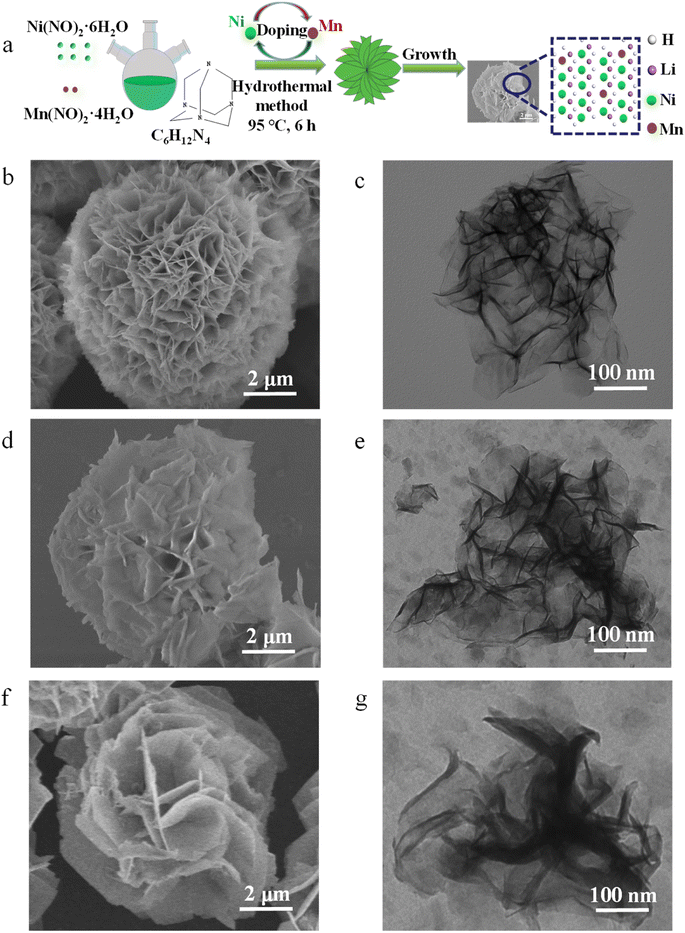 | ||
| Fig. 1 (a) Preparation method of petal-like Ni1−xMnx(OH)2 nanosheets. SEM images of (b) Ni(OH)2, (d) Ni1−xMnx(OH)2 and (f) NiMn-LDH. TEM images of (c) Ni(OH)2, (e) Ni1−xMnx(OH)2 and (g) NiMn-LDH. | ||
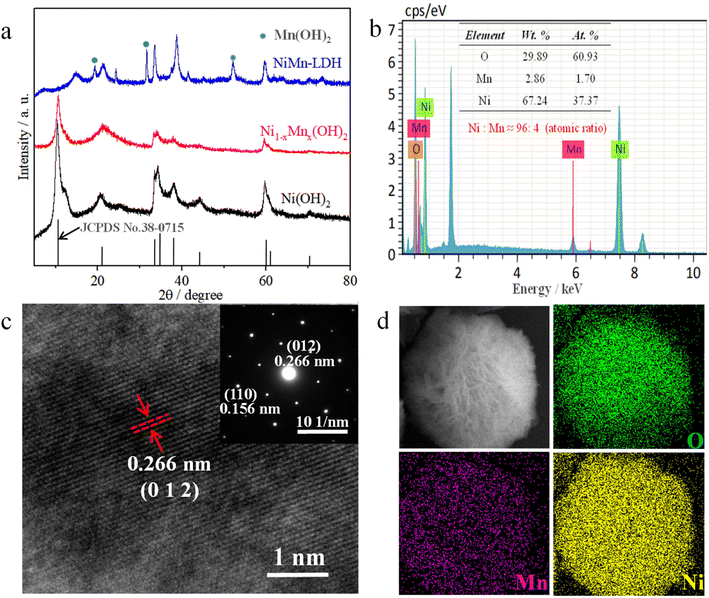
The SEM images in Fig. 1b and S1a† show that the Ni(OH)2 displayed an ultrathin petal-like sphere with an average diameter of about 5 μm. Some small-size nanosheets were grown in the core of the petal-like sphere, and other large-size nanosheets were wrapped in the small-size nanosheets. The thickness of the ‘flower-like’ nanosheets was about several nanometres, and their size was of several microns. Interestingly, with Mn doping, the nanosheet structure of Ni1−xMnx(OH)2 was distinctly rigid, and the thickness of these nanosheets exceeded that of the Ni(OH)2 nanosheets (Fig. 1d and S1b†). Such Ni1−xMnx(OH)2 structures provide several active sites for charge transport and electrochemical reaction. With increasing Mn doping, the NiMn-LDH nanosheet became thicker and more scattered than the Ni1−xMnx(OH)2 nanosheets (Fig. 1f and S1c†). The excessive Mn ions provided more selectivity as the growth of the crystal nucleus continued, and some Mn ions might not have been doped into Ni(OH)2. The TEM image of the Ni(OH)2 reveal that the thickness of the nanoscale petal-like slices was about 10 nm, and the layered overlay of the nanosheets was more obvious therein (Fig. 1d). Further, TEM observations reveal that the thickness and shape of Ni1−xMnx(OH)2 (Fig. 1e) and NiMn-LDH (Fig. 1g) were similar to those of Ni(OH)2. N2 adsorption/desorption testing was performed to further identify the surface area of Ni1−xMnx(OH)2 and Ni(OH)2. The adsorption/desorption curves of Ni1−xMnx(OH)2 and Ni(OH)2 exhibited typical IV isotherms (Fig. S2†). The specific surface area of Ni(OH)2 was measured to be about 65.25 m2 g−1, which is significantly smaller than that of Ni1−xMnx(OH)2 (approximately 84.75 m2 g−1). These results prove that Mn doping in Ni(OH)2 can increase the surface areas of and defects in Ni(OH)2, significantly increasing the contact area between the electrolyte and electrode materials of Li–S batteries.
The crystallinities and structural characterisations of Ni(OH)2, Ni1−xMnx(OH)2 and NiMn-LDH were inspected via XRD (Fig. 2a). The results show that all the main diffraction peaks of Ni(OH)2 were ascribable to α-Ni(OH)2 (JCPDS No. 38-0715), and no other obvious diffraction peaks were observed.18,19 This indicates that α-Ni(OH)2 was the main species of the above-prepared material. However, the intensity of the diffraction peaks was weaker than that of Ni(OH)2, indicating that Mn ions have been doped into Ni(OH)2; this result agrees with the HRTEM scans and SAED patterns for Ni1−xMnx(OH)2. The intensity and position of the main diffraction peaks with the sample (the atomic ratio of Ni![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) Mn was 90
Mn was 90![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10) obviously differed from those of α-Ni(OH)2, and had obvious new diffraction peaks, which agreed with the results obtained for Mn(OH)2 (JCPDS No. 18-0787).20 The results revealed that the amount of Mn ions doped in Ni(OH)2 was limited under such hydrothermal reaction conditions. The main diffraction peaks of the sample (which only contained Mn2+) corresponded to pure Mn3O4 (JCPDS No. 24-0734), revealing that Mn(OH)2 easily converted to oxides under the presence of oxygen and heating.
10) obviously differed from those of α-Ni(OH)2, and had obvious new diffraction peaks, which agreed with the results obtained for Mn(OH)2 (JCPDS No. 18-0787).20 The results revealed that the amount of Mn ions doped in Ni(OH)2 was limited under such hydrothermal reaction conditions. The main diffraction peaks of the sample (which only contained Mn2+) corresponded to pure Mn3O4 (JCPDS No. 24-0734), revealing that Mn(OH)2 easily converted to oxides under the presence of oxygen and heating.
The EDS elemental analysis of the sample (Mn![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) Ni atomic ratio of 5
Ni atomic ratio of 5![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 95) showed that the atomic ratio of Ni
95) showed that the atomic ratio of Ni![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) Mn was about 96
Mn was about 96![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 4 (Fig. 2b), demonstrating that Ni atoms were replaced by a small amount of Mn atoms in the Ni–Mn hydroxides, defined as Ni1−xMnx(OH)2 (x ≈ 0.04). The element mapping images of Ni1−xMnx(OH)2 show that the O, Mn and Ni elements were homogenously distributed across majority of the flower-like nanosheet area (Fig. 2d). Compared with the Ni signal, the Mn signal was obviously minor in terms of content but was clearly visible. The HRTEM image of Ni1−xMnx(OH)2 from Fig. 2c shows a lattice space of 0.266 nm, which matched well with the (0 1 2) plane of α-Ni(OH)2. The characteristic crystal planes of Ni1−xMnx(OH)2 were also matched well with (0 1 2) and (1 1 0) planes of α-Ni(OH)2 in the SAED pattern.
4 (Fig. 2b), demonstrating that Ni atoms were replaced by a small amount of Mn atoms in the Ni–Mn hydroxides, defined as Ni1−xMnx(OH)2 (x ≈ 0.04). The element mapping images of Ni1−xMnx(OH)2 show that the O, Mn and Ni elements were homogenously distributed across majority of the flower-like nanosheet area (Fig. 2d). Compared with the Ni signal, the Mn signal was obviously minor in terms of content but was clearly visible. The HRTEM image of Ni1−xMnx(OH)2 from Fig. 2c shows a lattice space of 0.266 nm, which matched well with the (0 1 2) plane of α-Ni(OH)2. The characteristic crystal planes of Ni1−xMnx(OH)2 were also matched well with (0 1 2) and (1 1 0) planes of α-Ni(OH)2 in the SAED pattern.
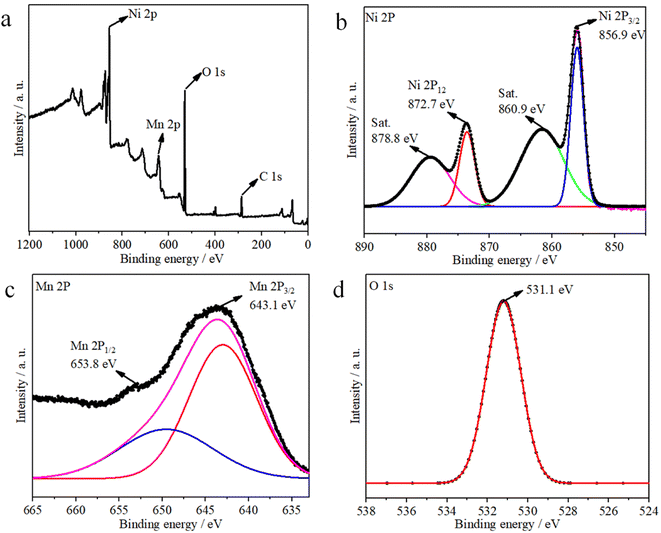
The corresponding XPS results shown in Fig. 3 indicate the chemical valence states and composition of the Ni1−xMnx(OH)2. The survey spectrum indicates the presence of Ni, Mn, O and C elements in the Ni1−xMnx(OH)2 sample (Fig. 3a). For the Ni 2p spectra shown in Fig. 3b, two spin–orbit split doublet binding energies at 872.7 and 856.9 eV were matched to Ni 2p1/2 and Ni 2p3/2, and the two peaks observed at around 860.9 and 878.8 eV, respectively, were corresponded with the shake-up satellites of Ni 2p (identified as ‘Sat.’). The Mn 2p spectra showed two binding energies at 653.9 and 642.7 eV (Fig. 3c), matched to Mn 2p1/2 and Mn 2p3/2, respectively. Note that the O 1s peak (Fig. 3d) centred at 531.1 eV corresponded to a hydroxyl group, supporting the existence of Ni and Mn hydroxides.21,22
Fig. S3† shows the Li2S6 adsorption tests between Ni1−xMnx(OH)2 and Ni(OH)2 to further confirm the effect of absorption with polysulphide. Compared to that of the Ni(OH)2 powder, the colour of Li2S6 containing Ni1−xMnx(OH)2 powder changed from dark yellow to transparent after 5 h, indicating that Ni1−xMnx(OH)2 had a more obvious adsorption effect on Li2S6 than Ni(OH)2. Additionally, the acid immersion treatment and TGA measurement clarified the composition of Ni1−xMnx(OH)2, S and CNT in the composite, and Fig. S4a† shows the fraction of S to be approximately 75 wt% and that of Ni1−xMnx(OH)2 to be 10 wt%. The composition of Ni(OH)2/S/CNT indicates the fractions of S to be approximately 74 wt% and Ni(OH)2 at 10 wt% (Fig. S4b†). The composition of S/CNT indicated the fraction of S to be approximately 75 wt% (Fig. S4c†).
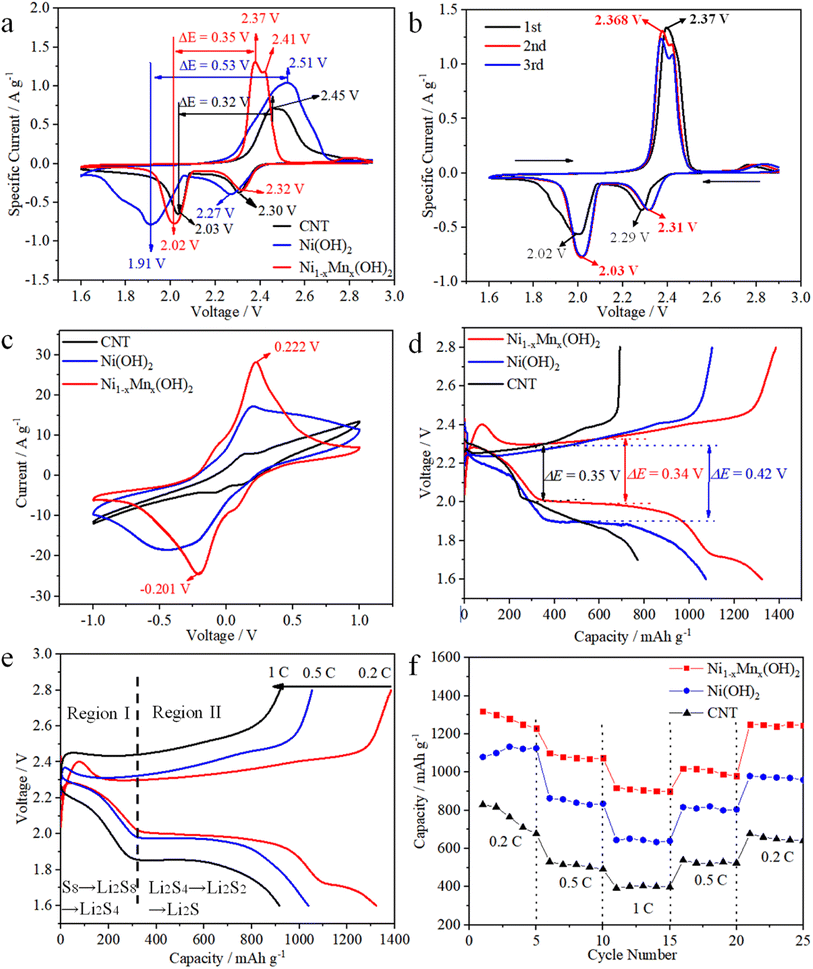
CV were measured to examine the electrochemical activities of various electrodes in cells, wherein the test voltage window was 1.6–2.9 V at 0.1 mV s−1. The Ni1−xMnx(OH)2 electrode displayed reduction peaks at 2.32 and 2.02 V, involving the conversion of S8 into solution LiPSs and further into Li2S2/Li2S (Fig. 4a). Conversely, the oxidation peaks at 2.37 and 2.41 V signified the converse process of Li2S2/Li2S conversion into solution LiPSs and S8, and the potential difference (PD) was 0.35 V. The two reduction peaks of the Ni(OH)2 electrode were observed at 2.30 and 2.03 V, the oxidation peak was located only at 2.51 V and the PD was up to 0.53 V, which is considerably higher than that observed for the Ni1−xMnx(OH)2 electrode. The Ni1−xMnx(OH)2 electrode also showed a few increases in current sharpness compared with the Ni(OH)2 electrode, again confirming that Ni1−xMnx(OH)2 can efficiently accelerate polysulphide conversion with reduced polarisation. The PD of the CNT electrode (0.32 V) was smaller than Ni1−xMnx(OH)2 electrode (0.35 V), which could be caused by the higher conductivity of CNT than that of Ni1−xMnx(OH)2. The specific current of the CNT electrode was significantly smaller than that of the Ni(OH)2 and Ni1−xMnx(OH)2 electrodes, implying that Ni(OH)2 and Ni1−xMnx(OH)2 have excellent electrochemical activity.23,24
The initial three CV cycles of the Ni1−xMnx(OH)2 electrode at 0.1 mV s−1 were tested in order to estimate the electrochemical stability (Fig. 4b). The two reduction peaks of the first cycle were at 2.32 and 2.02 V, and the oxidation peak was located at 2.51 V. In comparison, the two reduction peaks of the second cycle were at 2.31 and 2.03 V, and the oxidation peak was located at 2.368 V, implying that the cell had formed a stable solid electrolyte interface (SEI) film and irreversible decomposition of the electrolyte occurred.25 The superior overlap of the second and third cycles of the CV curve proves the stability and better reversibility of the cell.
CV curves of the symmetrical cell based on the Ni(OH)2 electrode exhibited one pair of wider redox peaks resulting from the repeated reduction reactions of Li2S8 to short-chain LiPSs, revealing the sluggish electrochemical kinetics of Ni(OH)2 (Fig. 4c).26–28 The CV of the Ni1−xMnx(OH)2 electrode exhibited one pair of distinct reversible peaks at −0.201 and 0.222 V, which displayed considerably higher current densities and smaller polarisation compared to the CNT and Ni(OH)2 electrodes. Thus, Ni1−xMnx(OH)2 effectively enhanced the redox kinetics of polysulphides more than CNT and Ni(OH)2.29 The representative discharge/charge curves between 1.7 and 2.8 V at 0.2C are shown in Fig. 4d to demonstrate the role of various electrodes in Li–S batteries. The first discharge/charge capacity of the Ni1−xMnx(OH)2 electrode was 1375/1386 mA h g−1, and the curve of the Ni1−xMnx(OH)2 electrode exhibited smaller capacity loss and more steady voltage platforms than that of the Ni(OH)2 electrode. Furthermore, ΔE (the potential gap between the charge and discharge plateaus) for the cell with Ni1−xMnx(OH)2 electrode (0.34 V) was smaller than that of the Ni(OH)2 electrode (0.42 V). The decrease in ΔE demonstrates that the Ni1−xMnx(OH)2 electrode relieved the redox polarisation in the cells. Compared with semiconducting Ni(OH)2, the introduction of Mn primarily contributed to the presence of half-metallic Ni1−xMnx(OH)2, leading to ion and electron transmission, which further reduced charge-transfer resistance and improved electrochemical performance.30 ΔE for the cell with the CNT electrode (0.35 V) was similar to that of the cell with the Ni1−xMnx(OH)2 electrode (0.34 V). However, the curve of the CNT electrode exhibited a larger capacity loss and less steady voltage platforms than those of the Ni1−xMnx(OH)2 electrode, thus demonstrating that Ni1−xMnx(OH)2 effectively enhanced the redox kinetics of polysulphides. The discharge/charge curves of the Ni1−xMnx(OH)2 electrode at 0.2, 0.5 and 1C are shown in Fig. 4e. The curve also maintained a stable flat discharge platform even at 1C, and exhibited light distortion at high current density.
The rate performances of Ni1−xMnx(OH)2, Ni(OH)2 and CNT electrodes are depicted in Fig. 4f. The first discharge specific capacities of the Ni1−xMnx(OH)2 electrode at 0.2, 0.5 and 1C were 1320, 1100 and 920 mA h g−1, and the specific capacity returned to 1250 mA h g−1 when turned back to 0.2C. Nevertheless, the initial discharge specific capacities of the Ni(OH)2 electrode at 0.2, 0.5 and 1C were 1080, 863 and 645 mA h g−1, and the reversible specific capacity was only 980 mA h g−1 when turned back to 0.2C. Obviously, the Ni1−xMnx(OH)2 electrode can achieve higher reversible redox reactions than the Ni(OH)2 electrode. The CNT electrode exhibited worse electrochemical performance than those of the two abovementioned electrodes because of the lack of functional materials.
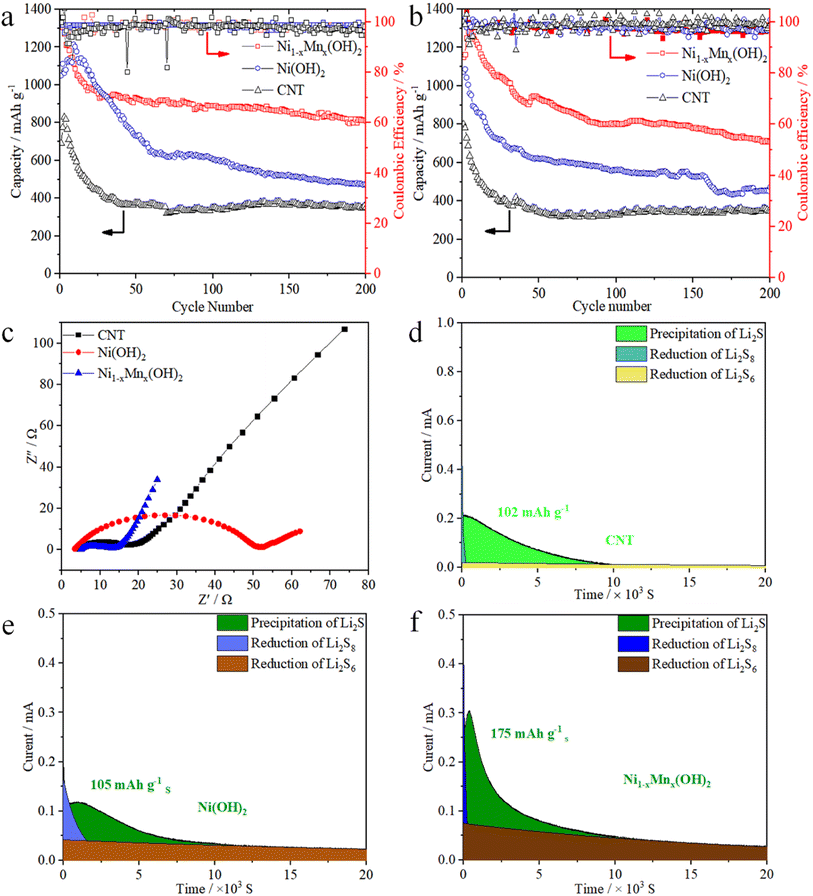
Fig. 5a compares the cycling performances of the CNT, Ni(OH)2 and Ni1−xMnx(OH)2 electrodes at 0.2C. The first discharge specific capacities of Ni1−xMnx(OH)2, Ni(OH)2 and CNT electrodes were 1323, 1050 and 690 mA h g−1, and the reversible specific capacities of the above electrodes were 813, 472 and 350 mA h g−1, respectively, after 200 cycles. The Ni1−xMnx(OH)2 electrode exhibited a more stable cycling performance than the Ni(OH)2 electrode; this performance was substantially higher than the CNT electrode. The initial discharge specific capacity of the Ni1−xMnx(OH)2 electrode at 0.5C was 1150 mA h g−1, which subsequently increased to 1283 mA h g−1; the reversible specific capacity was 714 mA h g−1 after 200 cycles. The discharge specific capacities slightly increased between the second and fifth cycle, probably because of Ni1−xMnx(OH)2 undergoes an initial activation process during dischargee/charge.8,31 In comparison, the discharge specific capacity of the Ni(OH)2 electrode decreased to 474 mA h g−1 after 200 cycles, which was still considerably higher than that of the CNT electrode. The decay trends of the discharge specific capacity of the Ni1−xMnx(OH)2 and CNT electrodes were similar under 0.2 and 0.5C because of the perfect conductivity and minor polarisation of the two abovementioned compounds. Conversely, the Ni(OH)2 electrode showed inferior cyclic stability because of the worse conductivity of Ni(OH)2.
EIS was performed on the cells after 200 cycles based on Ni1−xMnx(OH)2, Ni(OH)2, and CNT electrodes, and the corresponding Nyquist plots are shown in Fig. 5c. Apparently, the Ni1−xMnx(OH)2 electrode had a considerably smaller semicircle at high frequency than the Ni(OH)2 electrode, implying that the Ni1−xMnx(OH)2 electrode had lower interface charge-transfer resistance (Rct, 10.1 Ω) than the Ni(OH)2 electrode (Rct, 48.4 Ω). These results imply that the Ni1−xMnx(OH)2 electrode is favourable for promoting ionic mobility and electronic conductivity on the electrolyte–electrode interface.32 In addition, the Rct (13.8 Ω) of the CNT electrode was substantially smaller than that of the Ni(OH)2 electrode, confirming that the electronic conductivity of the CNT electrode is significantly higher than that of the Ni(OH)2 electrode and similar to that of the Ni1−xMnx(OH)2 electrode. The Ni1−xMnx(OH)2 electrode was significantly better than Ni(OH)2 electrode in terms of electrochemical activity based on the slopes of the three electrodes in the low-frequency region.
The capacity of solid Li2S deposition from Li2S8 was tested using the variously prepared electrodes and test methods presented in Section 2.4. The results (Fig. 5d–f) show that the Ni1−xMnx(OH)2 electrode had the strongest current peak and the highest nucleation capacity of Li2S (175 mA h g−1). The CNT and Ni(OH)2 electrodes exhibited current peaks of 102 mA h g−1 and 105 mA h g−1, respectively. The results suggest that the presence of the Ni1−xMnx(OH)2 electrode could reduce the Li2S nucleation energy, strengthen the adsorption of LiPSs, and accelerate the rapid phase transformation of LiPSs to solid Li2S. Thus, Ni1−xMnx(OH)2 promoted the liquid–solid nucleation and growth kinetics of Li2S.33–36 In a previous study, we discussed the key role of Ni(OH)2 in improving the redox reaction kinetics in Li–S batteries.37 However, Ni(OH)2 also has some disadvantages, such as poor conductivity and few electrochemically active areas, which limit its kinetic diffusion. The O-coordinated Mn atoms doped in Ni(OH)2 induce a large binding energy between LiPSs and the active sites that accelerates redox reaction kinetics during the discharge/charge process.38,39 Similar to that in the CV test and EIS analysis, the relatively low Li2S deposition on Ni(OH)2 also resulted from the poorer conductivity of Ni(OH)2 relative to Ni1−xMnx(OH)2.40,41
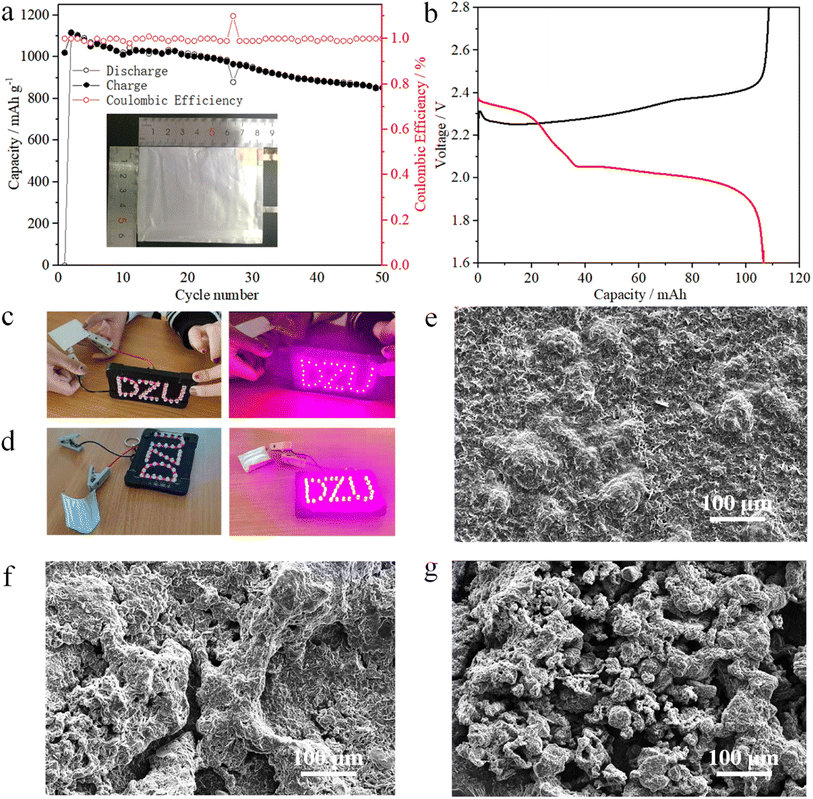
The preparation of the Ni1−xMnx(OH)2 cathode slurry was the same as those of the coin and pouch cells but with the electrodes of the pouch cell having a higher sulphur mass loading of 6.4 mg cm−2. The first discharge capacity of the pouch cell was 105 mA h (Fig. 6b), and the corresponding specific capacity was 1150 mA h g−1 (matched with 4.37 mA h cm−2, Fig. 6a). After 50 cycles, the pouch cell still maintained a markedly high areal capacity (about 3.12 mA h cm−2). The folded pouch cell could still make ‘DZU’ LED light similar to the smooth pouch cell (Fig. 6c and d). Thus, the pouch cell has certain application prospects in the fields of wearable electronic equipment and special equipment.
SEM images of the Li anode after cycles are shown in Fig. 6e–g to further investigate the effects of different electrodes with Li anodes. Compared with Ni(OH)2 and CNT, the surface of the Li anode cycled with Ni1−xMnx(OH)2 was smoother with only a few cracks, as shown in Fig. 6e, attributable to the faster redox kinetics of Ni1−xMnx(OH)2 polysulphides. It also exhibited relatively stable cycling performance. Moreover, the surface of the Li anode with Ni(OH)2 was loose and mossy, as shown in Fig. 6f, caused by the slower redox kinetics of the Ni(OH)2, and the specific capacity decay was faster than that of Ni1−xMnx(OH)2. The surface of the Li anode with CNT showed numerous particles and even ‘dead lithium’ (Fig. 6g), resulting in worse electrochemical performance than that of Ni(OH)2.42,43 A comparison of the electrochemical performance of Ni1−xMnx(OH)2 with that of carbon-based functional materials presented in previous literature is shown in Table S1:† Ni1−xMnx(OH)2 performed well among the electrodes that have been studied in the literature, evidencing the importance of Mn-doped Ni(OH)2 materials in improving electrochemical performance and enhancing S redox kinetics.
4. Conclusions
Petal-like Ni1−xMnx(OH)2 (x ≈ 0.04) nanosheets were synthesised in this study via a simple hydrothermal method. With high S loading (about 5 mg cm−2) on the cathode, the Ni1−xMnx(OH)2 electrode exhibited discharge specific capacities up to 1375 and 1150 mA h g−1 at 0.2 and 0.5C, respectively. The discharge specific capacity was retained at 813 and 714 mA h g−1 after 200 cycles, which exhibited better cycling stability and specific capacity in Li–S batteries. The results of the cyclic stability, symmetrical electrode and cells of CV measurements, EIS and the nucleation and growth of Li2S prove that Ni1−xMnx(OH)2 plays a critical role in Li–S batteries compared with Ni(OH)2. The superior electrochemical performance of Ni1−xMnx(OH)2 has two advantages. First, Ni1−xMnx(OH)2 has a larger specific surface area than Ni(OH)2, providing better adsorption performance for LiPSs. Second, the conductivity performance of Ni1−xMnx(OH)2 was significantly improved compared with that of Ni(OH)2, resulting in the acceleration of the electrochemical reaction kinetics of the discharge/charge process.Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Science and Technology Development Fund of Shandong Province (2022TSGC2560) and Dezhou City (2022TSGC019).References
- J. Q. Huang, X. F. Liu, Q. Zhang, C. M. Chen, M. Q. Zhao, S. M. Zhang, W. C. Zhu, W. Z. Qian and F. Wei, Entrapment of sulfur in hierarchical porous graphene for lithium-sulfur batteries with high rate performance from -40 to 60 °C, Nano Energy, 2013, 2, 314–321 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. C. Jeong, J. H. Kim, S. Nam, C. R. Park and S. J. Yang, Rational design of nanostructured functional interlayer/separator for advanced Li–S batteries, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2018, 28, 1707411 CrossRef.
- S. Rehman, K. Khan, Y. F. Zhao and Y. L. Hou, Nanostructured cathode materials for lithium– sulfur batteries: progress, challenges and perspectives, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2017, 5, 3014–3038 RSC.
- W. G. Lim, S. Kim, C. Jo and J. Lee, A comprehensive review of materials with catalytic effects in Li–S batteries: enhanced redox kinetics, Angew, Chem. Int. Ed., 2019, 58, 18746–18757 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Son, J. S. Lee, Y. Son, J. H. Jang and J. Cho, Recent advances in lithium sulfide cathode materials and their use in lithium sulfur batteries, Adv. Energy Mater., 2015, 5, 1500110–1500123 CrossRef.
- J. P. Yue, M. Yan, Y. X. Yin and Y. G. Guo, Progress of the interface design in all-solid-state Li – S batteries, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2018, 28, 1707533 CrossRef.
- H. Y. Shao, B. C. Huang, N. Q. Liu, W. K. Wang, H. Zhang, A. B. Wang, F. Wang and Y. Q. Huang, Modified separators coated with a Ca(OH)2–carbon framework derived from crab shells for lithium-sulfur batteries, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2016, 4, 16627–16634 RSC.
- J. Jiang, J. Zhu, W. Ai, X. Wang, Y. Wang, C. Zou, W. Huang and T. Yu, Encapsulation of sulfur with thin-layered nickel-based hydroxides for long-cyclic lithium-sulfur cells, Nat. Commun., 2015, 6, 8622–8630 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. L. Dai, L. Y. Hu, M. Q. Wang, Y. M. Chen, J. Han, J. Jiang, Y. Zhang, B. L. Shen, Y. B. Niu, S. J. Bao and M. W. Xu, Uniform α-Ni(OH)2 hollow spheres constructed from ultrathin nanosheets as efficient polysulfide mediator for long-term lithium-sulfur batteries, Energy Storage Mater., 2017, 8, 202–208 CrossRef.
- S. D. Min, C. J. Zhao, Z. M. Zhang, G. R. Chen, X. Z. Qian and Z. P. Guo, Synthesis of Ni(OH)2/RGO pseudocomposite on nickel foam for supercapacitors with superior performance, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2015, 3, 3641–3650 RSC.
- J. Yan, Z. J. Fan, W. Sun, G. Q. Ning, T. Wei, Q. Zhang, R. F. Zhang, L. J. Zhi and F. Wei, Advanced asymmetric supercapacitors based on Ni(OH)2/graphene and porous graphene electrodes with high energy density, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2012, 22, 2632–2641 CrossRef CAS.
- X. H. Sun, Q. Shao, Y. C. Pi, J. Guo and X. Q. Huang, A general approach to synthesise ultrathin NiM (M = Fe, Co, Mn) hydroxide nanosheets as highperformance low-cost electrocatalysts for overall water splitting, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2017, 5, 7769–7775 RSC.
- W. Y. Lim, Y. F. Limb and G. W. Ho, Pseudomorphic-phase transformation of NiCo based ternary hierarchical 2D-1D nanostructures for enhanced electrocatalysis, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2017, 5, 919–924 RSC.
- Y. Li, S. W. Guo, T. Jin, Y. L. Wang, F. Y. Cheng and L. F. Jiao, Promoted synergy in core-branch CoP@NiFe-OH nanohybrids for efficient electrochemical-photovoltage-driven overall water splitting, Nano Energy, 2019, 63, 103821 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Y. Hwang, H. M. Kim, S. Shin and Y. K. Sun, Designing a high-performance lithium-sulfur batteries based on layered double hydroxides-carbon nanotubes composite cathode and a dual-functional graphene-polypropylene-Al2O3 separator, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2018, 28, 1704294 CrossRef.
- G. Y. Jiang, N. Zheng, X. Chen, G. Y. Ding, Y. H. Li, F. G. Sun and Y. S. Li, In-situ decoration of MOF-derived carbon on nitrogen-doped ultrathin MXene nanosheets to multifunctionalize separators for stable Li–S batteries, Chem. Eng. J., 2019, 373, 1309–1318 CrossRef CAS.
- D. Guo, F. W. Ming, H. Su, Y. Q. Wu, W. D. Wahyudi, M. L. Li, M. N. Hedhili, G. Sheng, L. J. Li, H. N. Alshareef, Y. X. Li and Z. P. Lai, MXene based self-assembled cathode and antifouling separator for high-rate and dendrite-inhibited Li–S battery, Nano Energy, 2019, 61, 478–485 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Yang, Y. Q. Wu, R. C. Rao and H. Wang, Methanol promoted synthesis of porous hierarchical a-Ni(OH)2 for the remove of Congo red, Powder Technol., 2017, 320, 377–385 CrossRef CAS.
- J. W. Wu, W. Liu, X. Xiang, K. Sun, F. H. Liu, C. Cai, S. B. Han, Y. Y. Xie, S. Li and X. T. Zu, From Ni(OH)2/Graphene composite to Ni@Graphene core-shell: a selfcatalyzed epitaxial growth and enhanced activity for nitrophenol reduction, Carbon, 2017, 117, 192–200 CrossRef CAS.
- T. H. Xu, G. Y. Li, X. H. Yang, Z. X. Guo and L. J. Zhao, Design of the seamless integrated C@NiMn-OH-Ni3S2/Ni foam advanced electrode for supercapacitors, Chem. Eng. J., 2019, 362, 783–793 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. J. Wei, L. Y. Yan, C. Z. Wang, X. G. Xu, F. Wu and G. Chen, Effects of Ni doping on [MnO6] octahedron in LiMn2O4, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2004, 108, 18547 CrossRef CAS.
- J. W. Zhao, J. L. Chen, S. M. Xu, M. F. Shao, Q. Zhang, F. Wei, J. Ma, M. Wei, D. G. Evans and X. Duan, Hierarchical NiMn layered double hydroxide/carbon nanotubes architecture with superb energy density for flexible supercapacitors, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2014, 24, 2938–2946 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Cao, C. Chen, Q. Zhao, N. Zhang, Q. Lu, X. Wang, Z. Niu and J. Chen, A flexible nanostructured paper of a reduced graphene oxide-sulfur composite for high-performance lithium–sulfur batteries with unconventional configurations, Adv. Mater., 2016, 28, 9629–9636 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. J. Peng, G. Zhang, X. Chen, Z. W. Zhang, W. T. Xu, J. Q. Huang and Q. Zhang, Enhanced electrochemical kinetics on conductive polar mediators for lithium–sulfur batteries, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2016, 128, 13184–13189 CrossRef.
- Y. Jiang, H. Q. Liu, X. H. Tan, L. M. Guo, J. T. Zhang, S. N. Liu, Y. J. Guo, J. Zhang, H. F. Wang and W. G. Chu, Monoclinic ZIF-8 nanosheet-derived 2D carbon nanosheets as sulfur immobilizer for high-performance lithium sulfur batteries, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2017, 9, 25239–25249 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Li, X. Zhang, G. H. Liu, A. Gerhardt, K. Evans, A. Z. Jia and Z. S. Zhang, Oxygen-deficient titanium dioxide supported cobalt nano-dots as efficient cathode material for lithium-sulfur batteries, J. Energy Chem., 2020, 48, 390–397 CrossRef.
- H. Y. Zhou, Z. Y. Sui, K. Amin, L. W. Lin, H. Y. Wang and B. H. Han, Investigating the Electrocatalysis of a Ti3C2/Carbon Hybrid in Polysulfide Conversion of Lithium–Sulfur Batteries, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2020, 12, 13904–13913 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- F. Zhou, Z. Li, X. Luo, T. Wu, B. Jiang, L. L. Lu, H. B. Yao, M. Antonietti and S. H. Yu, Low Cost Metal Carbide Nanocrystals as Binding and Electrocatalytic Sites for High Performance Li–S Batteries, Nano Lett., 2018, 18, 1035–1043 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Z. Yuan, H. J. Peng, T. Z. Hou, J. Q. Huang, C. M. Chen, D. W. Wang, X. B. Cheng, F. Wei and Q. Zhang, Powering lithium-sulfur battery performance by propelling polysulfide redox at sulfiphilic hosts, Nano Lett., 2016, 16, 519–527 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. W. Chen, X. Wang, J. X. Wang and P. S. Lee, Sulfidation of NiMn-Layered Double Hydroxides/Graphene Oxide Composites toward Supercapacitor Electrodes with Enhanced Performance, Adv. Energy Mater., 2016, 6, 1501745 CrossRef.
- X. X. Gu, C. J. Tongc, B. Wen, L. M. Liu, C. Lai and S. Q. Zhang, Ball-milling synthesis of ZnO@sulphur/carbon nanotubes and Ni(OH)2@sulphur/carbon nanotubes composites for high-performance lithium-sulphur batteries, Electrochim. Acta, 2016, 196, 369–376 CrossRef CAS.
- Q. Li, Z. A. Zhang, Z. P. Guo, Y. Q. Lai and K. Zhang, Improved cyclability of lithium-sulfur battery cathode using encapsulated sulfur in hollow carbon nanofiber@nitrogen-doped porous carbon core-shell composite, Carbon, 2014, 78, 1–9 CrossRef CAS.
- G. Xia, Z. Q. Zheng, J. J. Ye, X. T. Li, M. J. Biggs and C. Hu, Carbon microspheres with embedded FeP nanoparticles as a cathodeelectrocatalyst in Li-S batteries, Chem. Eng. J., 2021, 406, 126823 CrossRef CAS.
- H. C. Gao, S. L. Ning, J. S. Zou, S. Men, Y. Zhou, X. J. Wang and X. W. Kang, The electrocatalytic activity of BaTiO3 nanoparticles towards polysulfides enables high-performance lithium–sulfur batteries, J. Energy Chem., 2020, 48, 208–216 CrossRef.
- S. Z. Huang, X. M. Zhang, Y. Wang, Y. Zheng, D. Z. Kong, M. Ding, S. Y. Yang and H. Y. Yang, Regulating the polysulfide redox conversion by iron phosphide nanocrystals for high-rate and ultrastable lithium-sulfur battery, Nano energy, 2018, 51, 340–348 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Fan, S. Z. Huang, M. E. Pam, S. Chen, Q. Y. Wu, J. P. Hu, Y. Wang, L. K. Ang, C. C. Yan, Y. M. Shi and H. Y. Yang, Design multifunctional catalytic interface: toward regulation of polysulfide and Li2S redox conversion in Li–S batteries, Small, 2019, 1906132 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. F. Zhao, X. X. Yang, G. Xia, J. L. Liu, W. Q. Zhang, J. Xue, S. F. Hou and C. Hu, Enhanced sulfur redox kinetics and polysulfide regulations with petal-like nickel hydroxide nanosheets/rGO modified separators in Li-S batteries, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2021, 551, 149393 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. N. Liu, Z. Y. Wei, B. Zhong, H. T. Wang, L. Xia, T. Zhang, X. M. Duan, D. C. Jia, Y. Zhou and X. X. Huang, O-, N-Coordinated single Mn atoms accelerating polysulfides transformation in lithium-sulfur batteries, Energy Storage Mater., 2021, 35, 12–18 CrossRef.
- S. M. Qiao, D. Lei, Q. Wang, X. S. Shi, Q. Zhang, C. H. Huang, A. M. Liu, G. H. He and F. X. Zhang, Etch-evaporation enabled defect engineering to prepare high-loading Mn single atom catalyst for Li–S battery applications, Chem. Eng. J., 2022, 442, 136258 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. S. He, M. J. Li, Y. G. Zhang, Z. Z. Shan, Y. Zhao, J. D. Li, G. H. Liu, C. Y. Liang, Z. Bakenov and Q. Li, All-purpose electrode design of flexible conductive scaffold toward high-performance Li–S batteries, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2020, 30, 2000613 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Zhao, H. J. Peng, B. Q. Li, X. Chen, J. Xie, X. Y. Liu, Q. Zhang and J. Q. Huang, Electrochemical phase evolution of metal-based pre-catalysts for high-rate polysulfide conversion, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2020, 132, 9096–9102 CrossRef.
- C. Yan, X. B. Cheng, C. Z. Zhao, J. Q. Huang, S. T. Yang and Q. Zhang, Lithium metal protection through in-situ formed solid electrolyte interphase in lithium-sulfur batteries: The role of polysulfides on lithium anode, J. Power Sources, 2016, 327, 212–220 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Qie, C. X. Zu and A. Manthiram, A high energy lithium-sulfur battery with ultrahigh-loading lithium polysulfide cathode and its failure mechanism, Adv. Energy Mater., 2016, 6, 1502459 CrossRef.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available. See DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/d3ra00032j |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2023 |