Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleCreative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported Licence
Reassembly of wood to plastic- and paper-like films via ultra-mild dissolution in formic acid†
Naoko
Kobayashi
 *af,
Tomohiro
Hashizume
bf,
Keiko
Kondo
cdf,
Kenji
Kitayama
b,
Masato
Katahira
cdef and
Takashi
Watanabe
*af,
Tomohiro
Hashizume
bf,
Keiko
Kondo
cdf,
Kenji
Kitayama
b,
Masato
Katahira
cdef and
Takashi
Watanabe
 *af
*af
aBiomass Conversion, Research Institute for Sustainable Humanosphere (RISH), Kyoto University, Gokasho, Uji 611-0011, Japan. E-mail: kobayashi.naoko.2c@kyoto-u.ac.jp; twatanab@rish.kyoto-u.ac.jp
bDaicel Corporation, Osaka Head Office, Grand Front Osaka Tower-B, 3-1, Ofuka-cho, Kita-ku, Osaka 530-0011, Japan
cInstitute of Advanced Energy, Kyoto University, Gokasho, Uji, Kyoto 611-0011, Japan
dIntegrated Research Center for Carbon Negative Science, Institute of Advanced Energy, Kyoto University, Gokasho, Uji, Kyoto 611-0011, Japan
eGraduate School of Energy Science, Kyoto University, Yoshida-hommachi, Sakyo-ku, Kyoto 606-8501, Japan
fBiomass Product Tree Industry-Academia Collaborative Research Laboratory, Kyoto University, Gokasho, Uji, Kyoto 611-0011, Japan
First published on 26th February 2024
Abstract
Wood is the most abundant lignocellulosic biomass and has the potential to be a resource to mitigate environmental impacts. Here, we present the dissolution of wood sawdust and chips in formic acid at 50 °C under ultra-mild conditions without using ball milling and added catalysts. We found that depressurization and occasional light pressurization of wood sawdust or chips during stirring in a formic acid solution significantly accelerated solubilization accompanied by the formylation of wood components. Multi-dimensional NMR analyses revealed formylation of lignin, hemicellulose and cellulose. Substituents of formyl groups broke the hydrogen bond networks among cell wall components, resulting in the disintegration and solubilization of wood. Casting the solution from the total dissolved solution of Eucalyptus globulus on a release film and natural evaporation gave a plastic-like film with tensile strength (61 MPa), Young's modulus (3097 MPa), and glass transition temperature (Tg = 177 °C) values comparable to those of acryl resin, and a paper-like sheet formed from Japanese cedar. These two types of films from wood were also compared among the films produced from agricultural waste. Thus, the three plant cell wall components in wood sawdust and chips were directly disintegrated through formylation under ultra-mild conditions and reassembled to the films just by casting.
Introduction
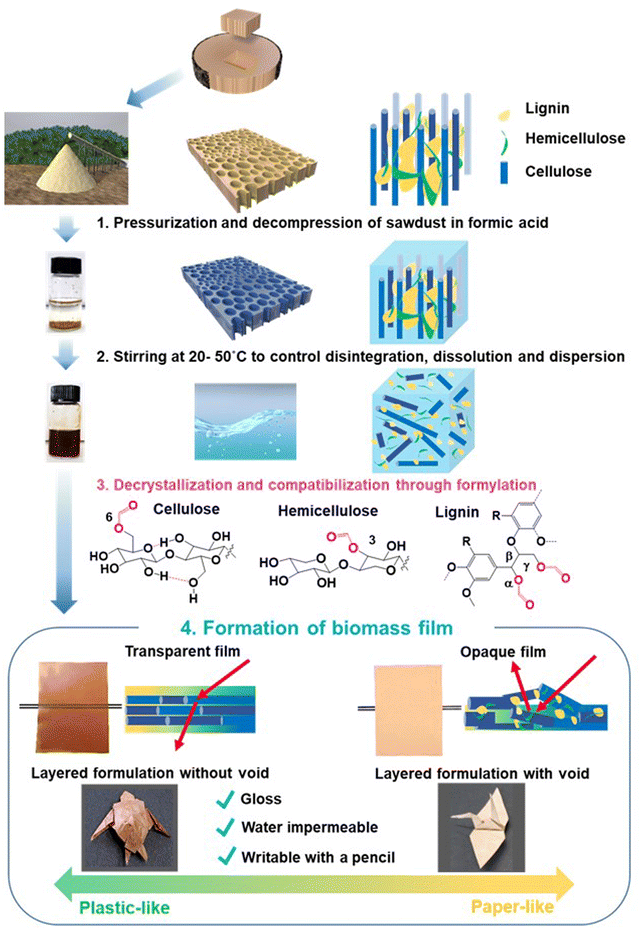
Plastics and paper are essential in modern society. Petroleum-derived plastics disrupt the Earth's carbon balance1,2 and cause microplastic and nanoplastic issues.3–5 Despite wood's potential as a resource for mitigating environmental issues, current plasticized wood products are made by blending wood with synthetic polymers, copolymerization with petroleum-derived monomers, or flow moulding after chemical modification.6Lignocellulosic biomass is the most abundant renewable resource. Plant secondary cell walls comprise a heterogeneous aromatic polymer, such as lignin, and structural polysaccharides, such as cellulose and hemicelluloses.7,8 Hemicelluloses are associated with cellulose microfibrils mainly by hydrogen bonding and cross-linked with lignin by covalent linkages to form lignin–carbohydrate complexes (LCCs).9,10 These components form rigid matrices via noncovalent bonds, such as hydrogen bonds, van der Waals forces, and hydrophobic interactions.9,10 To date, lignin-depolymerizing reactions have been extensively studied in order to separate cellulose and obtain reducing sugars via enzymatic saccharification. However, we believe that wood components may be dissolved and separated if the rigid cell wall matrices can be unbundled by breaking noncovalent linkages through the impregnation of solvents into the cell walls, accompanied by the insertion of functional groups into polysaccharides and lignin.
In contrast to the lignin-depolymerizing strategy, we focused on the dissociation of wood cell wall components by breaking the noncovalent network under mild conditions using conventional solvents, and found that a ball-milled wood powder of Eucalyptus globulus and Japanese birch was dissolved in α-keto and aldehydic acid at room temperature and that casting of the solution yielded a foldable transparent film.11,12 In the previous study, disruption of the cell wall structures by ball milling prior to the dissolution process was necessary. Through pulverization by ball milling with a strong impact pressure, the polysaccharides in the cell walls are exposed, and the solubility in solvents and the reactivity with catalysts dramatically increase. However, ball milling is not economically feasible due to its huge energy consumption (130 MJ kg−1). To develop biomaterials through the low-energy dissolution of wood, methods for solubilizing wood sawdust and chips in formic acid have been investigated. As a result of many trials such as screening of metal added catalysts, heating by microwave and so on, we found that depressurization and occasional light pressurization of a formic acid solution containing wood sawdust or chips during stirring significantly accelerated solubilization accompanied by the formylation of wood components, and these solid materials were dissolved under mild conditions of 40–50 °C (Fig. 1 and 3). After dissolving wood in formic acid (Fig. 1 and 4), the wood solution was cast on a release sheet to form new materials such as an opaque paper-like film from Japanese cedar wood and transparent plastic-like film with strength comparable to acrylic resins from Eucalyptus globulus (Eucalyptus) wood. 2D and 3D NMR analyses revealed that the mixing of wood with formic acid caused the formylation of cellulose, hemicelluloses, and lignin, thereby cleaving the hydrogen bond networks of the cell wall components. Casting and natural evaporation caused the reassembling of the three components into the corresponding films. These findings provide a new strategy to produce biomass-based plastics and paper without the use of petroleum-derived polymers and lignin degradation under harsh conditions.
Materials and methods
Materials and chemicals
Eucalyptus (Eucalyptus globulus), Japanese cedar (Cryptomeria japonica), Japanese beech (Fagus crenata), Japanese cypress (Chamaecyparis obtuse), Japanese red pine (Pinus densifora), and moso bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis) were Willy-milled and used without removal of extractives. Sugarcane bagasse, rice fir, and wheat bran were used without pre-extraction or mechanical grinding. Formic acid (98–100%) was purchased from Nacalai Tesque Co. (Japan). Lignin dimer {1-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-2-(2-methoxyphenoxy)-1,3-propanediol}, xylan, and cellobiose were purchased from Fujifilm Wako Co., Sigma-Aldrich, and TCI, respectively.Film formation from woody sawdust
Three different sizes of sawdust from Eucalyptus, Japanese cedar sapwood and heartwood were separated by different apertures of an electric sieve (Nitto electric sieve ANF-30, Japan): 1.05–355, 355–500, and 500–1000 μm. The separated sawdust of Eucalyptus and Japanese cedar, Willy-milled wood powder of Japanese cedar (Yoshino), Japanese beech, Japanese cypress, Japanese red pine, and bamboo, and dried materials of sugarcane bagasse, rice fir, and wheat bran (100 mg each) were added in 10 ml of 80% (v/v) formic acid. The mixture was depressurised in a desiccator at −0.1 MPa for 30 min and stirred at 400 rpm in an oil at different dissolving temperatures of 30–90 °C for 7 days. The temperatures are described in Fig. S1a (ESI†) in detail. The dissolved solution was cast onto an OPP sheet (Fuji Pack Co. Ltd., 40 μm × 900 mm × 30 m, Japan), which was adjusted to fit in the polystyrene Petri dish (diameter 8.5 cm) and dried overnight in a fume hood with a Petri dish lid. The films were then peeled from the OPP sheet after drying. The formed films inserted between weighing papers were placed in a plastic bag and kept at room temperature until they were used.Measurement of whiteness and transmittance degrees
Biomass film whiteness was measured at five points of the film using a CR-14 Whiteness Index colour reader (Minolta Co. Ltd, Japan). Ultraviolet-visible absorption spectra of the films were recorded by scanning from 220 to 800 nm using a UV-2700 UV-VIS Spectrometer (Shimadzu Co. Ltd, Japan). The transmittance values at 800 nm were calculated from the measurement of five points in each film.Scanning electron microscopy (SEM)
SEM images of the biomass films with 355–500 mm thickness from Eucalyptus and Japanese cedar heartwood were acquired using a VE-9800 3D real surface view microscope (Keyence Corporation, Japan) after gold coating. Vertical cross-sections of the biomass films from Eucalyptus, Japanese cedar, Japanese beech, sugarcane bagasse, and wheat bran were platina-coated and subjected to SEM analysis using a Schottky field emission scanning electron microscope (SU5000, Hitachi, Japan).Mechanical tests
Wood solutions from the 355–500 μm particles of Eucalyptus, Japanese cedar sapwood and heartwood; powder of Japanese beech; and dried materials of sugarcane bagasse and wheat bran (each 100 mg) were cast onto the OPP sheet.The formed films were stored overnight at 23 °C and 50% humidity and then punched into the dumbbell mould using a Super Dumbbell Cutter (Model: SDMP-1000, Dumbbell Co. Ltd., Japan). The tensile strength of the punched dumbbell samples was determined by stretching them at 2 mm min−1 with Universal Testing Instruments (Tensilon RTG B10, A & D Company, Japan). While the dynamic viscoelasticity of the films was measured by RSA G2 (TA Instruments-Waters LLC, USA), dynamic mechanical analysis (DMA) was performed under a N2 atmosphere at 10 Hz with 0.05% strain by increasing the temperature from −30 °C to 300 °C at 5 °C min−1. The formed films were prepared for five pieces to perform mechanical tests and the average was calculated.
Separation of 2MeTHF, aqueous, and precipitate fractions
One gram of sawdust from Eucalyptus and Japanese cedar heartwood (355–500 μm) was added into 100 ml of 80% (v/v) formic acid, depressed in a desiccator at −0.1 MPa for 30 min, and stirred in an oil bath at dissolving temperatures of 30 °C, 40 °C, 50 °C, and 60 °C for 7 days. The dissolved solution was cast onto the OPP sheet with 10 layers of double-sided tape to adjust the size to 5.5 × 4.0 cm in the polyethylene Petri dish (diameter 8.5 cm) and dried overnight in a fume hood with a lid. The formed films (total weight 600 mg, 24–30 pieces) were redissolved in 10 ml of formic acid (98–100%) and stirred overnight at room temperature; 20 ml of 2-methyltetraforan (2MeTHF) and 80 ml of Milli-Q water were added to 10 ml of the dissolved film solution (dissolution solution![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 2MeTHF
2MeTHF![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) H2O = 1
H2O = 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 2
2![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 8). The mixture was vortexed, divided into four 50 ml falcon tubes, and centrifuged at 12
8). The mixture was vortexed, divided into four 50 ml falcon tubes, and centrifuged at 12![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 000 g for 20 min to yield phase-partitioned fractions (Fig. S3c, ESI†).
000 g for 20 min to yield phase-partitioned fractions (Fig. S3c, ESI†).
Preparation of authentic formylated standards
A phenolic β-O-4 lignin dimer model compound (guaiacylglycerol-β-guaiacyl ether), xylan, and cellobiose (50 mg each) were added separately to 5 ml of 80% aq. formic acid and stirred for 7 days. The mixed solution was dried by blowing N2 gas.NMR analyses
The dried 2MeTHF and aqueous fractions (10 mg each) were dissolved in 0.5 ml of DMSO-d6 and 0.5 ml of DMSO-d6 containing 10% (v/v) D2O, respectively. The aqueous fraction in DMSO-d6/D2O was sonicated for 15 min. The dried precipitate fraction was ball-milled under a N2 atmosphere with 90 cycles of 1 min milling at 550 rpm and 1 min pause using a planetary mono mill PULVERISETTE 6 (Fritsch Japan Co., Ltd, Japan) to suppress heat increase. The ball-milled precipitate (50 mg) was resuspended in a 0.5 ml mixture of DMSO-d6 and pyridine-d5 (4![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1, v/v) and sonicated for 3 h in an NMR tube. NMR spectra were recorded at 298 K on a Bruker AVANCE III HD 600 spectrometer equipped with a cryogenic probe and Z gradient (Brucker BioSpin, USA). The 2D 1H–13C HSQC, edited-HSQC, HMBC, and 3D TOCSY–HSQC spectra were recorded using Bruker standard pulse programmes (hsqcetgpsisp2.2, hsqcedetgpsp.3, hmbcgplpndqf, and mlevhsqcetgp3d, respectively). The HMBC experiment was optimised for a long-range coupling constant of 5 or 8 Hz. The TOCSY–HSQC experiment was acquired with a 60-ms mixing time. NMR data were processed with TopSpin (version 3.5) or Poky.13 The 1H and 13C chemical shifts were calibrated with the signal of DMSO (δH = 2.49 ppm, δC = 39.6 ppm).
1, v/v) and sonicated for 3 h in an NMR tube. NMR spectra were recorded at 298 K on a Bruker AVANCE III HD 600 spectrometer equipped with a cryogenic probe and Z gradient (Brucker BioSpin, USA). The 2D 1H–13C HSQC, edited-HSQC, HMBC, and 3D TOCSY–HSQC spectra were recorded using Bruker standard pulse programmes (hsqcetgpsisp2.2, hsqcedetgpsp.3, hmbcgplpndqf, and mlevhsqcetgp3d, respectively). The HMBC experiment was optimised for a long-range coupling constant of 5 or 8 Hz. The TOCSY–HSQC experiment was acquired with a 60-ms mixing time. NMR data were processed with TopSpin (version 3.5) or Poky.13 The 1H and 13C chemical shifts were calibrated with the signal of DMSO (δH = 2.49 ppm, δC = 39.6 ppm).
Results and discussion
Morphological and mechanical properties of transparent and opaque films
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) was used to analyse the microstructures of the transparent film from Eucalyptus and those of the opaque films from Japanese cedar sapwood and heartwood. While the transparent Eucalyptus film prepared at 50 °C exhibited a smooth surface on which cellulose microfibrils were filled with the dissolved components’ matrix (Fig. 2(a) and (b)), its vertical cross-section revealed void-free, tightly stacked layers (Fig. 2(c)). In contrast, the SEM image of the film formed from Japanese cedar heartwood prepared at 50 °C revealed a rough surface (Fig. 2(d)), and the vertical cross-section showed many voids between the layers (Fig. 2(e)).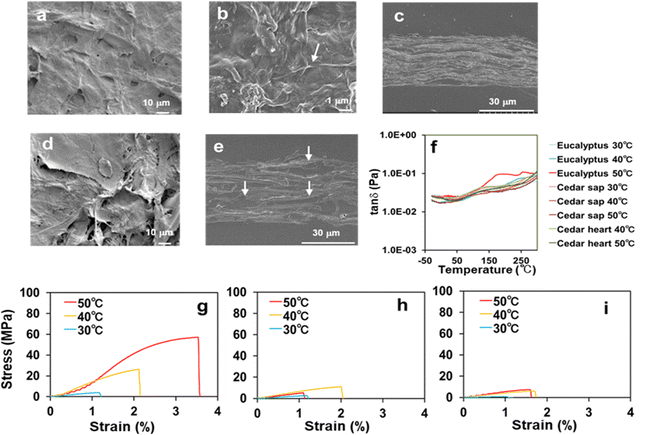 | ||
Fig. 2 Morphological and mechanical properties of transparent and opaque films formed from Eucalyptus and Japanese cedar. (a) SEM image of the Eucalyptus film at a dissolving temperature of 50 °C showed a smooth surface. (b) Magnified SEM image of the film from Eucalyptus at 50 °C. The arrow shows cellulose microfibers. (c) Vertical cross-section of the film prepared by dissolution of Eucalyptus at 50 °C. SEM image showed void-free, tightly stacked layers. (d) SEM image of the film prepared by dissolution of Japanese cedar heartwood at 50 °C. SEM image showed a rough surface of the film. (e) Vertical cross-section of the film prepared by dissolution of Japanese cedar heartwood at 50 °C. The photo showed the layers with voids and embedding agents (arrows). (f) Comparison of glass transition temperatures of the films from Eucalyptus, Japanese cedar sapwood and heartwood under dissolving temperatures of 30–50 °C by DMA. The marked inflection point of tan![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) δ was observed at 177 °C and higher temperatures for the film from Eucalyptus, which was prepared by dissolving at 50 °C (red), whereas those from the other films were constant levels. Comparison of tensile stress–strain curves from the films of Eucalyptus (g), Japanese cedar sapwood (h) and heartwood (i) under dissolving temperatures of 30–50 °C. The stress–strain values are presented in Table 1. δ was observed at 177 °C and higher temperatures for the film from Eucalyptus, which was prepared by dissolving at 50 °C (red), whereas those from the other films were constant levels. Comparison of tensile stress–strain curves from the films of Eucalyptus (g), Japanese cedar sapwood (h) and heartwood (i) under dissolving temperatures of 30–50 °C. The stress–strain values are presented in Table 1. | ||
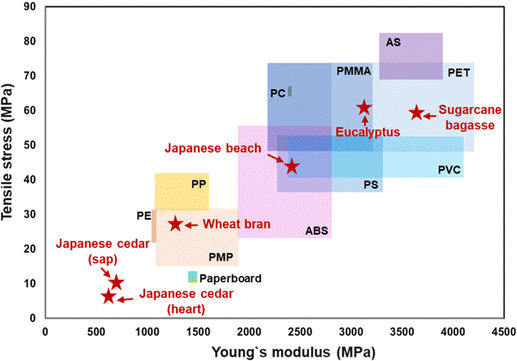 | ||
| Fig. 4 Comparison of Young's modulus and tensile stress between general-purpose plastics and the biomass films formed from Eucalyptus, Japanese cedar (sap- and heartwood), Japanese beech, wheat bran, and sugarcane bagasse. The data for plastics were obtained from plastic processing technology companies of KDA CORP.14 and SANPLATEC CORP.16 | ||
Glass transition temperatures (Tg) of the films from Eucalyptus, Japanese cedar sapwood and heartwood at dissolving temperatures (30–50 °C) were measured by dynamic mechanical analysis (DMA) (Fig. 2(f) and Table 1). The Tg value of the Eucalyptus film prepared at 50 °C was 177 °C with the peak of loss tangent (tan![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) δ, E′′/E′), which was close to that of cellulose acetate (180 °C). These results indicated that the transparent Eucalyptus film had plastic properties, whereas the opaque films from Japanese cedar were porous and characterized as paper-like sheets. Tensile testing was conducted to evaluate the mechanical properties of the three films prepared at each dissolving temperature between 30 °C and 50 °C (Fig. 2(g–i) and Table 1). The Young's modulus and tensile strength of the Eucalyptus film prepared at 50 °C were 3096.7 and 60.98 MPa, respectively, which were comparable to those of acrylic resin (PMMA) (2200–3200 and 48–73 MPa)14 and polyethylene terephthalate (PET) (2800–4200 and 48–73 MPa),14 whereas those of Japanese cedar films were ≤685.7 and <10.61 MPa, respectively, for all specimens prepared from 30 °C to 50 °C, and were comparable to those of paperboard at 1440 and 13 MPa, respectively15 (Table 1 and Fig. 4). The maximum strain values in Eucalyptus and Japanese cedar were 3.2% and 1.9%, respectively, which were comparable to those of copy paper, paperboard, regenerated cellulose, and cellulose (2–7%).15,16 Folding these Eucalyptus and Japanese cedar films was sufficient to create origami (Fig. 1).
δ, E′′/E′), which was close to that of cellulose acetate (180 °C). These results indicated that the transparent Eucalyptus film had plastic properties, whereas the opaque films from Japanese cedar were porous and characterized as paper-like sheets. Tensile testing was conducted to evaluate the mechanical properties of the three films prepared at each dissolving temperature between 30 °C and 50 °C (Fig. 2(g–i) and Table 1). The Young's modulus and tensile strength of the Eucalyptus film prepared at 50 °C were 3096.7 and 60.98 MPa, respectively, which were comparable to those of acrylic resin (PMMA) (2200–3200 and 48–73 MPa)14 and polyethylene terephthalate (PET) (2800–4200 and 48–73 MPa),14 whereas those of Japanese cedar films were ≤685.7 and <10.61 MPa, respectively, for all specimens prepared from 30 °C to 50 °C, and were comparable to those of paperboard at 1440 and 13 MPa, respectively15 (Table 1 and Fig. 4). The maximum strain values in Eucalyptus and Japanese cedar were 3.2% and 1.9%, respectively, which were comparable to those of copy paper, paperboard, regenerated cellulose, and cellulose (2–7%).15,16 Folding these Eucalyptus and Japanese cedar films was sufficient to create origami (Fig. 1).
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) δ) of films from Eucalyptus, Japanese cedar sapwood and heartwood at dissolving temperatures of 30 °C to 50 °C. The values are averages of five replicates. Standard deviations are in Table S1 (ESI)
δ) of films from Eucalyptus, Japanese cedar sapwood and heartwood at dissolving temperatures of 30 °C to 50 °C. The values are averages of five replicates. Standard deviations are in Table S1 (ESI)
| Wood powder | Temperature (°C) | Density (g cm−3) | Stress (Mpa) | Strain (%) | Young's modulus (Mpa) | E′ | E′′ | tanδ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Tg/°C) | ||||||||
| Eucalyptus | 30 | 0.37 | 3.09 | 1.16 | 334.75 | 230 | 143 | n.d. |
| 40 | 0.56 | 31.15 | 2.73 | 1745.84 | 239 | 243 | n.d. | |
| 50 | 0.66 | 60.98 | 3.21 | 3096.73 | 118 | 175 | 177 | |
| Japanese cedar (sapwood) | 30 | 0.54 | 2.17 | 1.19 | 209.93 | 245 | 265 | n.d. |
| 40 | 0.52 | 10.61 | 1.94 | 685.74 | 251 | n.d. | n.d. | |
| 50 | 0.50 | 5.49 | 1.35 | 475.71 | 261 | 118 | n.d. | |
| Japanese cedar (heartwood) | 30 | 0.23 | 0.59 | 1.10 | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. |
| 40 | 0.50 | 6.10 | 1.68 | 453.45 | 269 | 124 | n.d. | |
| 50 | 0.64 | 7.15 | 1.41 | 614.81 | 276 | 114 | n.d. | |
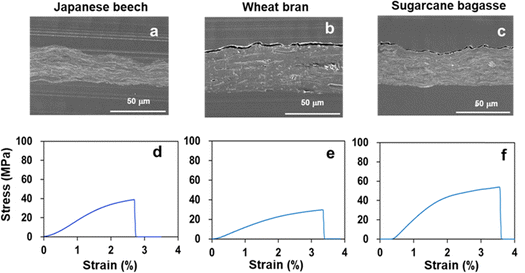
The microstructural and mechanical properties of transparent films from Japanese beech, wheat bran, and sugarcane bagasse were compared. The SEM image of the vertical cross-section of the films (Fig. 3(a–c)) revealed void-free, tightly stacked layers, a characteristic of plastic-like transparent films. The Tg values of the transparent films from Japanese beech, wheat bran, and sugarcane bagasse were 248 °C, 171 °C, and 177 °C, respectively, indicating their plastic-like properties (Table S2, ESI†). The Young's modulus and tensile strength of Japanese beech were comparable to those of poly vinyl chloride (PVC) (2400–4100 and 41–51 MPa)14 or poly styrene (PS) (2200–2300 and 36–52 MPa)14 and sugarcane bagasse films were PET (Fig. 4 and Table S2, ESI†). The Young's modulus and tensile strength of the wheat bran film were comparable to those of polymethyl pentene (PMP) (1100–1900 and 15–31 MPa)19 (Fig. 4 and Table S2, ESI†). The maximum strain values of Japanese beech, wheat bran, and sugarcane bagasse films were 2.6%, 3.3%, and 3.3% (Table S2, ESI†), which were comparable to those of copy paper, paperboard, regenerated cellulose, and cellulose (2–7%).12,14
Thus, the formic acid dissolving method converts wood sawdust, chips, and agricultural wastes into paper and plastic-like films without the use of added catalysts and synthetic resins. The reassembled films from hardwood and sugarcane bagasse provides the biomass films with high mechanical strength comparable to general-purpose plastics.
Characterization of the optical properties of biomass films produced from wood and agricultural residues
The effects of dissolving temperature on the optical properties of biomass films were investigated. Different particle sizes of wood sawdust of Eucalyptus and Japanese cedar were dissolved at temperatures between 30 °C and 90 °C (Fig. 5 and Fig. S1, ESI†). The Eucalyptus sawdust film after dissolution at 50 °C and 60 °C was transparent, whereas the films of sapwood and heartwood of Japanese cedar prepared at 40 °C to 60 °C and the Eucalyptus films at 40 °C were opaque, regardless of the particle size (Fig. 5a and Fig. S1a (ESI†); red box). These results indicate that film formation at dissolving temperatures of 40 °C and 50 °C is critical for the dissolution and formation of transparent films.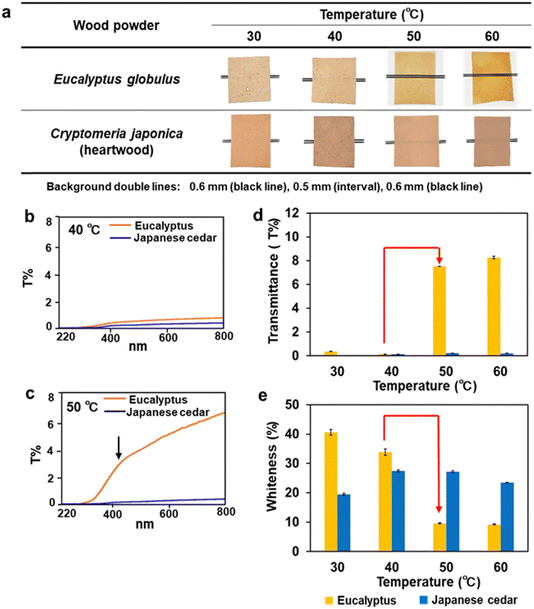 | ||
| Fig. 5 Formation and characterization of transparent and opaque films from Eucalyptus and Japanese cedar heartwood. (a) Film formation from Eucalyptus and Japanese cedar sawdust with a particle size of 355–500 μm at dissolving temperatures of 30–60 °C. (b) Transmittance spectra of the opaque films from Eucalyptus and Japanese cedar prepared by dissolution at 40 °C. (c) Transmittance spectrum of the transparent Eucalyptus film prepared by dissolution at 50 °C. (d) Transmittance of the Eucalyptus films prepared by dissolution at 50 °C and 60 °C (Table S3, ESI†). (e) Whiteness degrees of the opaque films from Eucalyptus at 30 °C and 40 °C and Japanese cedar at 30–60 °C (Table S4, ESI†). | ||
To characterize the optical properties of films, transmittance and whiteness degrees were measured. The transmittance spectra of the films made from Eucalyptus and heartwood and sapwood of Japanese cedar after dissolution at 30–90 °C, were monitored (Fig. 5(b) and (c) and Fig. S1(b), ESI†). The transmittance at 800 nm of the Eucalyptus films produced by dissolution at 50 °C and 60 °C ranged from 7.5 to 9.9 T%. The spectra revealed that UV light was not transmitted through the film, whereas visible light passed through as the wavelength increased. In contrast, the transmittance of opaque films was below 0.56 T%, resulting from partially dissolved wood tissues. The effect of dissolving temperatures on the transmittance and whiteness levels is shown in Fig. 5(d) and (e), together with Fig. S2 and Tables S3, S4 (ESI†). The Eucalyptus transparent films prepared at 50 °C with the 355–500 μm particle size showed a 50-fold increase in transmittance levels and a 3.5-fold decrease in whiteness levels compared with those of the dissolving temperatures at 40 °C, whereas the opaque Japanese cedar films showed extremely low transmittance and constant levels of whiteness for all dissolving temperatures and wood particle sizes used.
Opaque films from Japanese cedar had a rough surface which causes light scattering and decreases transparency, while Eucalyptus films with low porosity had high transparency with less light scattering. This is because hemicelluloses and lignin surrounding cellulose microfibrils in Eucalyptus are solubilized to a higher extent than Japanese cedar and large bundles composed of cellulose microfibrils associated with insoluble components remain in Japanese cedar. The lower disintegration in the softwood makes the physical barrier when forming the film by casting and natural evaporation. Mechanical compression of the Japanese cedar film after evaporation may decrease the porosity and light scattering, but the transmittance and physical properties of the film will not reach the level of the Eucalyptus film.
Film formation via dissolution in formic acid was examined using nine plant bioresources: rice fir, Japanese beech, Japanese cypress, Japanese red pine, wheat bran, sugarcane bagasse, bamboo, and sapwood and heartwood of Japanese cedar wood (Fig. 6 and Table S5, ESI†). Except for rice fir and Japanese cedar, transparent films were obtained, as observed in Eucalyptus wood. The wood's transparent films exhibited transmittance spectra with high UV light absorption below 400 nm and an upwardly sloping graph starting from 320 nm. Similar transmittance spectra were recorded for films made from sugarcane bagasse and bamboo, whereas the film made from wheat bran, which contains less lignin content,17,18 was transparent to UV light, indicating that lignin in the film absorbed UV light. Rice fir opaque films achieved the same degree of whiteness as Japanese cedar films.
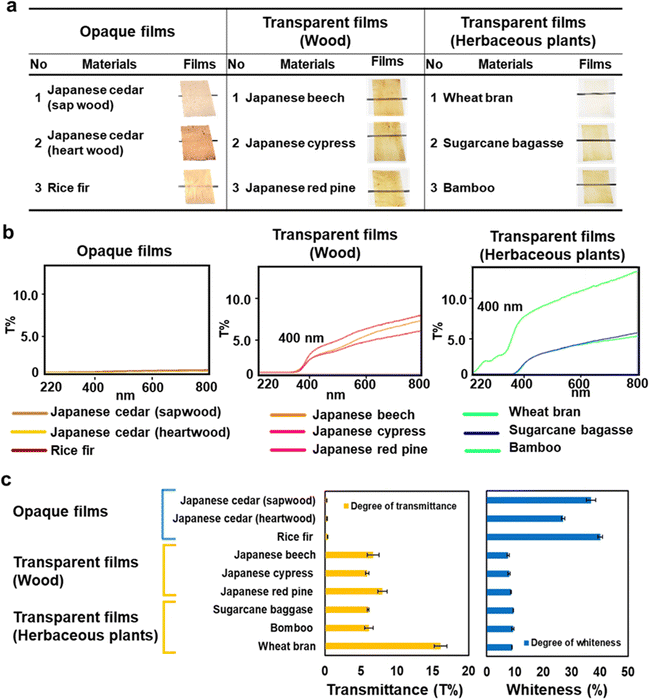 | ||
| Fig. 6 Optical characteristics of biomass films from various plant resources. (a) The films formed from sapwood and heartwood of Japanese cedar, rice fir, Japanese beech, Japanese cypress, Japanese red pine, and the herbaceous plants of wheat bran, sugarcane bagasse, and bamboo. (b) Transmittance spectra from 220 to 800 nm of the biomass films. (c) Transmittance at 800 nm and whiteness of the biomass films from nine different resources. The transmittance and whiteness of the films are summarized in Table S5 (ESI†). | ||
Formic acid, the simplest organic acid has the properties of both a carboxylic acid and an aldehyde. During the wood dissolution process and a storage of the film for over a year, colorization or discoloration due to the formyl group was not observed. After casting the wood solution in a fume hood, unreacted volatile formic acid was evaporated, and no pungent odour was detected from the formed film.
Dissolution mechanism of the wood sawdust and “plastic-like wood film”
To understand the mechanism underlying the dissolution and formation of transparent and opaque films, 1H–13C HSQC and HMBC NMR of Eucalyptus and Japanese cedar heartwood films prepared by dissolution between 30 °C and 60 °C were recorded (Fig. 7 and Fig. S4, Tables S6, S7, ESI†). Formylation at the α and/or γ positions of β-O-4 and the γ position of β-5 of lignin linkages, the 6th position of the glucose residue in cellulose, and the 3rd position of the xylose residue in xylan was demonstrated. The formylation of these three components significantly contributes to the disintegration of cell walls by breaking intermolecular and intramolecular noncovalent hydrogen bond cross-linkages.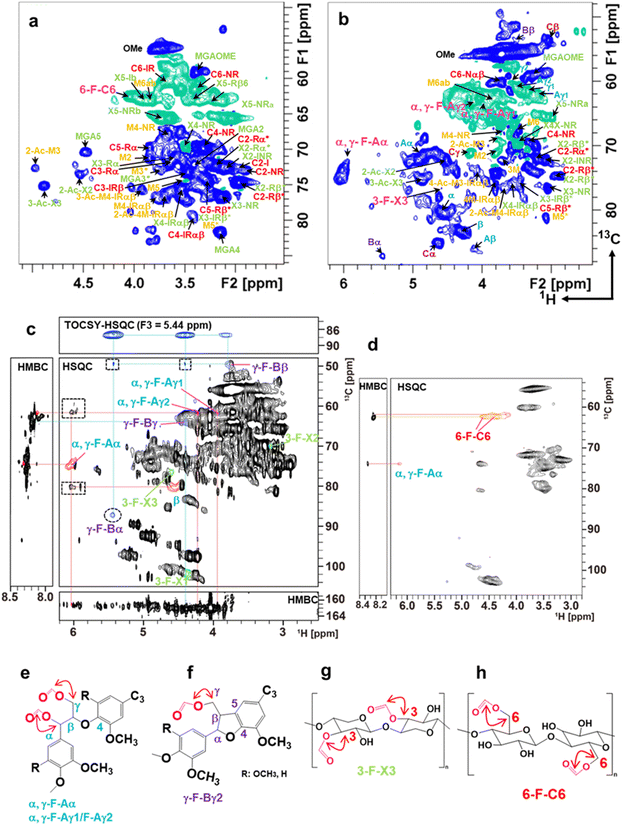 | ||
| Fig. 7 Aliphatic sidechain region of 2D 1H–13C HSQC spectra and 2D 1H–13C HMBC and 3D TOCSY–HSQC NMR of the fractions from the Eucalyptus film formed at 50 °C. (a) Aliphatic sidechain region of 2D 1H–13C HSQC spectrum from the aqueous fraction characterized as the polysaccharide-rich fraction. The signals belonging to cellulose, glucuronoxylan, glucomannan, and formylated compounds were presented in red, green, yellow/red, and pink, respectively. (b) Aliphatic sidechain region of the 2D 1H–13C HSQC spectrum from the 2MeTHF fraction characterized as the lignin-rich fraction. The lignin linkages of β-O-4, β–β, β-5, and lignin–carbohydrate complex (LCC) are shown in blue, brown, purple, and yellow, respectively. Free β-O-4 lignin units are distinguished as Aα and Aβ to those of LCC as α and β. The mannose unit of glucomannan was presented as 1 M to M6/M6′ in yellow. The signal assignment is summarized in Tables S6 and S7 (ESI†). (c) NMR spectra of the aliphatic region of the lignin-rich-2MeTHF fraction. Signals from the formylated α and γ positions of the β-O-4 unit are labelled as α, γ-F-Aα and α, γ-F-Aγ1/F-Aγ2, respectively. Those from the γ position in β-5 and 3 positions of xylose units in xylan are labelled as γ-F-Bα/γ-F-Bβ and 3-F-X3, respectively. Signals in the dot squares and circles in the HSQC box are the inter-unit correlations of formylated β-O-4 and β-5, respectively. The 3D TOCSY–HSQC spectrum is the F1–F2 plane sliced at F3 = 5.44 ppm (the proton resonance of β-5α). Signals of β-O-4, β-5, and xylose units are shown in blue, purple, and green, respectively. (d) Aliphatic region of 2D 1H–13C HSQC and HMBC spectra of the precipitate. The signal of formylated 6-OH of glucose residues in cellulose is labelled 6-F-C6. The α position of the β-O-4 unit in lignin is labelled as α, γ-F-Aα. Correlation of formyl units with α and γ positions in β-O-4 (e), γ position in β-5 (f), the 3rd position of the xylose residue in xylan (g), the 6th position of the glucose residue in cellulose (h). | ||
The biomass films of Eucalyptus and Japanese cedar were insoluble in acetone, chloroform, methanol, THF, Me-THF and water but soluble in formic acid and DMSO, showing the resistance against a wide range of conventional organic solvents (Fig. S3(a) and (b), ESI†).
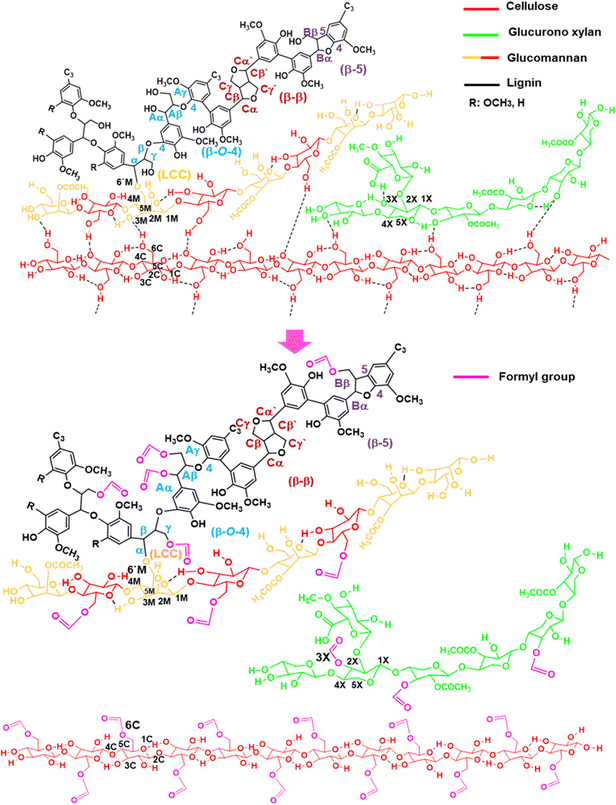
After solubilizing the biomass films in formic acid, distilled water and 2Me-THF were added to the solution and separated into three phases—a lignin-rich 2Me-THF layer, a soluble carbohydrate-rich aqueous layer, and a cellulose-rich precipitate—by vigorous shaking and subsequent centrifugation (Fig. S3(c), ESI†). Because formic acid was incorporated into the wood components, the total recoveries of films prepared at 50 °C from Eucalyptus (105%) and Japanese cedar heartwood (118%) exceeded 100% (Fig. S3(d), ESI†). The structures of wood components in lignin-rich 2MeTHF and carbohydrate-rich aqueous fractions from Eucalyptus and Japanese cedar heartwood were analysed by 1H–13C HSQC NMR spectra (Fig. 7(a) and (b) and Fig. S4(a), (b), Tables S6, S7, ESI†). Signals of the main wood components in Eucalyptus, a hardwood, were assigned to lignin with syringyl and guaicyl nuclei, glucuronoxylan, glucomannan, and cellulose (Scheme 1), whereas those in Japanese cedar, a softwood, were assigned to guaicyl lignin, arabinoglucuronoxylan, galactoglucomannan, and cellulose19–23 (Fig. S4(c), ESI†). As the signal of lignin–carbohydrate linkages, signals from ether linkages between the α-position of the β-O-4 lignin subunit (α, δH/δC = 4.55 ppm/80.20 ppm) (blue) and the 6th position of the mannose residue (M6′, δH/δC = 3.49 ppm/67.83 ppm) (yellow)23–26 in glucomannan were observed in the HSQC NMR spectrum of the 2 MeTHF fraction. The C–H signals of lignin–carbohydrate linkages differed from the signals of the α position in the β-O-4 unit having an α-OH group (δH/δC = 4.86 ppm/71.51 ppm) (Aα, blue) and a non-esterified mannose residue (M6ab, δH/δC = 3.84 ppm/62.66 ppm) (yellow) (Fig. 7(b) and Fig. S4(b), Tables S6, S7, ESI†).
To elucidate the structures incorporating formic acid, 2D 1H–13C HSQC and HMBC spectra of the 2MeTHF and aqueous fractions of the Eucalyptus film prepared at 50 °C were recorded, together with the authentic standards of the formylated lignin dimer model compound, cellobiose, and xylan. Chemical shifts in formylated Aα (α, γ-F-Aα) and Aγ1/γ2 (α, γ-F-Aγ1/Φ−Aγ2) positions of the β-O-4 substructure were assigned to δH/δC = 6.02/73.69 ppm, 3.92/63.27 ppm, the 4.18/63.07 ppm, respectively. The formylated 6th position of the glucose residue (6-F-C6) in cellulose was assigned to δH/δC = 4.04/62.48 ppm. The formylated 3rd position of the xylose residue (3-F-X3) in xylan was assigned to δH/δC = 4.61/76.72 ppm (Fig. 7 and Fig. S4, Tables S6, S7, ESI†). To obtain clear evidence for the formylated structures, the 2Me-THF and precipitate fractions from the Eucalyptus film prepared at 50 °C were analysed by 2D 1H–13C HSQC, edited-HSQC, HMBC, and 3D-TOCSY–HSQC spectroscopy (Fig. 7(c)). For the 2Me-THF fraction, intra-unit correlations of α, γ-F-Aα and α, γ-F-Aγ1/F-Aγ2 and correlations from α, γ-F-Aα and α, γ-F-Aγ1/F-Aγ2 to the formyl group were observed in the HSQC and HMBC spectra (Fig. 7(c) and (e)). These results demonstrated that lignin β-O-4 substructures were formylated at both α and γ positions. Furthermore, the signals of formylated β-5 in lignin were also assigned through the HMBC and 3D TOCSY–HSQC spectra. A downfield shift in β and γ2 proton due to formylation at the γ position of the β-5 substructure was observed (Fig. 7(c) and (f)). The HSQC signal at position 3-F-X3 was observed in xylan structural analysis (Fig. 7(c) and (g)). Cellulose in the precipitate fraction was analysed, and a correlation between 6-F-C6 and the formyl proton was found using HMBC, revealing that the 6th position of glucose in cellulose was formylated (Fig. 7(d) and (h)).
By the experiments of titration and IR, the formylation of carboxylic acids in wood was roughly estimated to be one formyl group in several constituent units of carbohydrates and lignin. The degree of formylation in the wood components was estimated to be less than 1%. Due to the equilibrium between dehydration and hydrolysis, full formylation of all the hydroxyl groups in wood did not occur.
Furthermore, the signals of cellulose, hemicelluloses, and lignin in the fractions separated from Eucalyptus and Japanese cedar wood films prepared by dissolution at 30–60 °C were semi-quantified by HSQC NMR (Fig. S5 and Tables S6, S7, ESI†). Xylan signal intensities increased as the dissolving temperatures (30–40 °C) decreased, whereas those of cellulose units increased at higher temperatures (50–60 °C). While cellulose and xylan showed no significant differences between Eucalyptus and Japanese cedar in terms of signal intensity, Eucalyptus had significantly stronger lignin signal intensities than Japanese cedar.
The following is the proposed mechanism underlying Eucalyptus wood sawdust dissolution in formic acid (Scheme 1). Wood sawdust was dissolved in formic acid at 50 °C. In Eucalyptus wood dissolution, the α and γ positions of the β-O-4 substructure of lignin, the 3rd position of the xylose residue in xylan chains, and the 6th position of the glucose residue in cellulose were formylated (1), resulting in the cleavage of the cross-linkages of hydrogen bonds among cellulose, hemicelluloses, and lignin10,27,28 (2). In addition, the O-glycosidic bonds in cellulose and hemicelluloses were partially hydrolysed (3). The partially depolymerized hemicelluloses were liberated, penetrating amorphized cellulose gaps to form smooth films (4). Furthermore, lignin in Japanese cedar was formylated at the α and γ positions of the β-O-4 substructure but less substituted than Eucalyptus (Fig. S5 and Tables S6, S7, ESI†). Cellulose and hemicelluloses were partially hydrolysed, as observed in Eucalyptus.
New wood-based materials have recently been reported.29–31 For instance, healed wood from low-value wood for crack repair32 and densified wood from bulk wood with a 11.5- and 10-fold increase in strength and toughness, respectively33 The biomass film described in this study was produced under ultra-mild conditions at 50 °C under ambient pressure using woody biomass and formic acid, which can be produced by reacting CO2 and H2, the free radical reaction of oxalic acid,11 or light-driven C–H oxygenation of methane from fermented biomass.34 Cellulose acetate has been industrially produced much more widely than cellulose formate. The lower production cost of acetic acid and higher suitability of cellulose acetate for various applications such as liquid crystals, photo and X-ray films, coatings, fabrics and filters may be the major factors for the different marketability. In contrast to the existing applications of cellulose acetates, this study breaks new ground of formylated lignocelluloses produced by the disintegration and reassembly of woody and agricultural biomass using formic acid.
As mentioned above, this research is a method of producing new materials by using all wood components, and the purpose is different from that of the pulping method that involves the use of cellulose by depolymerization of lignin under harsh conditions. To further increase the feasibility of the new process, optimization of the process including an increase in the solid to liquid ratio during solubilization and formic acid recovery based on the analysis of product properties and LCA will be carried out.
Cellulose, hemicellulose, lignin, and LCCs are tightly packed in plant cell walls through hydrogen bonds and other noncovalent interactions, including van der Waals force, hydrophobic interactions, and π–π stacking. Stirring wood in formic acid breaks these interactions as a formyl group is incorporated in all these components. Evaporation of formic acid induced a rearrangement of the components by retrieving the noncovalent bonds among cell wall components, which originally exhibited high affinity, thereby producing physically strong biomass films.
Biomass films, a renewable resource that is free of synthetic polymers and adhesives, have many potential uses, including in packaging, moulding, and coating.
Conclusions
Current plasticized wood products depend on the mass consumption of petroleum-derived chemicals such as wood polyolefin composites which are widely used for decking and flooring materials. The mixture of petroleum-derived polymers and woody biomass creates a further problem in reusing the carbon resources. The production of high-quality paper and dissolving the pulp requires harsh conditions using sulphur to depolymerize the recalcitrant lignin. In this study, materials with paper- and plastic-like properties were produced simply by dissolving wood sawdust/chips in formic acid under ultra-mild conditions at 50 °C. The wood solution resulted in the formation of a transparent plastic-like film with a glass transition point of 177 °C (Eucalyptus) or opaque paper-like materials (Japanese cedar). In addition, transparent films were made from various non-wood biomass such as sugarcane bagasse and wheat bran. Two-fold helix xylan is bound to cellulose microfibrils mainly by hydrogen bonds, and three-fold helix xylan dissociates from cellulose microfibrils, forming crosslinks of multiple cellulose microfibrils.35 Galactoglucomannan also closely associates with cellulose microfibrils to crosslink the multiple cellulose microfibrils. These hemicellulose chains are covalently linked to lignin, forming LCCs. Lignin is packed into these networks to strengthen the cell wall structure with the aid of LCC as a compatibilizer. 2D and 3D NMR spectra revealed that the mixing of wood with formic acid in the absence of added catalysts caused the formylation of cellulose, hemicelluloses, and lignin, thereby cleaving the cross-linkages of hydrogen bonds to break the intermolecular and intramolecular networks of these three components, accompanied by partial hydrolysis of polysaccharides. The proposed method is extremely benign and straightforward, requiring neither sulphur nor alkali at any production stage. Neither lignin degradation under harsh conditions nor petroleum-derived polymers were required in the material manufacturing process. Overall, these findings provide new insights into the production of biomass-based plastics and paper by rearranging the noncovalent bonds of cell wall components.Author contributions
N. K., T. H., K. K. (Daicel Co.), and T. W. designed research. N. K. performed dissolution, film formation, measurement of transmittance and whiteness degrees, SEM and 1H–13C HSQC and HMBC NMR analyses of Eucalyptus and Japanese cedar films at different dissolving temperatures. T. H. obtained the cross-sectional and magnified SEM images, mechanical tests, and DMA. K. K. (Kyoto University) and M. K. performed the 1H–13C HSQC, HMBC and TOCSY experiments and analyses of the Eucalyptus film at 50 °C. N. K. and T. W. wrote the manuscript. K. K. (Kyoto University), M. K., T. H. and K. K. (Daicel Co.) revised the manuscript.Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the “Joint Usage/Research Program on Zero-Emission Energy Research”, Institute of Advanced Energy, Kyoto University (ZE2022A-16) and Mission 5-2 program from Research Institute for Sustainable Humanosphere, Kyoto University. This study was funded by Daicel Corporation.Notes and references
- G. Viglione, Nature, 2021, 593, 26–28 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Gjermundsen, A. Nummelin, D. Olivié, M. Bentsen, Ø. Seland and M. Schulz, Nat. Geosci., 2021, 14, 724–731 CrossRef CAS.
- Z. Akdogan and B. Guven, Environ. Pollut., 2019, 254(113011), 1–23 Search PubMed.
- R. Geyer, J. R. Jambeck and K. L. Law, Sci. Adv., 2017, 3, e1700782 CrossRef PubMed.
- Q. Zhang, E. G. Xu, J. Li, Q. Chen, L. ma, E. Y. Zeng and H. Shi, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2020, 54, 3740–3751 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. Iwata, H. Gan, A. Togo and Y. Fukata, Polym. J., 2021, 53, 221–238 CrossRef CAS.
- G. Gellerstedt, M. Ek and G. Henriksson, Pulp and Paper Chemistry and Technology, Paper Chemistry and Technology. de G, Berlin, Germany, 2016, vol. 3, p. 408. ISBN 978-3-11-048343-7 Search PubMed.
- S. Eero, Wood Chemistry Fundamentals and Applications, 2nd ed, Academic Press Inc, NY, USA, 1993, pp. 1–223 Search PubMed.
- H. Zhu, W. Luo, P. N. Ciesielski, Z. Fang, J. Y. Zhu, G. Henriksson, M. E. Himmel and L. Hu, Chem. Rev., 2016, 116, 9305–9374 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- B. M. Upton and A. M. Kasko, Chem. Rev., 2016, 116, 2275–2306 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Nishiwaki-Akine and T. Watanabe, Green Chem., 2014, 16, 3569–3579 RSC.
- Y. Nishiwaki-Akine, S. Kanazawa, T. Uneyama, K. Nitta, R. Yamamoto-Ikemoto and T. Watanabe, ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng., 2017, 5, 11536–11542 CrossRef CAS.
- W. Lee, M. Rahimi, Y. Lee and A. Chiu, Bioinformatics, 2021, 37(18), 3041–3042 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- KDA corporation, manufacturing technologies of plastic parts. Available from: https://www.kda1969.com/materials/pla_mate_pmma2.htm..
- T. Yokoyama, T. Odamura and K. Nakai, J. JSEM, 2007, 7, 35–41 Search PubMed.
- SUNPLATEC CORP., manufacturing technologies of plastic parts. Available from: https://www.sanplatec.co.jp/uploads/files/chemical-resistance/pla_busseihyou.pdf.
- Z. Merali, S. R. A. Collins, A. Elliston, D. R. Wilson, A. Käsper and K. W. Waldron, Biotechnol. Biofuels, 2015, 8, 23 CrossRef PubMed.
- M. E. F. Bergmans, G. Beldman, H. Gruppen and A. G. J. Voragen, J. Cereal Sci., 1996, 23, 235–245 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Kim and J. A. Ralph, RSC Adv., 2014, 4, 7549–7560 RSC.
- H. Kim and J. Ralph, Org. Biomol. Chem., 2010, 8, 576–591 RSC.
- J. Berglund, S. Azhar, M. Lawoko, M. Lindström, F. Vilaplana, J. Wohlert and G. Henriksson, Cellulose, 2019, 26, 2155–2175 CrossRef CAS.
- D. J. Yell, J. Ralph and C. R. Frihart, Holzforschung, 2011, 65, 131–143 Search PubMed.
- L. H. Campestrini, J. L. Silveira, M. E. Duarte, H. S. Koop and H. S. M. D. Noseda, Carbohydr. Polym., 2013, 94, 511–519 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Nishimura, A. Kamiya, T. Nagata, M. Katahira and T. Watanabe, Sci. Rep., 2018, 8, 6538 CrossRef PubMed.
- M. Lawoko, G. Henriksson and G. Gellerstedt, Biomacromolecules, 2005, 6, 3467 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- N. Giummarella, Y. Pu, A. J. Ragauskas and M. A. Lawoko, Green Chem., 2019, 21, 1573–1595 RSC.
- M. Åkerholm and L. Salmén, Polymer, 2001, 42, 963–969 CrossRef.
- K. H. Gardner and J. Blackwell, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1974, 343, 232–237 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. Li, X. Zhang, S. D. Lacey, R. Mi, X. Zhao, F. Jiang, J. Song, Z. Liu, G. Chen, J. Dai, Y. Yao, S. Das, R. Yang, R. M. Briber and L. Hu, Nat. Mater., 2019, 18, 608–613 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Luo, Z. Wang, L. Xu, A. C. Wang, K. Han, T. Jiang, Q. Lai, Y. Bai, W. Tang, F. R. Fan and Z. L. Wang, Nat. Commun., 2019, 10, 5147 CrossRef PubMed.
- X. Yang, S. K. Biswas, J. Han, S. Tanpichai, M. Li, C. Chen, S. Zhu, A. K. Das and H. Yano, Adv. Mater., 2021, 33, e2002264 CrossRef PubMed.
- X. Dong, W. Gan, Y. Shang, J. Tang, Y. Wang, Z. Cao, Y. Xie, J. Liu, L. Bai, J. Li and O. J. Rojas, Nat. Sustain., 2022, 5, 628–635 CrossRef.
- J. Song, C. Chen, S. Zhu, M. Zhu, J. Dai, U. Ra, Y. Li, Y. Kuang, Y. Li, N. Quispe, Y. Yao, A. Gong, U. H. Leiste, H. A. Bruck, J. Y. Zhu, A. Vellore, H. Li, M. L. Minus, Z. Jia, A. Martini, T. Li and L. Hu, Nature, 2018, 554, 224–228 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K. Ohkubo and K. Hirose, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2018, 57, 2126–2129 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Kirui, W. Zhao, F. Deligey, H. Yang, X. Kang, F. Mentink-Vigier and T. Wang, Nat. Commun., 2022, 13(538), 1–12 Search PubMed.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available. See DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/d3ma00789h |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2024 |