Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleCreative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported Licence
From green chemistry to biomedicine: the sustainable symphony of cobalt oxide nanoparticles
Annu
 *a,
Muskan Sahu
b,
Somesh Singh
b,
Satypal Prajapati
b,
Dinesh K. Verma
*b and
Dong Kil Shin
*a
*a,
Muskan Sahu
b,
Somesh Singh
b,
Satypal Prajapati
b,
Dinesh K. Verma
*b and
Dong Kil Shin
*a
aMaterials Laboratory, School of Mechanical Engineering, Yeungnam University, 280 Daehak-ro, Gyeongsan-si, Gyeongsanbuk-do 38541, Republic of Korea. E-mail: annuchem92@gmail.com; dkshin@yu.ac.kr
bDepartment of Chemistry, Prof. Rajendra Singh (Rajju Bhaiya) Institute of Physical Sciences for Study and Research, V.B.S. Purvanchal University, Jaunpur-222003, India. E-mail: dineshkv.rs.chy15@iitbhu.ac.in
First published on 17th October 2024
Abstract
Deciphering the importance of nanostructures in advanced technologies for a broad application spectrum has far-reaching implications for humans and the environment. Cost-effective, abundant cobalt oxide nanoparticles (NPs) are among the most attractive and extensively utilized materials in biomedical sciences due to their high chemical stability, and biocompatibility. However, the methods used to develop the NPs are hazardous for human health and the environment. This article precisely examines diverse green synthesis methods employing plant extracts and microbial sources, shedding light on their mechanism, and eco-friendly attributes with more emphasis on biocompatible properties accompanied by their challenges and avenues for further research. An in-depth analysis of the synthesized cobalt oxide NPs by various characterization techniques reveals their multifaceted functionalities including cytotoxicity, larvicidal, antileishmanial, hemolytic, anticoagulating, thrombolytic, anticancer and drug sensing abilities. This revelatory and visionary article helps researchers to contribute to advancing sustainable practices in nanomaterial synthesis and illustrates the potential of biogenically derived cobalt oxide NPs in fostering green and efficient technologies for biomedical applications.
1. Introduction
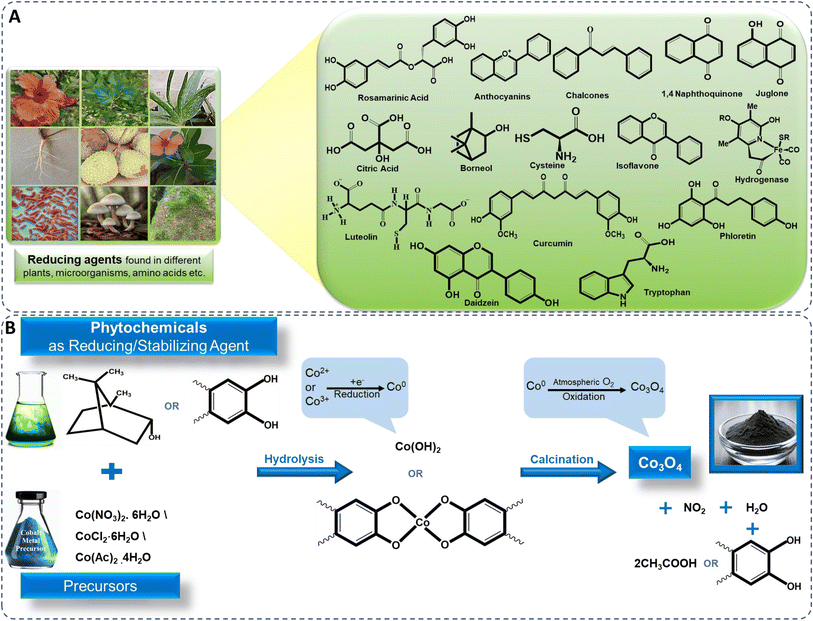
With the advancement of interdisciplinary research in nanoscience, there is a growing need for producing NPs through sustainable and eco-friendly methods to prevent harm to the environment and nearby mammalian communities. Nanotechnologists are thus developing controlled, eco-friendly approaches for NP synthesis, leveraging their small size, porosity, and large surface-to-volume ratio for applications in medicine, catalysis, industry, and environmental remediation.1–6 Traditionally, harmful chemicals were used, raising environmental concerns. However, with the NP market projected to grow by 2026, green synthesis using plant-derived phytochemicals is becoming pivotal, aligning with United Nations sustainable development goals.7,8Metal oxide NPs are widely used in industries such as building materials, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, textiles, electronics, environmental protection, and renewable energy.8–14 Common metal oxides like ZnO, Al2O3, TiO2, NiO, CeO2, CuO, and MgO exhibit significant toxicity, causing cytotoxicity, oxidative stress, DNA damage, and inflammation. For instance, ZnO NPs are particularly harmful to human pulmonary cells, and TiO2 NPs cause DNA damage.15,16 In contrast, cobalt oxide (Co3O4) NPs are less toxic and environmentally benign, making them attractive for various scientific and technological applications due to their cost-effectiveness and eco-friendly properties.17
The cost-effectiveness and abundance of cobalt oxide make it an economically viable choice for large-scale production, ensuring widespread accessibility and affordability. Its exceptional chemical stability ensures durability and longevity in various conditions. Cobalt oxide exists in four forms: CoO, CoO2, Co2O3, and Co3O4,18 where cobalt exhibits in (Co2+, Co3+, and Co4+) oxidation states (Fig. 1A) with CoO and Co3O4 being the most stable. In the spinel structure (AB2O4), Co2+ occupies eight tetrahedral sites (A-sites) and Co3+ sixteen octahedral (B-sites). Co3O4, with its spinel structure, is stable below 891 °C and decomposes to CoO above this temperature. It has a favorable band gap (1.48–2.19 eV), making it useful in supercapacitors.20–23 Cobalt oxide NPs are cost-effective, abundant, antiferromagnetic p-type semiconductors with high resistance to oxidation and corrosion.24–28 They are used in gas sensing,29 antimicrobial and anticancer applications,30,31 supercapacitors,32 electrocatalysis,33 lithium-ion batteries,34 energy storage,35 water splitting,36 dye removal,24 CO2 reduction,37 and drug delivery.38
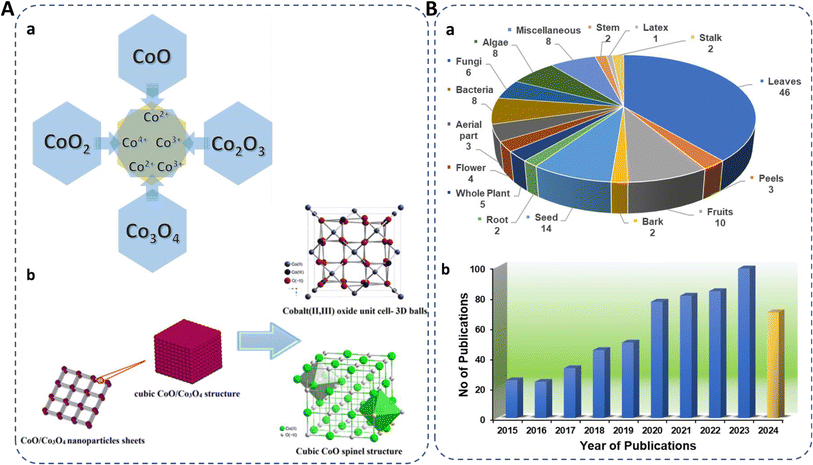 | ||
| Fig. 1 (A) (a) Existing forms of cobalt oxide, their oxidation states, and (b) spinel structure.19 (B) (a) Representation of biosynthesized cobalt oxide NPs from different biological sources (miscellaneous included gum, sucrose, starch, egg white, cloves, dye powder, walnut skin, endemic species). (b) Number of publications on green synthesis of cobalt oxide NPs in the past eight years using “Green synthesis of cobalt oxide nanoparticles” as cumulative keywords (source: Web of Science) reported till 21st Sep, 2024. | ||
Conventional synthesis methods, such as hydrothermal,39 co-precipitation,40 sol–gel method,41 chemical reduction method,42 spray pyrolysis,43 chemical vapor deposition (CVD),44 microwave-assisted,45 solvothermal,46 thermal decomposition,47 casting and irradiation technique,48 auto combustion,49 microemulsion,50 sonochemical,51 laser ablation,52 mechanochemical processes,53 ionic liquid assisted method,54 reflux method,55 polyol,56 pulsed laser deposition,57 template method,58 and wet synthesis59 are expensive, environmentally hazardous, and time-consuming. For instance, hydrazine hydrate (NH2NH2), and sodium borohydride (NaBH4) were commonly used toxic reducing agents.60,61 In contrast, biogenic methods, using plant extracts, microorganisms, algae, and waste materials, are cost-effective, environmentally friendly, and quicker. Green synthesis avoids toxic chemicals and surfactants, leading to biocompatible, stable NPs with low band gap energy due to quantum confinement effects. This makes biogenic cobalt oxide NPs more sustainable and less harmful to the environment.62–64
Researchers are increasingly focusing on environmentally friendly methods for fabricating cobalt oxide NPs, with a notable rise in publications on plant-based synthesis, reflecting a growing interest in sustainable approaches (Fig. 1B). The very recent studies on green synthesized cobalt oxide NPs are reported in Table 1. In a recent study, lemon extract was employed for cobalt oxide NP formation for LPG gas sensor application.29 Similarly, the utilization of rotten apple juice was investigated for preparing surface-modified cobalt oxide nanostructures for efficient oxygen evolution.28 The collective recent studies on the green synthesis of cobalt oxide NPs using various natural extracts demonstrate their potential in antibacterial, anticancer, and antioxidant activities along with supercapacitor performance, photocatalytic, as well as gas sensing applications, highlighting their multifunctionality and efficacy across diverse fields.62,81,82
| Natural source | Precursors | Part | Shape/morphology | Size | Applications | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carica papaya | Co(NO3)2·6H2O | Leaves | Spherical | 22 nm | Anti-oxidant, anti-cancer | 65 |
| Cocos nucifera | Co(NO3)2·6H2O | Fruit | — | 18.44 nm | Photocatalytic and antibacterial | 66 |
| Aloe vera | Co(NO3)2·6H2O | stem | Rod shape | — | Oxygen evolution reaction | 67 |
| Blumea lacera | CoCl2·7H2O | Leaves | Spherical | 5–10 nm | Antimicrobial | 68 |
| Punica granatum L. | CoCl2·6H2O | Seed oil | Spheroidal | 129.6 nm | Antimicrobial and anticancer | 69 |
| Punica granatum L. | Co(NO3)2·6H2O | Fruit | Nano-spherical with a few nano-rod | 17.19 nm | Bimedical | 70 |
| Croton Macrostachyus | Co(NO3)2·6H2O | Leaves | Spherical and irregular | 12.75 nm | Antibacterial activity | 71 |
| Carboxymethyl cellulose | Co(NO3)2·6H2O | Sugarcane straw | Spherical | 27.2 nm | Biological activities | 72 |
| Ziziphus oenopolia | CoCl2·6H2O | Leaves | Irregular | 27 nm | Antimicrobial | 73 |
| Lawsonia inermis | Co(NO3)2·6H2O | Leaves and bark | Rough cubic and spherical | 98 nm | Bimedical | 74 |
| Spent coffee | Co(NO3)2·6H2O | Seed | Spherical and irregular | 29.01 nm | Catalytic and photocatalytic dye degradation | 75 |
| Citrus tangerina | Co(NO3)2·6H2O | Leaves | Octahedral | 90–130 nm | Antimicrobial, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory | 76 |
| Jasminum mesnyi | Co(NO3)2·6H2O | Leaves | Spherical | 59.9 nm | dye degradation | 77 |
| Spirulina platensis | CoCl2·6H2O | Blue-green algae | Octahedral | 26.1 nm | Catalytic CO oxidation | 78 |
| Chlorella vulgaris | CoCl2·6H2O | Green algae | Nanosheets | 16.4 nm | Catalytic CO oxidation | 78 |
| Haematococcus pluvialis | CoCl2·6H2O | Green algae | Nanosheets | 18.4 nm | Catalytic CO oxidation | 78 |
| Nodosilinea nodulosa | CoCl2·6H2O | Algae | Spherical and irregular | 41 nm | Therapeutics | 79 |
| Luminescent bacterium Vibrio sp. VLC | Co(NO3)2·6H2O | Bacteria | Spherical | 65–67 nm | Antioxidant, antibacterial, and anticancer | 80 |
Previously published review articles on green-synthesized cobalt oxide NPs have largely overlooked their biomedical applications, focusing instead on other areas such as photocatalytic degradation, etc. For instance, a recent review by Imtiyaz et al.83 did not cover biomedical uses in particular. While Iravani et al.84 touched on biomedical applications, their review primarily emphasized catalytic activities and was published in 2020. Since then, substantial advancements have been made in the field. Similarly, the review by Mubraiz et al.85 focused solely on antimicrobial properties, providing a limited scope of biomedical potential. This review seeks to address these gaps by offering a comprehensive overview of the biomedical applications of green-synthesized cobalt oxide nanoparticles. It aims to provide timely insights for researchers seeking sustainable approaches in this field, setting it apart from previous works and aligning with the current surge of interest in eco-friendly nanomaterials for medical use.
This review provides a comprehensive analysis of innovative green synthesis techniques utilizing plant extracts and microbial sources. We highlight the mechanisms and eco-friendly attributes of these methods, which present a significant advancement over traditional, hazardous synthesis processes. We delve into the diverse biomedical functionalities of cobalt oxide NPs, including cytotoxicity, larvicidal, antileishmanial, hemolytic, anticoagulating, thrombolytic, anticancer, and drug sensing abilities. This extensive range of applications showcases the versatility and potential of these NPs in medical science. The review highlights the importance of sustainability in nanomaterial synthesis. By utilizing natural resources and biological agents, we demonstrate how cobalt oxide NPs can be synthesized in a cost-effective, sustainable, and biocompatible manner, addressing the environmental concerns associated with conventional methods. This article provides a prospective analysis on the future of cobalt oxide NPs in biomedicine. By highlighting the gaps in current research and the avenues for further exploration, we aim to inspire researchers to advance sustainable practices in nanotechnology and contribute to the development of innovative solutions for human and environmental well-being.
2. Synthesis of green synthesized cobalt oxide NPs
Biogenic synthesis provides an eco-friendly, biocompatible alternative to conventional methods for cobalt oxide NPs production. Plants and microorganisms serve as sustainable sources for NP synthesis, utilizing phytochemicals and biomolecules such as flavonoids, proteins, and enzymes to stabilize NPs, minimizing the need for chemical reagents like stabilizers or reducers. This green approach aligns with principles of green chemistry by avoiding harmful chemical waste.64 Fig. 2 illustrates the most frequently used synthesis methods and highlighted the importance of green synthesized cobalt oxide NPs. Moreover, plants and microbes offer essential compounds that act as reducing and capping agents, facilitating NP formation. Various shapes, sizes, and properties of cobalt oxide NPs have been achieved through this method.64,86,87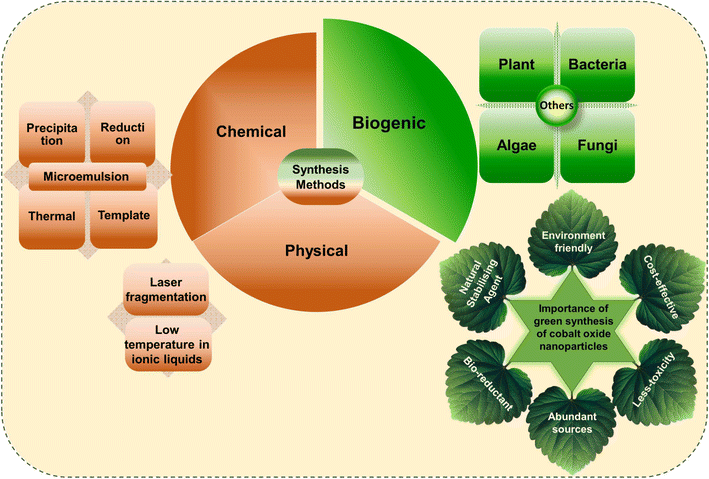 | ||
| Fig. 2 Representation of frequently used conventional and green methods for cobalt oxide NPs synthesis and their importance. | ||
2.1 Source-based synthesis protocol for green synthesized cobalt oxide NPs
2.2 Role of bio-reductants in green synthesis of cobalt oxide NPs
Bio-reductants from natural resources, particularly plants, are extensively used to reduce cobalt metal precursors and stabilize cobalt oxide NPs. Plant extracts, rich in biomolecular compounds like flavonoids, terpenoids, alkaloids, and phenols, contain functional groups such as hydroxyl (–OH), carboxyl (–COOH), carbonyl (–C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O), which play crucial roles in NP reduction and stabilization (Fig. 4A). For example, flavonoids chelate with metal ions, reducing them to form NPs, while other biomolecules prevent agglomeration and stabilize NPs, controlling morphology.89,98 Various plant extracts like Azadirachta indica,24 Calotropis gigantea,91 Curcuma longa,99 Punica granatum,100 and microbes like Aerva javanica, Fusarium oxysporum, Bacillus subtilis,85 Grateloupia sparsa,62 Aspergillus nidulans,101 etc. are used in cobalt oxide NP synthesis. Algae contains several secondary metabolites such as proteins, organic molecules, like carbohydrates and polyphenols, polysaccharides, and phytochemicals having –NH2, –OH, and –COOH functional groups, also act as reducing agents.62,82 Similarly, fungi, containing bioactive compounds and redox enzymes, and bacteria that utilize bioreduction, contribute to cobalt oxide NP formation, offering renewable, non-toxic alternatives to hazardous chemicals.85
O), which play crucial roles in NP reduction and stabilization (Fig. 4A). For example, flavonoids chelate with metal ions, reducing them to form NPs, while other biomolecules prevent agglomeration and stabilize NPs, controlling morphology.89,98 Various plant extracts like Azadirachta indica,24 Calotropis gigantea,91 Curcuma longa,99 Punica granatum,100 and microbes like Aerva javanica, Fusarium oxysporum, Bacillus subtilis,85 Grateloupia sparsa,62 Aspergillus nidulans,101 etc. are used in cobalt oxide NP synthesis. Algae contains several secondary metabolites such as proteins, organic molecules, like carbohydrates and polyphenols, polysaccharides, and phytochemicals having –NH2, –OH, and –COOH functional groups, also act as reducing agents.62,82 Similarly, fungi, containing bioactive compounds and redox enzymes, and bacteria that utilize bioreduction, contribute to cobalt oxide NP formation, offering renewable, non-toxic alternatives to hazardous chemicals.85
 | ||
| Fig. 4 Illustration of (A) bioreduction and (B) mechanistic approach for biosynthesis of cobalt oxide NPs. | ||
2.3 Mechanism involved in green synthesis of cobalt oxide NPs
Plants produce NPs due to phytochemicals like phenolic acids, flavonoids, tannins, and vitamins, which act as ligands. These biomolecules prevent NP aggregation, regulate morphology, and stabilize the NPs.23,102 These phytochemicals have the ability to bind to cobalt ions. Most common precursors used for the synthesis of cobalt oxide NPs are cobalt sulphate, the hydrated salts of cobalt nitrate (Co(NO3)2·6H2O), cobalt chloride (CoCl2·6H2O), and cobalt acetate (Co(OAc)2·4H2O).17 Single step in situ green synthesis procedure involves both growth and nucleation processes. These processes occur through the reduction of cobalt ions into neutral cobalt atoms, which leads the particles to nucleate and stabilises, with the help of biomolecules present in extracts. The phenolic groups contain –OH and –COOH, which allows strong affinity to combine with metals, this affinity is particularly evident when these compounds conjugate with ortho-phenolic hydroxyl groups and ester oxygen atoms.100 The hydroxyl aromatic ring groups of the component of the extract react with a cobalt precursor, undergoes hydrolysis due to the presence of hydroxyl groups in the aromatic portion of the biomolecules, leading to the formation of a complex-ligand with cobalt ions or triggering the formation of hydroxide (Co(OH)2). This includes electron donation by the phytochemical compound to cobalt ions (Co2+ or Co3+) derived from cobalt precursor compound, leading to the reduction of cobalt ions to cobalt metal atoms on the surface of NPs,100 (Fig. 4B), depicted in eqn (i) and (ii).| Co2+ + 2bioreducant-OH → Co + bioreducant-O + 2H+ | (i) |
| Co(NO3)2 + polyphenol-OH → Co + oxidized polyphenol-O + HNO3 | (ii) |
The resulting Co(OH)2 and complex-ligand with cobalt ions are subsequently subjected to calcination, leading to its decomposition and the release of water, ultimately yielding cobalt oxide NPs. The cobalt metal atoms aggregate to form small nuclei and simultaneously, oxygen molecules either from the reaction environment or atmosphere react with cobalt metal atoms to form cobalt oxide. This continuous process on the surface of cobalt metal nuclei to form cobalt oxide NPs,24,103 depicted in eqn (iii) and (iv).
| 6Co + 4O2 → Co3O4 | (iii) |
| 3Coo + 2/3O2 → Co3O4 | (iv) |
The additional phytochemical components present in the plant extracts are also serve as capping or stabilizing agents for the synthesized cobalt hydroxide before the calcination process. The chemical reactions including nucleation and shaping, contribute to the generation of stabilized NPs preventing agglomeration, depicted in eqn (v).
| Co3O4 + 2bioreducant-OH (ligand) → capped Co3O4 | (v) |
However, in the literature, there are no direct studies conducted on how cobalt oxide precursors affect the reactivity of these plant-based reagents. The actual mechanism is still unknown but the cobalt oxide precursors have the potential to engage in complexation with phytochemicals, that act as reducing and stabilizing agents thereby inducing chemical modifications that are influenced by pH and temperature parameters.83 They affect the solubility and dispersion characteristics, ultimately impacting the stability and degradation rate of plant-based reagents which influences their reactivity.1 Thus, by these factors cobalt oxide precursors affect the reactivity of plant-based reagents and optimized green synthesis process.
3. Characteristics of green synthesized cobalt oxide NPs
The fundamental characteristics of biogenically produced cobalt oxide NPs such as shape, size, crystallinity and stability are the important criteria in determining their application.3.1 Visual observation, UV-visible and FTIR spectroscopic analysis
Synthesis of cobalt oxide NPs can be predicted by analyzing the color change of the reaction mixture,104 or by analyzing UV-Vis-spectroscopic data, which shows significant peaks of cobalt oxide NPs in the range of 340 to 500 nm (Fig. 5A(a)).105 The green synthesized powdered cobalt oxide NPs are visually dark olive greenish in color. The peak around 400 nm is ascribed to surface plasmon resonance behaviour.62 Synthesized NPs should be centrifuged at high rpm to isolate cobalt oxide NPs followed by washing multiple times and drying at a mild temperature (∼50 °C).107 After drying and/or further calcination at around 400 °C, the NPs turned to black powder. Contrarily, in case of bacteria, for instance, Microbacterium sp. MRS-1, the color of nutrient broth changes from light pink to dark pink as initial confirmation of formation of extracellular cobalt oxide NPs.106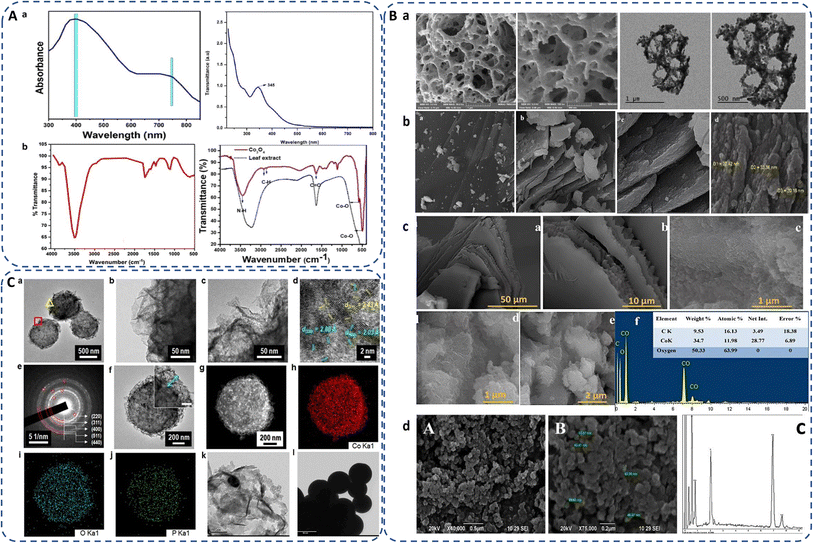 | ||
| Fig. 5 (A) (a) UV-Vis spectra of green synthesized cobalt oxide NPs using red marine algae extract (Grateloupia sparsa)62 and Curcuma longa root extract.105 (b) FTIR spectra of green synthesized cobalt oxide NPs using red marine algae extract (Grateloupia sparsa)62 and Mollugo oppositifolia leaf extract.21 (B) SEM images of biogenically synthesized cobalt oxide NPs employed with (a) Hyphaene thebaica fruit extract,88 (b) Rosmarinus officinalis leaf extract,19 (c) Grateloupia sparsa marine algae extract (with EDX)62 and (d) Microbacterium sp. MRS-1 metal resistant bacteria (with EDX).106 (C) (a–d) TEM and image of the microbe mediated Co3O4 NPs, (e) SAED pattern of porous-Co3O4/bacteria, (f) TEM image of single Co3O4 NPs, (g–j) HAADF STEM image of cobalt oxide NPs94 and (k and l) TEM images of sub-spherical cobalt oxide NPs prepared by rosemary leaf.20 | ||
Cobalt oxide NPs synthesized by Mollugo oppositifolia leaf extract shows a broad peak at 3465.93 cm−1 suggesting the presence of the N–H group of an amine moiety, C–H functional group alkanes signal appeared between 2800 and 3000 cm−1. The presence of both tetrahedral and octahedral Co–O vibrations can be verified by the peaks at 509.59 cm−1 and 584.80 cm−1, respectively (Fig. 5A(b)),21 showing the presence of surface ligands or organic biomolecules by detecting the shifting in characteristic absorption bands associated with metal–oxygen stretching vibrations. FTIR spectra of Co3O4 NPs prepared by red algae extract, exhibit a broad peak at about 3500 cm−1 indicating the presence of amide, primary and secondary amine groups, polyphenol, and alcohol groups due to OH–NH bending. The presence of aromatic rings in plant structures, the bending of –OH and C–O stretching in alcohols and carboxylic acids are indicated by peaks at 1669, 1413, and 1079 cm−1, suggesting their contribution to the formation of cobalt oxide NPs. Furthermore, the peaks at 760 and 562 cm−1 in the spectrum of Co3O4 NPs are connected to Co2+ and Co3+ vibrations in a tetrahedral hole in the spinal lattice (Fig. 5A(b)).62 If not calcinated, FTIR spectra exhibit additional peaks in green synthesis due to organic functional groups from the used biological source as compared to the chemical synthesis.83,108
3.2 Morphology
Green synthesis methods often involve the use of natural bioactive compounds or biomolecules that can functionalize the surface of NPs. SEM provides detailed images of the surface morphology of cobalt oxide NPs and assess their shape, uniformity, coverage, and aggregation behaviour, providing insights into the interaction between cobalt oxide NPs and their immediate environment to understand how green synthesis methods affect the physical properties of cobalt oxide NPs as well as provide optimization synthesis parameters to control their morphology for their reproducibility and consistency in various applications.24,109The morphology of biosynthesized cobalt oxide NPs are studied using FE-SEM and TEM. For instance, Shim et al.97 synthesized Bacillus subtilis-directed porous Co3O4 nanorods and most of the biosynthesized nanorods had a closed-end, but few of them were open-ended type. Fig. 5(B and C) depicts different types of morphologies observed by SEM and TEM analysis of the green synthesized Co3O4. Safdar et al. revealed porous structure of Hyphaene thebaica fruit extract mediated synthesized Co3O4 NPs.88 Semi-triangular pyramidal shape of rosemary leaf extract biosynthesized Co3O4 NPs was confirmed by TEM images.20 Sheet-like morphology was found in Rosmarinus officinalis mediated CoO/Co3O4 NPs.19 Similarly, cobalt oxide NPs synthesized using red algae extract also exhibit complicated sheet-like structures.62 Microbacterium sp. MRS-1 is a heavy metal resistant bacterium. Sundararaju et al. isolated the bacteria from the electroplating industrial effluent to reduce cobalt metal to cobalt oxide NPs and thus detoxification of metal ions from the wastewater. The agglomerated Co3O4 NPs were spherical and pentagon accompanied with 54![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 34 Co
34 Co![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) O elemental ratio in the range of 10–70 nm, observed by SEM-EDX (Fig. 5B(d)).106 Tables 2–6 displays the various morphologies and size range of green synthesized cobalt oxide NPs using different source as reducing or stabilizing agent and different precursors along with their applications.
O elemental ratio in the range of 10–70 nm, observed by SEM-EDX (Fig. 5B(d)).106 Tables 2–6 displays the various morphologies and size range of green synthesized cobalt oxide NPs using different source as reducing or stabilizing agent and different precursors along with their applications.
3.3 Size
The size of biogenically produced cobalt oxide NPs are generally analyzed by DLS study, TEM imaging and XRD of the NPs. The average crystallite size of cobalt oxide NPs can be determined by XRD peaks and calculated by using the Debye–Scherrer eqn (1) (ref. 21) as follows:
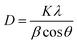 | (1) |
Raimundo et al.110 reported that cobalt oxide NPs synthesized using Rhodophyta showed an average size of 65 nm. Small sized 2–5 nm and 6.7 nm nanocrystals were produced using Ipomoea carnea leaf extract104 and Calotropis procera latex,111 respectively. Aerva javanica (plant), Bacillus subtilis (bacterial strain), and Fusarium oxysporum (fungus) derived cobalt oxide NPs revealed particle sizes of 39.23 nm, 31.2 nm and 33.4 nm respectively.85 High annealing temperature at 800 °C shows rapid increase in size to 39.44–53.56 nm for Arista leaves extract synthesized NPs.87 Shim et al. prepared Micrococcus lylae bacteria-mediated Co3O4 NPs had a crystalline size of 2–10 nm, forming mesoporous structures (Fig. 5C(a–j)).94 The smaller size of Co3O4 NPs allows them to penetrate bacterial membranes more easily. Smaller nanoparticles exhibit better dispersion and reduced aggregation, which ensures uniform distribution and more efficient antimicrobial action. After penetration, they can disrupt internal cellular processes, such as enzyme functions and DNA replication, enhancing their bactericidal properties.
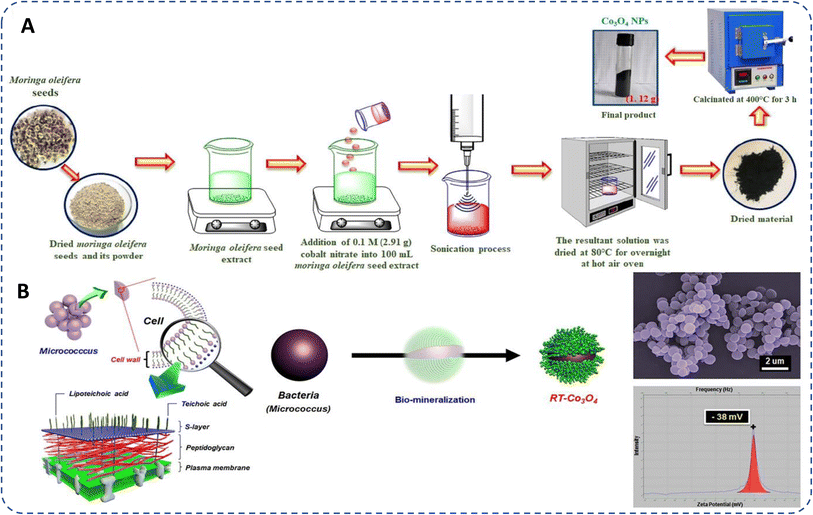
The hydrodynamic diameter,6,112,113 crucial for stability and dispersibility, was measured as 218 nm for Akhlaghi et al.114 Co3O4 NPs, larger than the SEM size of 6–20 nm, likely due to the presence water molecules layers on the surface of cobalt oxide NPs.20 Geranium wallichianum-derived NPs showed an aggregate size of 320 ± 2.33 nm in DLS analysis,26 Ipomoea carnea NPs measured 4–10 nm (mostly 7.83 nm).104 DLS analysis of red algae-synthesized NPs showed 48.1 ± 5.32 nm (Fig. 6A(a)).62 The Moringa seed extract mediated cobalt oxide NPs had an average size of 44.51 nm compared to 41.10 nm for chemically synthesized NPs (Fig. 6A(b)).93
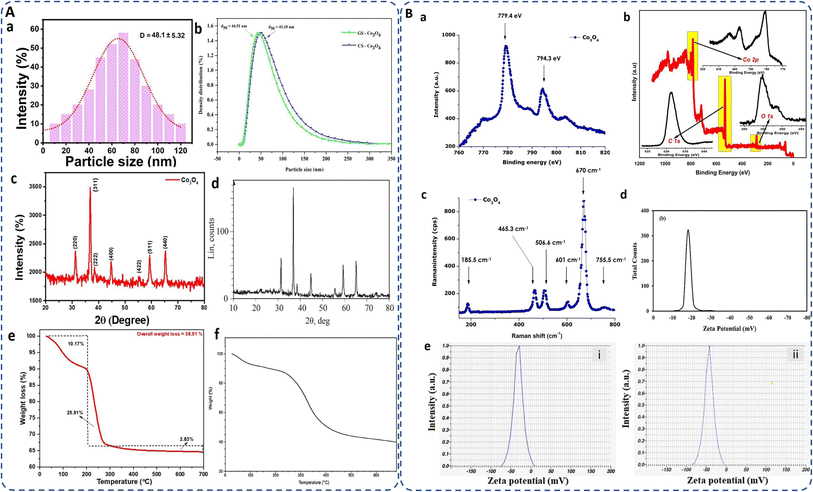 | ||
| Fig. 6 (A) (a and b) DLS analysis for particle size distribution of biosynthesized cobalt oxide NPs by utilizing marine red algae62 and Moringa seed extract;93 (c and d) XRD pattern of cobalt oxide NPs synthesized by Mollugo oppositifolia L. leaf extract21 and gelatin;115 (e and f) TG curve of Muntingia calabura116 and bacteria mediated (Microbacterium sp. MRS-1) biosynthesized cobalt oxide NPs.106 (B) (a and b) XPS of Aspalathus linearis plant extracNt117 and Muntingia calabura leaf extract116 mediated green synthesized cobalt oxide NPs; (c) Raman spectra of biosynthesized annealed cobalt oxide NPs;117 (d and e) zeta potential of Rosemary extract,20 and (e) lemon extract29 mediated green synthesized cobalt oxide NPs. | ||
Microbial Bacillus subtilis, Fusarium oxysporum, mediated cobalt oxide NPs exhibit 30.9191°, 36.5364°, 59.0089°, and 64.9460° diffraction peaks for the corresponding planes (220), (311), (511), and (440) and with average crystallite size 31.2 nm and 33.4 nm, respectively.85 Gowthami et al. reported a pure FCC spinel structure of cobalt oxide NPs using Mollugo oppositifolia L. leaf extract. Diffraction peaks at 31.2°, 37.6°, 38.7°, 44.8°, 55.6°, 59.8°, and 66.3° correspond to hkl values (220), (311), (222), (400), (422), (511), and (440) (Fig. 6A(d)).21 XRD pattern of highly pure cobalt oxide (CoO) NPs prepared by gelatin, as depicted in Fig. 6A(c), are observed in 2θ range of 10–80°, with average particle size of about 25 nm.115 Since, phytochemicals influence the nucleation and growth process to favor the fcc structure, overall, the fcc structural arrangement of cobalt oxide maximizes the density, stability and minimizes the repulsive interactions, i.e. high packing efficiency of the spinel structure by occupying interstitial sites within the oxygen lattice. However, the XRD peaks are often display sharper peak in case of chemical synthesis while broader peak in green synthesis indicating less crystallinity but contrarily minimizing their toxicity.
3.4 Surface interface: composition and chemistry
Surface of the NP plays a vital role in determining its applicability. Surface area of bio-inspired cobalt oxide NPs are estimated using Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) techniques. For instance, the BET surface area of cobalt oxide NPs synthesized by the Calotropis gigantea plant was found 46.7 m2 g−1. Generally, large surface area of NPs results in a significant increase in the number of active sites and a greater number of adsorbed substrates for the intended catalytic reaction.91 Recently, rice husk derived silica gel was used in synthesizing cobalt oxide NPs possessing 735 m2 g−1 surface area which were more than the Co3O4/MCM-41 nanocomposites, have a surface area of 608 m2 g−1. This increase in surface area leads to more exposed catalytic sites for light irradiation, and higher levels of acephate molecules adsorbed.118 It should be noted here that since the synthesis method and phytochemicals affect the size and dispersion of the NPs, they consequently influence the surface area of the cobalt oxide NPs. Smaller particles exhibit a high surface-to-volume ratio, resulting in a higher surface area, which enhances their utility in adsorption, catalysis, sensing, conductivity, and therapeutic applications. This high surface area allows for better interaction with cells and tissues, improves solubility, and enhances catalytic activity, making them more effective in therapeutic and diagnostic applications. However, the optimal surface area also depends on the specific biomedical application, with smaller NPs being more suitable for drug delivery, while slightly larger ones may be better for imaging or diagnostics. There are examples which shows varying surface area as per aforementioned reasons, such as Bacillus subtilis-directed porous cobalt oxide NPs observed surface area of bacteria and cobalt oxide NPs at 5.1 and 73.3 m2 g−1, respectively, but the thermal treatment enhanced the bacteria/cobalt oxide hybrid nanorod surface area to 11.2 m2 g−1.97 L-Cysteine,119 Grateloupia sparsa,62 and Terminalia chebula120 mediated Co3O4 NPs found 24.6 m2 g−1, 35.21 m2 g−1, and 22 m2 g−1 surface area, respectively.Additionally, XPS and Raman spectroscopy identify the elemental composition and oxidation states of cobalt and characterize the vibrational modes or chemical bonds associated with the crystal lattice present on the NP surface. For instance, Aspalathus lineari plant extract mediated cobalt oxide NPs shows the characteristic XPS peak of Co2p with O1s consistency and attributed binding energies of 2p1/2 and 2p3/2 at 779.4 and 794.3 eV, respectively (Fig. 6B(a)).117 Similarly, Vinayagam et al. reported two compatible peaks for Co3+ and Co2+ oxidation states of cobalt oxide NPs attributed to the binding energies at 797.13 (Co 2p1/2) and 781.02 (Co 2p3/2) eV accompanied by a 16.11 eV peak separation. For O 1s, a broad peak at 531.28 eV indicates its binding with both the oxidation states of cobalt. Furthermore, the organic components from the extract are involved by the presence of a C 1s peak at 284.81 eV (Fig. 6B(b)).116
Raman spectroscopy is sensitive to the presence of metal–oxygen bonds and can differentiate between different cobalt oxide phases (CoO and Co3O4). Diallo et al. reported tetrahedral (Co2+ (3d7)) and octahedral sites (Co3+ (3d6)) of biosynthesized cobalt oxide NPs, corresponds to the active modes of Co3O4 spinel, Fd3m symmetry as: Γ = A1g (R) + Eg (R) + F1g (IN) + 3F2g (R) + 2A2u (IN) + 2Eu (IN) + 4F1u (IR) + 2F2u (IN), where (IN), (IR), and (R) are the inactive, infrared-active, and Raman active vibrational modes, respectively. The characteristic Raman vibrational modes are present at ∼185.5, ∼465.3, ∼506.6, ∼601, ∼670, and ∼755.5 cm−1, with a combined octahedral site A1g, the Eg, and F2g modes combined with tetrahedral site with an average shift of Δν ∼ 5 cm−1 due to stress strain surface ratio (Fig. 6B(c)).117
3.5 Stability
The thermal and colloidal stability of biogenically synthesized cobalt oxide NPs are one of the important parameters that can be assessed using TGA and zeta potential. For instance, Muntingia calabura leaf-derived NPs exhibited a total weight loss of 38.91% between 28–300 °C due to moisture loss and organic breakdown, followed by a 2.83% loss at 300 °C indicating CoO to Co3O4 phase transformation (Fig. 6A(e)).116 Similarly, gelatin-mediated cobalt oxide nanocrystals displayed water loss at 50–110 °C, organic combustion at 350 °C, and pure cobalt oxide formation between 350-460 °C, with no weight loss beyond 460 °C, confirming stability.115 Grateloupia sparsa algae-derived NPs, lost 6.3% at 260 °C and 17.6% at 410 °C indicating gradual organic breakdown82 and Microbacterium sp. MRS-1 bacteria derived NPs displayed mass losses of 7%, 15%, and 50% at 100 °C, 225 °C, and 250–400 °C, respectively, remaining stable up to 700 °C (Fig. 6A(f)).106 For colloidal stability, Trigonella foenumgraceum-derived NPs114 had a negative zeta potential of −20.4 mV, indicative of surface hydroxyl groups, while Rosemary leaf-based NPs exhibited −18 mV (Fig. 6B(d))20, ensuring good colloidal stability. NPs synthesized from Geranium wallichianum26 and Cordia myxa demonstrated zeta potentials of −10.5 mV and −40 mV, respectively, indicating phytochemicals' influence on surface charge, promoting dispersion and preventing aggregation.92 Similarly, Bacillus subtilis mediated porous NPs presented −46 mV, due to peptidoglycan presence.97 Lemon extract derived NPs showed even higher zeta potentials of −33.4 mV (unheated) and −42.1 mV (heated), ensuring strong repulsion and dispersion stability (Fig. 6B(e)).29 Higher zeta potential values increase electrostatic repulsion, enhance stability and reduce aggregation in the medium. Overall, the functional groups of biomolecules, acting as natural stabilizers, on the surface of cobalt oxide NPs impart a surface charge that directly influences the zeta potential and hence enhanced their stability as compared to chemically synthesized NPs.4. Green synthesized cobalt oxide NPs: literature analysis
4.1 Using plant source
Nowadays, various plant sourced extracts have been employed in the green synthesis of cobalt oxide NPs, unveiling diverse applications, such as leaves, roots, fruits, peel, and bark, are used very often as capping, and reducing agents.93 For instance, Cirsium vulgare leaf extract produced NPs averaging 20 nm, exhibiting catalytic capabilities in L-cysteine oxidation.121 Sechium edule fruit extract facilitated the synthesis of monocrystalline spinal cobalt oxide NPs through biochemical reduction of CoOOH to Co(OH)2, achieving high reproducibility in H2O2 detection.122 Ipomoea carnea extract yielded cobalt oxide NPs with a diminutive size of 6.78 nm, demonstrating robust antibacterial activity against Staphylococcus aureus and Shigella flexneri, with inhibitory zones of 17.8 nm and 16.7 nm, respectively, comparable to vancomycin and ampicillin antibiotics.104 Bronzato et al. utilized tomato seed extract to synthesize cobalt oxide quantum dots (QDs) sized at 4.5 nm, effective in Ciprofloxacin degradation.123 Rosemary leaf extract, rich in carnosol, carnosic acid, rosmanol, isorosmanol, and caffeic acid, synthesized cobalt oxide NPs that displayed potent antioxidant properties and demonstrated efficacy as anticancer agents against Gep G2 and MCF7 cancer cells.20 There are a wide variety of plant source available to synthesize cobalt oxide NPs. A list of different plant source and their applications are presented in Table 2.| Natural source | Precursors | Part | Shape/morphology | Size | Applications | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mollugo oppositifolia | CoCl2·6H2O | Leaves | Spherical | 22.7 nm | Antimicrobial activity | 21 |
| Geranium wallichianum | Co(OAc)2·4H2O | Leaves | — | 21 nm | Enzyme inhibition, antioxidant, cytotoxic and antimicrobial | 26 |
| Palm kernel oil | CoCl2·6H2O and Co (NO3)2·6H2O | Seed | Diamond, hexagonal | 9–22 nm | 40 | |
| Phytolacca dodecandra | Co(NO3)2·6H2O | Leaves | Spherical | 10.79 nm | Antimicrobial activity | 63 |
| Rosmarinus officinalis (rosemary) | CoCl2·6H2O | Leaves | Sheets like | 19–33 nm | Anticancer activity | 19 |
| Arishta | CoCl2·6H2O | Leaves | — | 40–50 nm | Antibacterial, antifungal activity | 87 |
| Ziziphus oxyphylla (beri) | CoCl2·6H2O | Root | Irregular and spherical | 40–60 nm | Antibacterial activity | 89 |
| Hibiscus rosa sinensis | C4H6CoO4 | Leaves | Spherical or elliptical | 18.98 ± 8.45 nm | Biomedical applications | 90 |
| Cordia myxa | Co(NO3)2·6H2O | Leaves, roots, and fruit | Prism | 47–48 nm | Biological and photocatalytic activity | 92 |
| Aerva javanica | CoCl2·6H2O | Aerial | Poly shaped | 39.23 nm (methanolic extract) 68.9 nm (aq. Extract) | Antimicrobial activity | 85 |
| Curcuma longa | Co(NO3)2·6H2O | Leaves | Spherical | 22 nm | Photocatalytic and antibacterial | 99 |
| Litchi chinensis | Co(OAc)2·4H2O | Fruit | Spherical | 26–40 nm | — | 102 |
| Ipomoea carnea | CoCl2·6H2O | Leaves | Spherical | 6–10 nm | Micronutrient and antimicrobial activity | 104 |
| Curcuma longa | Co(NO3)2·6H2O | Root | Spherical | 97.5 ± 35.1 nm | Photocatalytic dye degradation, antimicrobial and anticancer activity | 105 |
| Trigonella foenumgraceum (Fenugreek) | CoCl2·6H2O | Leaves | Spherical | 13.2 nm | — | 114 |
| Calotropis procera | Co(OAc)2·4H2O | Latex | Spherical | 10 nm | Antibacterial activity | 111 |
| Aspalathus linearis | Co(NO3)2·6H2O | Leaves | Quasi-spherical | ∼3.6 nm | — | 117 |
| Sageretia thea (Osbeck) | Co(OAc)2·4H2O | Leaves | Cubic | 20.03 nm | Biological applications | 124 |
| Clitoria ternatea | CoCl3·6H2O | Flower | Spherical | 13–17 nm | Biological activities | 125 |
| Manihot esculenta Crantz (cassava) | CoCl2 | Root | Prism like-anchored octahedron | 36 nm | — | 126 |
| Aerva lanata | Co(NO3)2·6H2O | Leaves | Irregular, cubic, hexagonal, and spherical | 36.24 nm | Microbial and antioxidant activity | 127 |
| Populus ciliata plant (safaida) | Co(NO3)2·6H2O | Leaves | Square | 15–35 nm | Antibacterial activity | 128 |
| Caccinia macranthera | Co(NO3)2·6H2O | Seed | Granular shape | 30–45 nm | Cytotoxicity and photocatalytic activity | 129 |
| Sesbania sesban | Co(NO3)2·6H2O | Plant | Spherical | 15–30 nm | Antibacterial, antioxidant activity | 130 |
| Psidium guajava | Co(NO3)2·6H2O | Leaves | Spherical | 26–40 nm | Photocatalytic and biological activities | 131 |
| Momordica charantia | CoCl2·6H2O | Aerial | Irregular | 40–90 nm | Photocatalytic activity | 132 |
| Solanum lycopersicum (tomato) | Co(NO3)2·6H2O | Seed | Quantum dot | 5 nm | Degradation of ciprofloxacin | 133 |
| Piper nigrum | CoCl2·6H2O | Seeds | Triangular-like with irregular spherical | 40–60 nm | — | 134 |
| Salvia hispanica | Co(NO3)2·6H2O | Leaves | Spherical | 9.218 ± 0.93 nm | Biomedical and photocatalytic | 135 |
| Rosemary | CoCl2·6H2O | Leaves | Spherical | 50–100 nm | Anticancer activity | 136 |
| Ocimum tenuiflorum (tulsi) | Co(NO3)2·6H2O | Leaves | Rod | Antifungal activity and sensing | 137 | |
| Phoenix dactylifera | — | Seed | Spherical | ∼80 nm | Photocatalytic and antimicrobial | 138 |
| Citrus limon | CoCl2·6H2O | Fruit juice | — | — | Antimicrobial activity | 139 |
| Manilkara zapota (chikoo) | Co(NO3)2·6H2O | Leaves | — | 20.23 nm | Antifungal activity | 140 |
| Apium graveolens | Co(NO3)2·6H2O | Leaves | Irregular | 21–55 nm | Antibacterial activity | 141 |
| Camellia sinensis | Co(NO3)2·6H2O | Stalks | Irregular | 21–72 nm | Antibacterial activity | 141 |
| Rosmarinus officinalis | Co (OAc)2·4H2O | Leaves | — | ∼6.5 nm | Biomedical and photocatalytic application | 142 |
| Senna auriculata | Co(NO3)2·6H2O | Flower | — | 31.94 nm | Antibacterial and antifungal | 143 |
| Rhamnus virgata | Co(OAc)2·4H2O | Leaves | — | ∼17 nm | Biological applications | 144 |
| Spirulina platensis | CoCl2·6H2O | Plant | — | 13.28 nm | Antifungal activity | 145 |
| Juglans regia | CoCl2·6H2O | Bark | Spherical | — | Environmental, antibacterial, and cytotoxic potential | 146 |
| Withania coagulans | CoCl2·6H2O | Plant | Bead, cube | 49–59 nm | Antibiotic, antifungal and biofilm activity | 147 |
| Vitis vinifera | Co(NO3)2·6H2O | Seed | Nanorod | 10–20 nm | Catalytic, photocatalytic, and antibacterial activities | 148 |
| Gingko | Co(CH3COO)2 | Leaves | Irregular | 30–100 nm | Electrochemical biosensing | 149 |
| Mappia foetida | CoCl2 | Leaves | Spherical | — | Antimicrobial potential | 150 |
| Abies pindrow | C4H6CoO4·4H2O | Leaves | Spherical | 17 nm | dye degradation | 151 |
| Euphorbia tirucalli | CoSO4·7H2O | stem | Irregular and spherical | 1 μm- 100 nm | Breast cancer inhibition | 152 |
| Duranta repens | (CH3COO)2Co·4H2O | Leaves | — | ∼23 nm | Electrochemical analysis of tramadol | 153 |
| Hibiscus rosa sinensis | Co3O4 | Flower | Tubular like | 34.9 nm | Antibacterial activity | 154 |
| Spinacia Oleracea (Spinach) | CoCl2·6H2O | Leaves | Agglomerate and spherical | — | — | 155 |
| Punica granatum | Co(NO3)2·6H2O | Seed | Quasi-spherical | 3.5 nm | Photodegradation, catalytic hydrogenation, and antibacterial applications | 156 |
| Lawsonia inermis | Co(NO3)2·6H2O | Leaves, bark | Cubic and spherical | 98.05 nm. | Biological activity | 74 |
Overall, different plants have varying capabilities to stabilize and reduce cobalt ions due to their unique biochemical compositions, which can lead to differences in NP size and shape. Besides, the method of extracting these phytochemicals (e.g., boiling, soaking, or direct extraction) affects their concentration and efficacy in NP synthesis. Parameters such as pH, temperature, reaction time, and the concentration of plant extract and metal salts play critical roles in determining the size, shape, and morphology of the synthesized NPs. Optimization of these factors and selection of plant extracts, while avoiding harmful surfactants, are crucial for NP control. Despite challenges in precise control, biogenically synthesized cobalt oxide NPs offer sustainable solutions with diverse applications, warranting further research.
4.2 Using algae
The utilization of algae in green synthesis is gaining attention as it possesses a rapid growth rate, facilitate convenient harvesting, and offer a cost-effective means of scaling up, rendering them highly suitable for the biological synthesis of NPs. For instance, cobalt oxide NPs were synthesized by a one-pot hydrothermal technique using Grateloupia sparsa (marine red algae extract) for supercapacitor application.62 These red algae extract contain carbohydrates, fats, proteins antioxidants, and pigments like chlorophylls and phycobilins which act as reducing agents. Raimundo et al.157 reported the synthesis of Co3O4–CoO nanocomposite by using agar–agar (Rhodophyta) in two steps including proteic sol–gel and hydrothermal method, and revealed excellent electrocatalytic performance for OER applications. Their most recent investigations have been reported in Table 3.4.3 Using fungi
The cobalt oxide NPs synthesized by using fungi due to their manifestation of tolerance and metal bioaccumulation capability, as well as their high binding capacity and intracellular intake.158 The process is highly effective in generating NPs with well-defined morphologies (Table 4). For instance, Aspergillus brasiliensis fungus was used for the green fabrication of quasi-spherical shaped cobalt oxide NPs by adding fungus in cobalt sulphate under shaking conditions for 72 hours at pH 11 and 30 °C temperature, with an average particles size of 20–27 nm for antimicrobial applications and shows good magnetic properties.159| Natural source | Precursors | Part | Morphology | Size | Application | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bread fungus | Co(NO3)2·6H2O | Fungus | Cubic | 14–19 nm | Photocatalyst for water splitting | 36 |
| Fusarium oxysporum | CoCl2·6H2O | Fungus | Less cubic | 33.4 nm | Antimicrobial | 85 |
| Aspergillus nidulans | Cobalt(II) acetylacetonate | Fungus | Spherical | 20.09 nm | — | 101 |
| Aspergillus terreus | CoSO4·7H2O | Fungus | Various shapes | — | — | 107 |
| Aspergillus brasiliensis | CoSO4·7H2O | Fungi | Quasi-spherical | 20–27 nm | Antimicrobial | 159 |
| Yeast | CoCl2·6H2O | Fungi | Hollow spheres | 24 nm | — | 160 |
4.4 Using microbes or bacteria
Bacterial species have been widely used for the production of NPs because of their high yield, easy handling, and low purification cost.161 Bacteria can reduce metal ions present in the metal precursors during the formation of NPs.95 Table 5 shows several investigations reported the utilization of bacteria in the production of cobalt oxide NPs. Under ambient conditions, porous Co3O4 hollow rod-shaped cobalt oxide NPs were synthesized through the electrostatic interaction between the functional surface structures of B. subtilis bacteria and cobalt ions, exhibits exceptional electrochemical properties when utilized as electrode materials in rechargeable Li-ion batteries.97 The biosynthesized spherical cobalt oxide NPs were prepared by adding the bacterial biomass of Microbacterium sp. MRS-1 to the cobalt chloride solution. The reduction occurred outside the cell enables the straightforward retrieval of NPs without causing harm to cells, while simultaneously detoxifying toxic metal ions.106 Similarly, a 3D hierarchical, flower-like microsphere and porous-Co3O4 superstructures were facilitated by Micrococcus lylae, a Gram-positive bacterium for supercapacitor applications.165 Table 6 describes other different natural sources that are used in biogenic production of cobalt oxide NPs such as walnut, starch, onion, egg white, sucrose, etc.| Natural source | Precursors | Part | Morphology | Size | Application | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Micrococcus lylae | CoCl2·6H2O | Bacteria | Flower-like | 2–10 nm | Supercapacitor | 94 |
| Bacillus subtilis | CoCl2·6H2O | Bacterial strains | Rod-like | 31.2 nm | Antimicrobial | 85 |
| Bacillus pasteurii | Co(NO3)2·6H2O | Bacteria | Non-specific | 10–31 nm | Supercapacitor | 96 |
| Microbacterium sp. | CoCl2 | Bacteria | Spherical | 10–70 nm | — | 106 |
| Bacillus subtilis | CoCl2·6H2O | Bacteria | Rod | 3–5 nm | — | 162 |
| Brevibacterium casei | Co(OAc)2·4H2O | Bacteria | Quasi-spherical | 5–7 nm | — | 163 |
| Bacillus subtilis | CoCl2·6H2O | Bacteria | Hollow rod | 2–5 nm | Lithium storage | 164 |
| Natural source | Precursors | Part | Morphology | Application | Size | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Araucaria heterophylla | Co(NO3)2·6H2O | Plant gum | Spherical | Catalytic degradation, antimicrobial potential | 13 nm | 56 |
| Allium sativum | CoCl2 | Cloves | Fine powdered | Photo-catalytic activity | — | 81 |
| Egg white | Co(NO3)2·6H2O | Spongy clumps | Corrosion inhibitor | 10–20 nm | 166 | |
| Starch | CoSO4·7H2O | Square | Coating application | 18 nm | 167 | |
| Walnut green | Co(NO3)2·6H2O | Walnut green skin | Nearly spherical | — | ∼60–80 nm | 168 |
| Cochineal powder | Co(NO3)2·6H2O | dye | Agglomerate, nanoplate, uniform | Toxicological effect | 25–35 nm | 169 |
| Allium tuncelianum | Co(NO3)2·6H2O | Endemic species | Spherical | Anticancer activity | 23 nm | 170 |
| Sucrose | Co(NO3)2·6H2O | — | — | Removal of dye | <5 nm | 171 |
| Sucrose | CoCl2·6H2O | — | — | — | 30 nm | 172 |
| Glycogen | 36 nm | |||||
| Glucose | 23 nm |
5. Biomedical applicability of green synthesized cobalt oxide NPs
5.1 Antimicrobial activity
Antimicrobial activity refers to the ability to kill or inhibit the growth of microorganisms without harming neighboring tissues. Green synthesized NPs are more effective than those produced by conventional methods due to the presence of secondary metabolites in plants that inhibit microbial growth.63 Antimicrobial activities of green synthesized cobalt oxide NPs can vary from plant species to species. There are many methods for evaluating antimicrobial activity by plant extract including disc diffusion method,127 well diffusion,128 time-kill assay,173 agar dilution,159 broth dilution methods,174 etc. Out of which disc diffusion and well diffusion methods are the widely utilized methods. There are several types of antimicrobial activity such as antibacterial and antifungal activity which are discussed in this section.| Source | Test microorganism | Conc. | Method | Zone of inhibition (mm) or MIC (μg ml−1) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hibiscus Rosa sinensis | E. coli | 20 mg | Disc diffusion | 16 ± 1.13 mm | 90 |
| P. vulgaris | 21 ± 1.32 mm | ||||
| P. aeruginosa | 20 ± 1.47 mm | ||||
| Geranium wallichianum | P. aeruginosa | 700–21.875 μg ml | Agar disc diffusion | 175 μg ml−1 | 26 |
| B. subtilis | 21.875 μg ml−1 | ||||
| K. pneumonia | 175 μg ml−1 | ||||
| E. coli | 43.75 μg ml−1 | ||||
| S. aureus | 87.5 μg ml−1 | ||||
| Mollugo oppositifolia | E. coli | — | Standard agar method | 23.6 ± 1.25 μg ml−1 | 21 |
| P. aeruginosa | 34 ± 0.21 μg ml−1 | ||||
| S. aureus | 28 ± 1.12 μg ml−1 | ||||
| B. cereus | 26.56 ± 0.56 μg ml−1 | ||||
| Sageretia thea | P. aeruginosa | 1000 μg ml−1 to 31.25 μg ml−1 | Disc diffusion | 250 μg ml−1 | 124 |
| S. aureus | 31.25 μg ml−1 | ||||
| S. epidermis | 125 μg ml−1 | ||||
| E. coli | 31.25 μg ml−1 | ||||
| B. subtilis | 125 μg ml−1 | ||||
| K. pneumonia | 62.5 μg ml−1 | ||||
| Phytolacca dodecandra | E. coli | 50 μg ml−1 | Disc diffusion | 12.5 mm | 63 |
| S. aureus | 11.6 mm | ||||
| Grateloupia Sparsa | E. coli | 30 μg ml−1 | Zone of inhibition | 11.7 ± 3.2 mm | 82 |
| P. aeruginosa | 12.5 ± 3.9 mm | ||||
| B. subtilis | 14.3 ± 3.1 mm | ||||
| S. aureus | 17.6 ± 4.2 mm | ||||
| Arishta | S. aureus | — | Disc diffusion | 30 mm | 87 |
| S. mutans | 34 mm | ||||
| K. pneumonia | 40 mm | ||||
| E. coli | 29 mm | ||||
| Ziziphus oxyphylla (beri) | S. aureus | 16 mg ml−1 | Well diffusion | 14.8 ± 1 mm | 89 |
| E. coli | 23.1 ± 1.2 mm | ||||
| Clitoria ternatea | S. thermophilus | 500 μg ml−1 | — | 14 ± 0.7 mm | 125 |
| Calotropis procera | E. coli | 750 μg per disc | Disc diffusion | 17 mm | 111 |
| Alcaligenes sp. | 13 mm | ||||
| Enterococcus sp. | 14 mm | ||||
| Pseudomonas sp. | 12 mm | ||||
| Curcuma longa | E. coli | 100 μg ml−1 | Well diffusion | ∼14 mm | 99 |
| S. aureus | ∼11 mm | ||||
| Populus ciliata (safaida) | B. subtilis | 2, 4, 8 mg ml−1 | — | 21.8 ± 0.7 mm | 128 |
| B. licheniformis | 18.6 ± 0.8 mm | ||||
| K. pneumonia | 17.0 ± 0.6 mm | ||||
| E. coli | 14.0 ± 0.6 mm | ||||
| Sesbania sesban | S. aureus | 50 μl (50 μg) | Well diffusion | 7.5 mm | 130 |
| Psidium guajava | S. aureus | 200 μg ml−1 | Agar well diffusion | 18 mm | 131 |
| E. coli | 15 mm | ||||
| Citrus limon | S. aureus | — | Agar well diffusion | 27 mm | 139 |
| S. mutans | 28 mm | ||||
| K. pneumonia | 27 mm | ||||
| E. coli | 29 mm | ||||
| Rhamnus virgata | S. aureus | 1200 μg ml−1 | Disc diffusion method | ∼20 mm | 144 |
| E. coli | ∼20 mm | ||||
| K. pneumonia | ∼18 mm | ||||
| B. subtilis | ∼22 mm | ||||
| P. aeruginosa | ∼18 mm | ||||
| Vitis vinifera | S. aureus | 10 μl of 0.001 g/10 μl | Disc diffusion | — | 148 |
| B. subtilis | |||||
| P. aeruginosa | |||||
| E. coli | |||||
| Mappia foetida | S. aureus | — | Well diffusion | 33.5 mm | 150 |
| B. subtilis | 33.5 mm | ||||
| E. coli | 38.3 mm | ||||
| P. vulgaris | 37.3 mm | ||||
| Aspergillus brasiliensis | B. subtilis | 5 mg ml−1 | Agar diffusion | 15.6 ± 0.577 mm | 159 |
| S. aureus | 20 ± 0.288 mm | ||||
| P. aeruginosa | 11.3 ± 0.577 mm | ||||
| E. coli | 12 ± 0.288 mm |
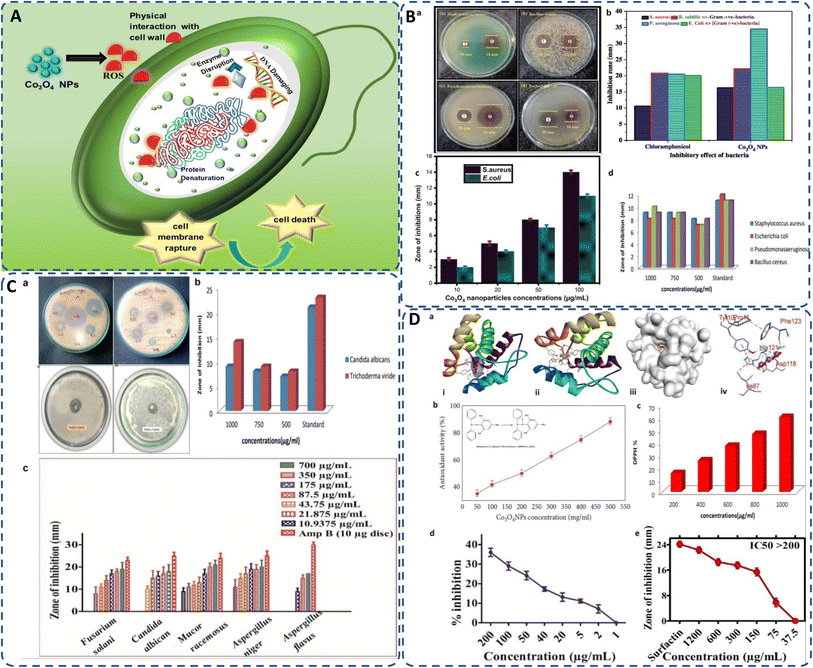 | ||
| Fig. 7 (A) General mechanism of antimicrobial activity of biogenic cobalt oxide NPs causing cell death; (B) antimicrobial activity of green synthesized CO3O4 NPs against (a) S. aureus, B. subtilis, P. aeruginosa, E. coli, (b) inhibitory effect of Co3O4 NPs in comparison with standard chloramphenicol;24 (c) against S. aureus, E. coli by Curcuma longa plant extract;99 (d) by Aerva lanata at different concentrations.127 (C) Antifungal activity of cobalt oxide NPs (a) against A. favus, A. niger,139 A. niger, C. albicans,147 (b) against Candida albicans and Trichoderma viride,127 (c) by Geranium wallichianum at different concentrations.26 (D) (a) Docking studies of green synthesized cobalt oxide NPs showing (i) helical structure, (ii) molecular surface, (iii) 3D display, and (iv) binding interaction with binding sites of 3OGN protein.21 Antioxidant activity of biogenically produced cobalt oxide NPs by (b) Grateloupia sparsa130 (inset reduction of DPPH82), and (c) Aerva lanata at different concentrations.127 (d) α-Amylase enzyme inhibition potential of Geranium wallichianum leaves extract mediated cobalt oxide NPs,26 and (e) protein kinase inhibition potential of Rhamnus virgata leaf extract mediated cobalt oxide NPs.144 | ||
5.2 Larvicidal activity and docking studies
The parasitology of green synthesized cobalt oxide NPs has been recently carried out by Gowthami et al. against urban mosquito larvae Culex quinquefasciatus, by using Mollugo oppositifolia L. aqueous leaf extract as bioreductant. The biosynthesized Co3O4 NPs displayed remarkable larvicidal activity, possessing 34.96 μg ml−1, LD50 value, compared to both the aqueous plant extract and the control, permethrin (Table 8).21 Similarly, the docking studies of green synthesized Co3O4 NPs with larvicidal odorant 3OGN binding protein revealed significant binding affinity of −8.5 kcal mol−1 as compared to the control, permethrin (–4.4 kcal mol−1). Since, the protein-ligand binding interaction is driven by the hydrogen bonding, therefore the hydrogen donor and acceptor bond distance should be less than 3.5 Å.21 The green synthesized Co3O4 NPs, in this case, exhibit three hydrogen bond interaction with amino acids Asp118, His121, and Phe123 attributing to bond distance, 2.10, 1.63, and 1.98, respectively (Fig. 7D(a)), indicating excellent inhibition ability in larvicidal mosquito 3OGN protein.21 Green cobalt oxide NPs exhibit potent larvicidal activity, particularly against mosquito larvae, due to their ability to generate ROS and disrupt cellular function in larvae. Their eco-friendly nature makes them a viable alternative to chemical pesticides, reducing environmental harm while effectively targeting vectors of diseases such as malaria and dengue.| Compound | Mortality (%)/concentration (μg ml−1) | LD50 (μg ml−1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | 75 | 50 | 25 | ||
| Aqueous plant extract | 60.20 ± 1.64 | 46.78 ± 0.24 | 24.16 ± 1.42 | 10.86 ± 0.84 | 82.41 |
| Co3O4 NPs | 100 ± 0.00 | 82.14 ± 1.25 | 68.48 ± 0.68 | 32.86 ± 1.20 | 34.96 |
| Permethrin (control) | 70 ± 0.67 | 46 ± 1.29 | 30 ± 1.78 | 16 ± 0.98 | 72.44 |
5.3 Antioxidant activity
Free radicals, regularly generated in the human body, can deteriorate lipids, DNA, and proteins, causing diseases like cancer and cardiovascular issues.131 The antioxidants present in the plant or microbial extract counteract these harmful effects.177 Cobalt oxide NPs, as electron donors, stop radical chain reactions by stabilizing free radicals.82 It has been observed that DPPH scavenging activity of green synthesized cobalt oxide NPs shows increased antioxidant activity with higher concentrations.178 Most commonly used DPPH assay (2,2-diphenylpicrylhydrazyl) tests the scavenging and antioxidant ability of cobalt oxide NPs by eqn (2):
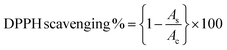 | (2) |
5.4 Enzyme inhibition
Green synthesized cobalt oxide (CoO) NPs have shown potential in inhibiting enzymes that can cause chronic diseases if persistent. The inhibition of the α-amylase enzyme, which helps prevent prolonged high glucose levels that can lead to diabetes, is recently studied. CoO NPs synthesized from G. wallichianum showed no inhibition at 1 μg ml−1 but achieved 36% inhibition at 200 μg ml−1 (Fig. 7D(d)). The study used a reaction mixture containing 25 μl enzyme, 15 μl PBS, 40 μl starch solution, and 10 μl cobalt oxide NPs, incubated for 30 minutes at 50 °C, with distilled water and acarbose as controls.26Similarly, bioinspired CoO NPs from Rhamnus virgata leaf extract were tested for inhibiting the cancer-related protein kinase enzyme Fig. 7D(e). While the enzyme itself doesn't cause cancer, it promotes phosphorylation, crucial for metabolic and genetic processes, and its malfunction can lead to carcinoma. The inhibition study using Streptomyces 85E fungal strains showed a zone of inhibition up to 18 mm at 1200 μg ml−1. The disc method involved incubating 10 μl of CoO NPs on a microbial lawn for 72 hours at 30 °C, with surfactin and DMSO as controls.144 Therefore, it suggests that the green-mediated cobalt oxide NPs have potential in managing neurological disorders and diabetes by inhibiting the responsible enzymes.
5.5 Anticancer activity
Cancer remains a leading cause of global mortality, with nearly 10 million deaths annually and an estimated economic burden of $25.2 trillion from 2020–2050.179,180 Researchers are exploring cost-effective alternatives to traditional anticancer agents, with cobalt oxide NPs emerging as promising candidates due to their lower toxicity,106 ferromagnetic properties,101 and cytotoxicity.181 Studies on Co3O4 NPs synthesized using rosemary leaf extract showed that at lower concentrations (≤31.25 μg ml−1), they were non-toxic to Hep G2 and MCF-7 cancer cells, but at 125 μg ml−1, metabolic activity decreased significantly (Fig. 8A(a–c))20 while G. sparsa mediated NPs showed 80% mortality against HepG2 cells at 500 μg ml−1 (Fig. 8A(d)).82 Another study on cobalt oxide NPs derived from Euphorbia tirucalli plant showed effectiveness against MCF-7 breast cancer cells at different concentrations, with the highest being 100 mg ml−1. For this, a 96-well microtiter plate was seeded with 1 × 105 cells per ml at 37 °C and incubated for 24 h with 5% CO2 in a humidified environment.152 Similarly, G. wallichianum leaves mediated cobalt oxide NPs exhibited ∼70% mortality at 500 μg ml−1 with an IC50 value of 31.4 μg ml−1 (Fig. 8A(e)).26 Another study using red algae-derived CoO NPs reported ∼80% mortality at 500 μg ml−1 and an IC50 value of 41.4 μg ml−1.31 Cobalt oxide NPs dissolved in acid present in the stomach having pH around 4.5 and overall, are capable to penetrate cell membranes and dissolve, leading to cell death.82 Overall, the green synthesized cobalt oxide NPs demonstrated cytotoxicity against cancer cells. Their small size and surface bioactivity allow them to interact with and penetrate cancer cells more efficiently, inducing apoptosis through oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction. These NPs can potentially be used for targeted cancer therapy with minimal toxicity to healthy cells and additionally warranting further investigation in in vivo models, 3D and 4D bioprinting of tissue engineering.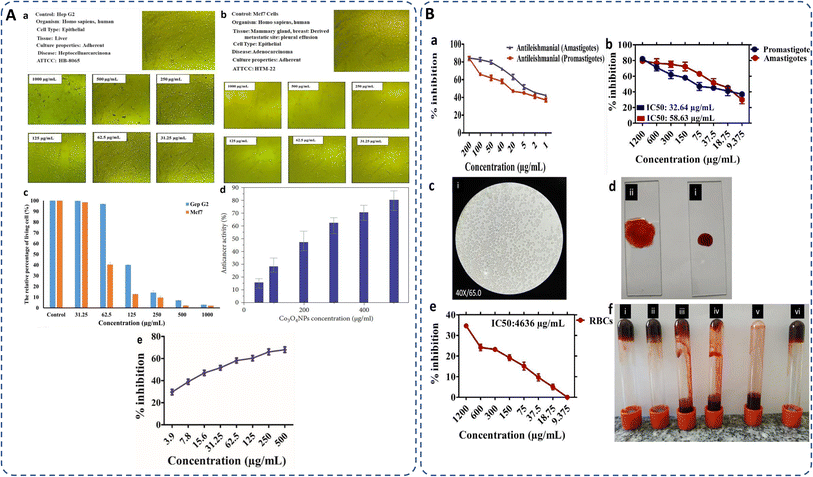 | ||
| Fig. 8 (A) Microscopic images of (a) Hep G2 and (b) Mcf7 cancer cells after treatment with various concentrations of Co3O4 NPs synthesized using rosemary leaf extract (c) The proportions of viable cells of Hep G2 and Mcf7 cancer cells following exposure to varying concentrations of Co3O4 NPs produced utilizing rosemary leaf extracts,20 (d) anticancer potency of cobalt oxide NPs against HepG2 cancer cell82 (e) cytotoxicity against HepG2 cancer cell line.26 (B) Antileishmanial activity of (a) G. wallichianum26 (b) Rhamnus virgata-assisted cobalt oxide NPs at different concentrations.144 (c) Microscopic images of less hemolytic activity of biosynthesized cobalt oxide NPs in red blood cells.31 (d) Thrombolytic activity of biosynthesized cobalt oxide NPs;31 (e) haemolytic activity of Rhamnus virgata mediated cobalt oxide (CoO) NPs against human RBCs144 and (f) anticoagulating behaviour of green synthesized cobalt oxide NPs.31 | ||
5.6 Antileishmanial activity
The capability of a substance to inhibit or kill Leishmania parasites (Leishmania tropica), causing the disease leishmaniasis, is referred to as antileishmanial activity. Leishmaniasis affects millions in over 98 countries, with current treatments being costly, toxic, and drug-resistant.22,182 Cobalt oxide NPs offer a promising solution due to their antileishmanial properties. Leishmania has a digenetic life cycle, existing as motile promastigotes outside the body and non-motile amastigotes inside the body.26,124 Khalil et al. for the first time demonstrated a dose-dependent antileishmanial response by Sageretia thea plant-mediated CoO NPs along with its vaccination-based prophylaxis.124 G. wallichianum biogenically produced cobalt oxide NPs showed higher activity against amastigotes (IC50: 3.12 μg ml−1) compared to promastigotes (IC50: 9.53 μg ml−1), with maximum inhibition at 200 μg ml−1. The MTT cytotoxic test confirmed higher susceptibility of amastigotes (Fig. 8B(a)).26 Similarly, R. virgata plant-derived CoO NPs revealed dose-dependent activity, with amastigotes (IC50: 58.63 μg ml−1) and promastigotes (IC50: 32.64 μg ml−1) when exposed to various concentrations (1200–9.375 μg ml−1) for 72 hours (Fig. 8B(b)).144 The efficacy of green synthesized cobalt oxide NPs in treating and vaccinating against leishmaniasis is largely dependent on the active chemicals present in the source extract, which determines the IC value. Despite varying IC values, these NPs exhibit a consistent trend of antileishmanial activity. Overall, green synthesized cobalt oxide NPs have shown promise in combating leishmaniasis and hold potential for treating other parasitic diseases which need further exploration.5.7 Haemolytic, anticoagulant and thrombolytic activity
The biocompatibility of cobalt oxide NPs is assessed through hemolytic assays.31 Increased hemolytic activity reduces antibacterial efficiency due to erythrocyte membrane interaction with peptide antibiotics, causing hemoglobin leakage.178 Materials with hemolysis activity over 5% are considered hemolytic, 2–5% as mildly hemolytic, and below 2% as non-hemolytic, per American Society recommendations.144,183 G. wallichianum leaf-derived cobalt oxide NPs are non-hemolytic at 2 μg ml−1, mildly hemolytic at 5–40 μg ml−1, and hemolytic above 45 μg ml−1.26 On comparing the hemolytic potential of cobalt oxide NPs, Trinton-X-100 shows 97.3% toxicity whereas red algae derived NPs shows only 5.3% toxicity.82 Similar results were observed by Ajarem et al. exhibiting 2.3% toxicity compared to 97.3% for Triton-X-100 and 1.01% for PBS (Fig. 8B(c)).31 R. virgata-derived NPs are non-hemolytic at 9.375 μg ml−1 but highly hemolytic at 1200 μg ml−1 (IC50: 4636 μg ml−1) (Fig. 8B(e)).144 So, overall, the green synthesized NPs exhibit dose-dependent least toxicity. Hemolytic activity is calculated as eqn (3):183
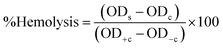 | (3) |
Additionally, biosynthesized cobalt oxide NPs possesses anticoagulating and thrombolytic activity. Evaluation studies revealed that blood samples thickened and formed clots in a dose-dependent manner with green-synthesized cobalt oxide NPs. Thrombolytic studies indicated that blood clots dissolved within 30 minutes of adding cobalt oxide NPs (Fig. 8B(d)). Fig. 8B(f) demonstrates that increasing Co3O4 NP concentration from 10 μl to 50 μl enhanced anticoagulating activity, reaching a maximum at 50 μl.31 Overall, green-synthesized cobalt oxide NPs have shown promise in biomedical applications related to blood. Studies indicate that these NPs can exhibit hemolytic activity at certain concentrations, making them a candidate for drug delivery applications. Additionally, their anticoagulant and thrombolytic properties suggest potential for treating blood clot-related disorders, but there is a limited amount of research on the biocompatibility of cobalt oxide NPs. In-depth studies on their anticoagulating and thrombolytic properties, with varying parameters, such as size and stability of NPs, need to be further explored.
Several studies have shown that such metal oxide NPs exhibit different toxicity levels depending on their concentration, route of administration, and the type of cells or organisms they interact with.79,184 Instead, green methods help mitigate the toxicity of cobalt oxide NPs. The toxicity of cobalt oxide NPs can indeed be dose-dependent.79 In a particular investigation,111 cobalt oxide NPs synthesized through a green method were eco-toxically evaluated; the findings indicate that these NPs were predominantly very minimal toxicity and possessed minimal risk to environmental systems. They reported that these NPs exhibit only lower toxicity at significantly high concentrations, specifically at 750 μg per disc, therefore, it is safe for living organisms and can be used for various applications, including in medicines.111 Most of the related studies generally do not focus on the amount of toxicity. But on the basis of other studies such as, cytotoxicity, hemolytic studies, we can analyze and develop an idea regarding their toxicity. Table 9 shows a generalized analysis of dose-dependent toxicity of the biosynthesized cobalt oxide NPs.
| Nanoparticle source | Toxicity dose | Tested organism/cells | Observations | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Geranium wallichianum | 2 μg ml | Human erythrocyte and macrophages | Non hemolytic | 26 |
| Geranium wallichianum | 5–40 μg ml | Human erythrocyte and macrophages | Slightly hemolytic | 26 |
| Geranium wallichianum | >45 μg ml | Human erythrocyte and macrophages | Hemolytic | 26 |
| Rosemary leaf extract | ≤31.25 μg ml | MCF-7 and Hep G2 cancer cells | Non-toxic | 20 |
| ≤62.5 μg ml | ||||
| Rosemary leaf extract | 125 μg ml | Hep G2 and MCF-7 cancer cells | Toxic effect | 20 |
| Grateloupia sparsa | 500 μg ml | HepG2 cell line | Anticancer activity (80%) | 82 |
| Red algae (aqueous extract) | 500 μg ml | HepG2 cell line | Anticancer activity | 31 |
| Nodosilinea nodulosa | 200 μg ml | Brine shrimp | High cytotoxicity | 79 |
| Nodosilinea nodulosa | 50 μg ml | Brine shrimp | Low cytotoxicity | 79 |
5.8 Drug sensing
Sensing activity of sensors is analyzed by calculating the sensors resistance in different environment. Recently, Elaeagnus angustifolia leaf extract-mediated cobalt oxide NPs has been explored as a bioreductant and stabilizing agent for drug sensing abilities. Dopamine (DA) and mefenamic acid (MFA) sensing abilities of cobalt oxide (Co3O4) NPs with graphene oxide (GO) and carbon paste electrode (CPE), were studied with enhancing electron transfer processes for DA and MFA. Under optimized conditions, the electrode showed a linear response to DA (0.5–250 μM) and MFA (1–500 μM) with detection limits of 0.15 μM for DA and 0.3 μM for MFA. Differential pulse voltammetry (DPV) analysis in phosphate buffer (pH 7) identified the best performance with 6% GO and 8% Co3O4 NPs modifications. The Co3O4NPs/GO/CPE configuration exhibited the highest oxidation peak currents, indicating superior sensitivity for simultaneous DA and MFA detection (Fig. 9).185 Overall, the drug-sensing capabilities of biogenically synthesized cobalt oxide NPs demonstrate their efficacy and potential for broader applications. These NPs can be further explored beyond drug sensing, encompassing areas such as motion detection, conductivity, mechanical properties, pulse monitoring, stress–strain measurement, and pressure sensing on nerves, thus highlighting their extensive applicability in the medical field.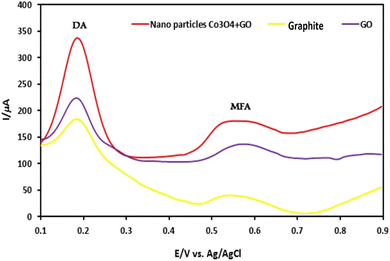 | ||
| Fig. 9 Differential pulse voltammogram (DPV) study showing sensing abilities of Elaeagnus angustifolia leaf extract mediated cobalt oxide NPs with GO on CPE for sensing dopamine (DA) and mefenamic acid (MFA).185 | ||
6. Enhanced activity of green synthesized cobalt oxide NPs
The green synthesized cobalt oxide NPs influence the controllable morphology, and improve the crystallinity of NPs which can lead to enhanced activity of NPs.83 In green methods, biomolecules from plant extracts can bind to the surface of the NPs, introducing functional groups like carboxyl, hydroxyl, or amino groups. These functional groups can enhance the interaction with reactants and promote specific properties.104 Plant extracts also contain biomolecules like proteins, enzymes, or polysaccharides, which can act as reducing, capping, and stabilizing agents during NP formation.131 These are the reasons behind the enhanced activity of green synthesized cobalt oxide NPs as compared to conventionally synthesized NPs. For instance, Adino et al. reported the enhanced antibacterial activity of green synthesized cobalt oxide NPs as compared to other conventionally synthesized cobalt oxide NPs, even at low concentrations (25 μg ml−1). This is because, in biologically synthesized Co3O4 NPs, the generation of reactive oxygen species is significantly high which facilitates the inhibition or kill the bacteria due to the presence of phytochemicals emanating from Phytolacca dodecandra (plant extract) and also due to the relatively higher surface area of NPs to volume ratio in case of green synthesized ones.1087. Challenges and future perspective
Despite the promising potential of biogenic synthesis methods for cobalt oxide NPs, several challenges need to be addressed for widespread application and scalability. One significant challenge is optimizing synthesis protocols to ensure reproducibility, uniformity, and control over the size, shape, and properties of the synthesized NPs. Variability in the composition of natural extracts and microorganisms can lead to inconsistencies in NPs synthesis, necessitating standardized protocols and rigorous quality control measures. Elucidating the underlying mechanisms governing biogenic NPs synthesis is another challenge. The precise interactions of bioreductants, reducing agents, and phytochemicals in NP formation remain poorly understood. Further research is needed to unravel these complex mechanisms and optimize synthesis conditions to improve yield and properties of cobalt oxide NPs. Scalability presents another challenge, especially for large-scale biomedical applications. Innovative research approaches, interdisciplinary collaboration, and concerted efforts from academia, industry, and regulatory bodies are essential to overcome these challenges.Although cobalt oxide NPs have shown promise in various biomedical applications, optimizing their biocompatibility is essential. Future research should focus on minimizing cytotoxicity through controlled synthesis techniques, ensuring safer interactions with biological tissues. The intrinsic antimicrobial and anticancer activities of cobalt oxide NPs are promising, future research coupled with bio-inspired synthesis methods with predictable mechanism, could enhance their therapeutic efficacy and promote their use in clinical applications.
Beyond antimicrobial and anticancer studies, more research is required to explore biological interactions such as drug delivery, biosensing, and protein binding. For targeted drug delivery, cobalt oxide NPs can be engineered for targeted drug delivery systems by functionalizing them with specific biomolecules. Continued advancements in surface modifications and smart nanocarrier designs could improve their efficiency in delivering drugs to diseased cells while reducing side effects. The development of multifunctional cobalt oxide NPs for theranostic applications, combining therapeutic and diagnostic capabilities, holds considerable promise. Future research should explore the integration of imaging, drug delivery, and therapeutic properties into a single nanoplatform for real-time disease monitoring and treatment.
Additionally, the efficacy, safety, and long-term stability of biogenic cobalt oxide NPs need comprehensive toxicity studies and in vivo assessments. Concerns related to biocompatibility, cytotoxicity, and potential environmental impact must be addressed to ensure the safe and responsible use of these NPs in tissue engineering, 3D bioprinting, biosensors, organ on chip and real-world applications. By addressing these issues, we can unlock the full potential of biogenic cobalt oxide NPs, harnessing their unique properties for critical societal, environmental, and technological applications.
8. Conclusion
Overall, the synthesis of cobalt oxide NPs via green and sustainable methods represents a significant advancement in nanomaterial synthesis particularly in biomedical applications. By exploring natural resources and harnessing the unique capabilities of plant, its parts, algae, fungi, and microorganisms as reducing and stabilizing agents, researchers can synthesize cobalt oxide NPs in a sustainable, eco-friendly, and cost-effective manner by circumventing the limitations associated with traditional synthesis methods. The biological source plays a vital role in determining the reducing efficacy, size and stability of the NPs resulting into their effect on biocompatibility. Since there is a gap and large avenue for diverse studies and factors affecting their biocompatibility which need to be explored. Therefore, we have highlighted the diverse sources, methods, probable mechanism involved in the biogenic synthesis of cobalt oxide NPs, emphasizing their eco-friendly attributes, by sophisticatedly analysing their structure, morphology, size and stability, and their biocompatibility potential for biomedical applications. The biogenically derived cobalt oxide NPs shows protean performance in biomedical field, including antibacterial, antifungal, larvicidal, antioxidant, enzyme inhibition, anticancer, antileishmanial, hemolytic, anticoagulant, thrombolytic activities and drug sensing ability. Therefore, the convergence of green synthesis approaches with nanotechnology holds great promise for advancing sustainable practices, addressing environmental, and adaptative challenges, and paving the way for the development of innovative environment benign solutions for the future medical approaches.Data availability
No primary research results, software or code have been included and no new data were generated or analysed as part of this review.Author contributions
Annu.: conceptualization, investigation, formal analysis, writing – original draft preparation, writing – reviewing and editing, visualization. Muskan Sahu: investigation, writing – original draft preparation. Somesh Singh: investigation, writing – original draft preparation. Satypal Prajapati: investigation, writing – reviewing and editing. Dinesh K. Verma: supervision. Dong Kil Shin: supervision, resources.Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict and competing interest that could have appeared to influence the paper.Acknowledgements
This work has not received any external funding.References
- M. Siddique, N. M. Khan, M. Saeed, S. Ali and Z. Shah, Z. Phys. Chem., 2021, 235, 663–681 CrossRef CAS.
- M. P. Nikolova and M. S. Chavali, Biomimetics, 2020, 5, 27 CrossRef CAS.
- W. Lin, Chem. Rev., 2015, 115, 10407–10409 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Rasheed, F. Nabeel, M. Bilal and H. M. N. Iqbal, Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol., 2019, 19, 101154, DOI:10.1016/j.bcab.2019.101154.
- W. J. Stark, P. R. Stoessel, W. Wohlleben and A. Hafner, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2015, 44, 5793–5805 RSC.
- Annu, M. Mittal, S. Tripathi and D. K. Shin, Polymers, 2024, 16, 294 CrossRef.
- M. Ovais, A. T. Khalil, A. Raza, N. U. Islam, M. Ayaz, M. Saravanan, M. Ali, I. Ahmad, M. Shahid and Z. K. Shinwari, Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 2018, 102, 4393–4408 CrossRef CAS.
- Annu, A. Ali and S. Ahmed, in Handbook of Ecomaterials, ed. L. M. T. Martínez, O. V. Kharissova and B. I. Kharisov, Springer International Publishing, Cham, 2018, pp. 1–45 Search PubMed.
- N. Alizadeh and A. Salimi, J. Nanobiotechnol., 2021, 19, 26 CrossRef CAS.
- F. Séby, in Analysis and Characterisation of Metal-Based Nanomaterials, ed. R. Milacic, J. Scancar, J. Vidmar and H. Goenaga-Infante, Elsevier, 2021, vol. 93, pp. 381–427 Search PubMed.
- R. Huang, S. Zhang, W. Zhang and X. Yang, IET Collab. Intell. Manuf., 2021, 3, 281–289 CrossRef.
- M. P. Browne, Z. Sofer and M. Pumera, Energy Environ. Sci., 2019, 12, 41–58 RSC.
- J. W. Na, H. J. Kim, S. Hong and H. J. Kim, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2018, 10, 37207–37215 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Liu, J. Iocozzia, Y. Wang, X. Cui, Y. Chen, S. Zhao, Z. Li and Z. Lin, Energy Environ. Sci., 2017, 10, 402–434 RSC.
- C. Wang, H. Wang, M. Lin and X. Hu, Process Saf. Environ. Prot., 2015, 93, 265–273 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Becker, S. Schroecksnadel, S. Geisler, M. Carriere, J. M. Gostner, H. Schennach, N. Herlin and D. Fuchs, Food Chem. Toxicol., 2014, 65, 63–69 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Pagar, S. Ghotekar, K. Pagar, S. Pansambal and R. Oza, J. Chem. Rev., 2019, 1, 260–270 CrossRef.
- S. N. F. Moridon, M. I. Salehmin, M. A. Mohamed, K. Arifin, L. J. Minggu and M. B. Kassim, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2019, 44, 25495–25504 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Raeisi, H. Q. Alijani, M. Peydayesh, M. Khatami, F. Bagheri Baravati, F. Borhani, M. Šlouf and S. Soltaninezhad, Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng., 2021, 44, 1423–1432 CrossRef CAS.
- N. Al-Qasmi, Molecules, 2022, 27, 8163 CrossRef CAS.
- P. Gowthami, A. Kosiha, S. Meenakshi, G. Boopathy, A. G. Ramu and D. Choi, Sci. Rep., 2023, 13, 1–11 CrossRef.
- A. Waris, M. Din, A. Ali, S. Afridi, A. Baset, A. U. Khan and M. Ali, Open Life Sci., 2021, 16, 14–30 CrossRef CAS.
- R. Srivastava, S. Bhardwaj, A. Kumar, R. Singhal, J. Scanley, C. C. Broadbridge and R. K. Gupta, Nanomaterials, 2022, 12, 1–15 Search PubMed.
- M. Sivachidambaram, J. J. Vijaya, K. Kaviyarasu, L. J. Kennedy, H. A. Al-Lohedan and R. Jothi Ramalingam, RSC Adv., 2017, 7, 38861–38870 RSC.
- J. S. Chen, T. Zhu, Q. H. Hu, J. Gao, F. Su, S. Z. Qiao and X. W. Lou, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2010, 2, 3628–3635 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Iqbal, B. A. Abbasi, R. Batool, A. T. Khalil, S. Hameed, S. Kanwal, I. Ullah and T. Mahmood, Mater. Res. Express, 2019, 6, 115407 CrossRef.
- F. Liu, H. Su, L. Jin, H. Zhang, X. Chu and W. Yang, J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2017, 505, 796–804 CrossRef CAS.
- A. J. Laghari, U. Aftab, A. A. Shah, M. Y. Solangi, M. I. Abro, S. I. Al-Saeedi, N. Naeim, A. Nafady, B. Vigolo, M. Emo, A. I. Molina, A. Tahira and Z. H. Ibhupoto, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2023, 48, 15447–15459 CrossRef CAS.
- R. V. Poonguzhali, E. R. Kumar, C. Srinivas, M. Alshareef, M. M. Aljohani, A. A. Keshk, N. M. El-Metwaly and N. Arunadevi, Sens. Actuators, B, 2023, 377, 133036 CrossRef CAS.
- E. Alsharaeh, Y. Mussa, F. Ahmed, Y. Aldawsari, M. Al-Hindawi and G. K. Sing, Ceram. Int., 2016, 42, 3407–3410 CrossRef CAS.
- J. S. Ajarem, S. N. Maodaa, A. A. Allam, M. M. Taher and M. Khalaf, J. Cluster Sci., 2022, 33, 717–728 CrossRef CAS.
- R. K. Nare, S. Ramesh, P. K. Basavi, V. Kakani, C. Bathula, H. M. Yadav, P. B. Dhanapal, R. K. R. Kotanka and V. R. Pasupuleti, Sci. Rep., 2022, 12, 1998 CrossRef CAS.
- V. Usai, T. Mugadza, F. Chigondo, M. Shumba, T. Nharingo, M. Moyo and P. Tshuma, Polyhedron, 2019, 157, 192–199 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Chen, Y. Wang and C. Xu, Mater. Lett., 2016, 163, 72–75 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Mukhiya, A. P. Tiwari, K. Chhetri, T. Kim, B. Dahal, A. Muthurasu and H. Y. Kim, Chem. Eng. J., 2021, 420, 129679 CrossRef CAS.
- Q.-Y. Chen, S. U. Haq, Z.-H. Xing and Y.-H. Wang, J. Photonics Energy, 2020, 10, 1–8 Search PubMed.
- J. Y. Choi, C. K. Lim, B. Park, M. Kim, A. Jamal and H. Song, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2019, 7, 15068–15072 RSC.
- S. Chattopadhyay, S. K. Dash, T. Ghosh, D. Das, P. Pramanik and S. Roy, Cancer Nanotechnol., 2013, 4, 103–116 CrossRef.
- J. Liu, C. Zhou, W. Yue, B. Yan, Y. Lin and A. Huang, Chem. Phys. Lett., 2020, 756, 137817 CrossRef CAS.
- C. N. Yonti, P. K. Tsobnang, R. L. Fomekong, F. Devred, E. Mignolet, Y. Larondelle, S. Hermans, A. Delcorte and J. L. Ngolui, Nanomaterials, 2021, 11, 2833, DOI:10.3390/nano11112833.
- S. A. Sardjono and P. Puspitasari, AIP Conf. Proc., 2020, 2231, 335–343 Search PubMed.
- A. Khalil, N. Ali, A. Khan, A. M. Asiri and T. Kamal, Int. J. Biol. Macromol., 2020, 164, 2922–2930 CrossRef CAS.
- T. A. H. Abbas, L. H. Slewa, H. A. Khizir and S. A. Kakil, J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron., 2017, 28, 1951–1957 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Büyükyazi, C. Hegemann, T. Lehnen, W. Tyrra and S. Mathur, Inorg. Chem., 2014, 53, 10928–10936 CrossRef.
- A. S. Bhatt, D. K. Bhat, C. Tai and M. S. Santosh, Mater. Chem. Phys., 2011, 125, 347–350 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Pang, G. Long, S. Jiang, Y. Ji, W. Han, B. Wang, X. Liu, Y. Xi, D. Wang and F. Xu, Chem. Eng. J., 2015, 280, 377–384 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Farhadi, M. Javanmard and G. Nadri, Acta Chim. Slov., 2016, 63, 335–343 CrossRef CAS.
- K. H. Mahmoud, Polym. Compos., 2016, 37, 1881–1885 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Kalpana, V. S. Bhat, G. Hegde, T. N. Prabhu and P. N. Anantharamaiah, Chem. Pap., 2024, 78, 343–356, DOI:10.1007/s11696-023-03093-8.
- J. Ahmed, T. Ahmad, K. V Ramanujachary, S. E. Lofland and A. K. Ganguli, J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2008, 321, 434–441 CrossRef CAS.
- Z. L. Goh, N. M. Saidi, N. K. Farhana, S. Bashir, J. Iqbal, K. Ramesh, S. Ramesh, S. Wageh and A. Kalam, Sustainable Energy Technol. Assess., 2022, 49, 101746 CrossRef.
- E. N. Ghaem, D. Dorranian and A. H. Sari, Phys. E, 2020, 115, 113670 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Yang, Y. Hu, X. Zhang and G. Qiu, Mater. Lett., 2004, 58, 387–389 CrossRef CAS.
- D. Zou, C. Xu, H. Luo, L. Wang and T. Ying, Mater. Lett., 2008, 62, 1976–1978 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Ozkaya, A. Baykal, M. S. Toprak, Y. Koseoğlu and Z. Durmuş, J. Magn. Magn. Mater., 2009, 321, 2145–2149 CrossRef CAS.
- G. Rathika, V. Suba, D. S. Lakshmi and R. Rani, J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater., 2022, 32, 3153–3169 CrossRef CAS.
- N. Patel, A. Santini, V. Bello, G. Mattei and A. Miotello, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2013, 235, 784–791 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Wang, X. Jiang, J. Liu, H. Guo and C. Liu, Electrochim. Acta, 2015, 182, 613–620 CrossRef CAS.
- P. S. Gaikar, S. T. Navale, V. V Jadhav, P. V Shinde, D. P. Dubal, P. R. Arjunwadkar, F. J. Stadler, M. Naushad, A. A. Ghfar and R. S. Mane, Electrochim. Acta, 2017, 253, 151–162 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Roy, O. Bulut, S. Some, A. K. Mandal and M. D. Yilmaz, RSC Adv., 2019, 9, 2673–2702 RSC.
- S. P. Patil, R. Y. Chaudhari and M. S. Nemade, Talanta Open, 2022, 5, 100083 CrossRef.
- B. A. Al Jahdaly, A. Abu-Rayyan, M. M. Taher and K. Shoueir, ACS Omega, 2022, 7, 23673–23684 CrossRef CAS.
- F. K. Sabir, E. T. Bekele, B. A. Gonfa, G. D. Edossa and A. T. Adino, J. Nanostruct., 2021, 11, 577–587 Search PubMed.
- A. K. Singh, Curr. Res. Green Sustainable Chem., 2022, 5, 100270 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Thulasi Krishnan, S. Parveen, A. S. El Newehy, G. Chandramohan and G. Kalaiarasi, J. Indian Chem. Soc., 2024, 101, 101187 CrossRef CAS.
- N. Sivagnanam, S. Pichai, P. Perumal and V. Kandan, Chem. Pap., 2024, 78, 5527–5544 CrossRef CAS.
- D. K. Sarkar, V. Selvanathan, M. Mottakin, M. A. Islam, H. Almohamadi, N. H. Alharthi and M. Akhtaruzzaman, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2024, 51, 700–712, DOI:10.1016/j.ijhydene.2023.07.042.
- A. Kashinath Kshirsagar, P. Ganesh Bhutekar, S. Shivaji Bankar, R. Tanaji More, S. Tanhaji More, S. Ramrao Mirgane and E. Adm, Theory Pract., 2024, 30, 3149–3154 Search PubMed.
- P. B. Chole and M. Bt, Plant Sci. Today, 2024, 11, 221–232 CAS.
- A. K. Saleh, A. S. Hussein, J. B. Ray and A. S. Elzaref, Nano-Struct. Nano-Objects, 2024, 38, 101174 CrossRef CAS.
- F. W. Alemu and T. D. Zeleke, Nanomed. J., 2024, 11, 80–92 CAS.
- S. A. Alshareef and A. E. Albalawi, Int. J. Biol. Macromol., 2024, 279, 135028 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Kavica, P. Rajesh, V. Velmani and G. T. Parethe, J. Environ. Nanotechnol., 2024, 13, 85–91 CrossRef CAS.
- L. A. Kolahalam, K. R. S. Prasad, P. M. Krishna and N. Supraja, Results Chem., 2024, 7, 101367 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Drummer, O. Mkhari and M. Chowdhury, Next Nanotechnol., 2024, 6, 100069 CrossRef.
- M. S. AlSalhi, G. Oza, I. Castillo-Maldonado and A. Sharma, Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol., 2024, 56, 103025 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Zeb, Z. Anjum, S. Mumtaz, M. Khalid and M. Hafeez, Desalin. Water Treat., 2024, 317, 100165 CrossRef.
- A. Sidorowicz, N. Yigit, T. Wicht, M. Stöger-Pollach, A. Concas, R. Orrù, G. Cao and G. Rupprechter, RSC Adv., 2024, 14, 4575–4586 RSC.
- F. Aslam, L. A. Minhas, M. Kaleem, A. Jabeen, A. Akram, H. A. Malik, H. M. U. Farooqi, M. W. Amin and A. S. Mumtaz, Bionanoscience, 2024, 1–15, DOI:10.1007/s12668-024-01551-5.
- F. Momen Eslamiehei, M. Mashreghi and M. M. Matin, Cancer Nanotechnol., 2024, 15, 22 CrossRef CAS.
- G. Asha, V. Rajeshwari, G. Stephen, S. Gurusamy and D. Carolin Jeniba Rachel, Mater. Today: Proc., 2019, 48, 486–493 Search PubMed.
- A. K. Hajri, M. A. Albalawi, I. Alsharif and B. Jamoussi, Bioinorg. Chem. Appl., 2022, 2022, 3977935, DOI:10.1155/2022/3977935.
- A. Imtiyaz, A. Singh and R. Gaur, Bionanoscience, 2024, 1–9, DOI:10.1007/s12668-024-01452-7.
- S. Iravani and R. S. Varma, Green Chem., 2020, 22, 2643–2661 RSC.
- N. Mubraiz, A. Bano, T. Mahmood and N. Khan, Agronomy, 2021, 11, 1–20 CrossRef.
- C. N. Hikaambo, L. Kaacha, S. Mudenda, M. N. Nyambe, B. Chabalenge, M. Phiri, L. L. Biete, T. M. Akapelwa, W. Mufwambi, M. Chulu and M. Kampamba, Pharmacol. Pharm., 2022, 13, 1–10 CrossRef CAS.
- C. T. Anuradha and P. Raji, J. Mol. Struct., 2022, 1262, 133065 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Safdar, H. E. A. Mohamed, K. Hkiri, A. Muhaymin and M. Maaza, Appl. Sci., 2023, 13, 9082, DOI:10.3390/app13169082.
- S. Y. Saeed, L. Raees, A. Mukhtiar, F. Khan, M. Khan, S. K. Shah, D. Ghafoor and K. Mazhar, Mater. Res. Express, 2022, 9, 105001, DOI:10.1088/2053-1591/ac9350.
- Kainat, M. A. Khan, F. Ali, S. Faisal, M. Rizwan, Z. Hussain, N. Zaman, Z. Afsheen, M. N. Uddin and N. Bibi, Saudi J. Biol. Sci., 2021, 28, 5157–5167 CrossRef CAS.
- J. K. Sharma, P. Srivastava, G. Singh, M. S. Akhtar and S. Ameen, Mater. Sci. Eng., B, 2015, 193, 181–188 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Batool, M. Hasan, M. Dilshad, A. Zafar, T. Tariq, A. Shaheen, R. Iqbal, Z. Ali, T. Munawar, F. Iqbal, S. G. Hassan, X. Shu and G. Caprioli, Biochem. Syst. Ecol., 2022, 105, 104535 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Savitha, S. Surendhiran, K. S. G. Jagan, A. Karthik, B. Kalpana and R. Senthilmurugan, J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron., 2023, 34, 1–19 CrossRef.
- H. W. Shim, A. H. Lim, J. C. Kim, E. Jang, S. D. Seo, G. H. Lee, T. D. Kim and D. W. Kim, Sci. Rep., 2013, 3, 1–9 Search PubMed.
- J. Singh, T. Dutta, K. H. Kim, M. Rawat, P. Samddar and P. Kumar, J. Nanobiotechnol., 2018, 16, 1–24 CrossRef.
- C. M. Hsu, Y. H. Huang, H. J. Chen, W. C. Lee, H. W. Chiu, J. P. Maity, C. C. Chen, Y. H. Kuo and C. Y. Chen, Mater. Today Commun., 2018, 14, 302–311 CrossRef CAS.
- H.-W. Shim, Y.-H. Jin, S.-D. Seo, S.-H. Lee and D.-W. Kim, ACS Nano, 2011, 5, 443–449 CrossRef CAS.
- N. Shreyash, S. Bajpai, M. A. Khan, Y. Vijay, S. K. Tiwary and M. Sonker, ACS Appl. Nano Mater., 2021, 4, 11428–11457 CrossRef CAS.
- P. Chelliah, S. M. Wabaidur, H. P. Sharma, M. J. Jweeg, H. S. Majdi, M. M. R. Munthir Mohammed, A. Iqbal and W. C. Lai, Water, 2023, 13, 910, DOI:10.3390/w15050910.
- I. Bibi, N. Nazar, M. Iqbal, S. Kamal, H. Nawaz, S. Nouren, Y. Safa, K. Jilani, M. Sultan, S. Ata, F. Rehman and M. Abbas, Adv. Powder Technol., 2017, 28, 2035–2043 CrossRef CAS.
- A. S. Vijayanandan and R. M. Balakrishnan, J. Environ. Manage., 2018, 218, 442–450 CrossRef CAS.
- D. C. Onwudiwe, M. P. Ravele and E. E. Elemike, Nano-Struct. Nano-Objects, 2020, 23, 100470 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Haq, F. Abbasi, M. Ben Ali, A. Hedfi, A. Mezni, W. Rehman, M. Waseem, A. R. Khan and H. Shaheen, Mater. Res. Express, 2021, 8, 075009 CrossRef CAS.
- D. Dayal Upadhyay, S. Singh, K. Bahadur Singh, N. Gautam, S. Shrivastava and G. Pandey, Inorg. Chem. Commun., 2023, 155, 110957 CrossRef CAS.
- R. Shanmuganathan, S. Sathiyavimal, Q. Hoang Le, M. M. Al-Ansari, L. A. Al-Humaid, G. K. Jhanani, J. Lee and S. Barathi, Environ. Res., 2023, 236, 116747 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Sundararaju, M. Arumugam and P. Bhuyar, Beni-Suef Univ. J. Basic Appl. Sci., 2020, 9, 1–9, DOI:10.1186/s43088-020-00070-y.
- E. S. R. El-Sayed, S. A. Mousa, D. A. M. Abdou, M. A. Abo El-Seoud, A. A. Elmehlawy and S. S. Mohamed, Saudi J. Biol. Sci., 2022, 29, 2463–2474 CrossRef CAS.
- A. T. Adino, G. D. Edosa, B. A. Gonfa, E. T. Bekele and F. K. Sabir, J. Nanostruct., 2021, 11, 577–587 CAS.
- Annu, S. Ahmed, G. Kaur, P. Sharma, S. Singh and S. Ikram, J. Appl. Biomed., 2018, 16, 221–231 CrossRef.
- R. A. Raimundo, J. N. Silva, T. R. Silva, A. J. M. Araújo, J. F. G. A. Oliveira, L. C. de Lima, M. A. Morales, M. M. Soares and D. A. Macedo, Mater. Lett., 2023, 341, 1–4 CrossRef.
- S. Dubey, J. Kumar, A. Kumar and Y. C. Sharma, Adv. Powder Technol., 2018, 29, 2583–2590 CrossRef CAS.
- Annu, S. Ahmed, G. Kaur, P. Sharma, S. Singh and S. Ikram, Toxicol. Res., 2018, 7, 923–930 CrossRef CAS.
- Annu, Z. I. Bhat, K. Imtiyaz, M. M. A. Rizvi, S. Ikram and D. K. Shin, Polymers, 2023, 15, 3477 CrossRef CAS.
- N. Akhlaghi, G. Najafpour-Darzi and H. Younesi, Adv. Powder Technol., 2020, 31, 3562–3569 CrossRef CAS.
- F. Chekin, S. M. Vahdat and M. J. Asadi, Russ. J. Appl. Chem., 2016, 89, 816–822 CrossRef CAS.
- R. Vinayagam, A. Hebbar, P. Senthil Kumar, G. Rangasamy, T. Varadavenkatesan, G. Murugesan, S. Srivastava, L. Concepta Goveas, N. Manoj Kumar and R. Selvaraj, Environ. Res., 2023, 216, 114766 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Diallo, A. C. Beye, T. B. Doyle, E. Park and M. Maaza, Green Chem. Lett. Rev., 2015, 8, 30–36 CrossRef CAS.
- M. R. AbuKhadra, A. S. Mohamed, A. M. El-Sherbeeny and M. A. Elmeligy, J. Hazard. Mater., 2020, 389, 122129 CrossRef CAS.
- T. M. Tien, C. H. Chen, C. T. Huang and E. L. Chen, Catalysts, 2022, 12, 1474, DOI:10.3390/catal12111474.
- T. N. J. I. Edison, R. Atchudan, M. G. Sethuraman and Y. R. Lee, J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng., 2016, 68, 489–495 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Fallahi and B. Norouzi, Ionics, 2020, 26, 1951–1961 CrossRef CAS.
- R. K. Das and A. K. Golder, Electrochim. Acta, 2017, 251, 415–426 CrossRef CAS.
- J. D. Bronzato, J. D. Bronzato, A. M. M. Brito, J. Bettini, M. R. Z. Passini, B. P. F. A. Gomes and I. L. Nantes, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2023, 609, 155193 CrossRef CAS.
- A. T. Khalil, M. Ovais, I. Ullah, M. Ali, Z. K. Shinwari and M. Maaza, Arabian J. Chem., 2020, 13, 606–619 CrossRef CAS.
- G. T. Parethe, P. Rajesh, P. Nathiya, M. Balaji and S. Kavica, World J. Adv. Res. Rev., 2023, 19, 001–009 CrossRef CAS.
- E. U. Ikhuoria, S. O. Omorogbe, B. T. Sone and M. Maaza, Sci. Technol. Mater., 2018, 30, 92–98, DOI:10.1016/j.stmat.2018.02.003.
- R. Manikandan, G. Vanitha, A. Prakasam, M. D. Navinkumar, K. Sathiyamoorthi and B. Dhinakaran, Pakistan Heart J., 2023, 56, 1162–1174 Search PubMed.
- M. Hafeez, R. Shaheen, B. Akram, Z. Ul-Abdin, S. Haq, S. Mahsud, S. Ali and R. T. Khan, Mater. Res. Express, 2020, 7, 025019, DOI:10.1088/2053-1591/ab70dd.
- A. Mohandes, M. Reza Aghamaali, Z. Sabouri and M. Darroudi, Mater. Sci. Eng., B, 2023, 297, 116782 CrossRef CAS.
- F. E. Ghadi, A. R. Ghara and A. Naeimi, Chem. Pap., 2018, 72, 2859–2869 CrossRef CAS.
- R. Govindasamy, V. Raja, S. Singh, M. Govindarasu, S. Sabura, K. Rekha, V. D. Rajeswari, S. S. Alharthi, M. Vaiyapuri, R. Sudarmani, S. Jesurani, B. Venkidasamy and M. Thiruvengadam, Molecules, 2022, 27, 5646, DOI:10.3390/molecules27175646.
- S. A. David, A. Doss, R. P. P. Pole, T. P. K. P. Rani, R. P. L. Reshmi and R. Rajalakshmi, Int. J. Nano Dimens., 2022, 13, 335–343 CAS.
- J. D. Bronzato, J. D. Bronzato, A. M. M. Brito, J. Bettini, M. R. Z. Passini, B. P. F. A. Gomes and I. L. Nantes, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2023, 609, 155193 CrossRef CAS.
- P. Saravanakumar, M. Muthukumar, R. R. Muthuchudarkodi and P. Ramkumar, Int. J. Recent Res. Aspects, 2018, 918–923 Search PubMed.
- M. Kiani, N. Rabiee, M. Bagherzadeh, A. M. Ghadiri, Y. Fatahi, R. Dinarvand and T. J. Webster, Nanomedicine, 2021, 32, 102331 CrossRef CAS.
- N. Al-Qasmi, Molecules, 2022, 29, 362–363 Search PubMed.
- T. Muthukumar, E. Arumugam, S. Chandrasekaran, C. Karuppiah and S. Kodirajan, Inorg. Chem. Commun., 2021, 123, 108305 CrossRef CAS.
- V. D. Rajeswari, A. S. Khalifa, A. Elfasakhany, I. A. Badruddin, S. Kamangar and K. Brindhadevi, Appl. Nanosci., 2023, 13, 1367–1375 CrossRef CAS.
- C. T. Anuradha and P. Raji, Appl. Phys. A: Mater. Sci. Process., 2021, 127, 1–9 CrossRef.
- S. Manzoor, G. Yasmin, N. Raza, J. Fernandez, R. Atiq, S. Chohan, A. Iqbal, S. Manzoor, B. Malik, F. Winter and M. Azam, Polymers, 2021, 13, 2669, DOI:10.3390/polym13162669.
- A. A. Urabe and W. J. Aziz, World News Nat. Sci., 2019, 24, 356–364 Search PubMed.
- A. Sani, A. Murad, D. Hassan, G. M. Channa, A. El-Mallul and D. I. Medina, Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res., 2023, 30, 20736–20745 CrossRef CAS.
- C. T. Anuradha and P. Raji, Ceram. Int., 2023, 49, 11689–11695 CrossRef CAS.
- B. A. Abbasi, J. Iqbal, Z. Khan, R. Ahmad, S. Uddin, A. Shahbaz, S. A. Zahra, M. Shaukat, F. Kiran, S. Kanwal and T. Mahmood, Microsc. Res. Tech., 2021, 84, 192–201 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Sidorowicz, V. Margarita, G. Fais, A. Pantaleo, A. Manca, A. Concas, P. Rappelli, P. L. Fiori and G. Cao, PLoS One, 2022, 17, e0274753 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Faisal, F. A. Jan, S. Saleem, R. Ullah, N. Wajidullah, N. Ullah and Salman, Nanotechnol. Environ. Eng., 2022, 7, 675–689 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Hasan, A. Zafar, I. Shahzadi, F. Luo, S. G. Hassan, T. Tariq, S. Zehra, T. Munawar, F. Iqbal and X. Shu, Molecules, 2020, 25, 1–17 CrossRef.
- K. Kombaiah, J. J. Vijaya, L. J. Kennedy, K. Kaviyarasu, R. J. Ramalingam and H. A. Al-Lohedan, J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol., 2018, 19, 2590–2598 CrossRef.
- L. Han, D. P. Yang and A. Liu, Biosens. Bioelectron., 2015, 63, 145–152 CrossRef CAS.
- J. B. Patil, S. J. Takate, S. T. Moharekar, B. H. Zaware and S. S. Moharekar, Orient. J. Chem., 2021, 37, 979–983 CAS.
- I. Shaheen and K. S. Ahmad, J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol., 2020, 95, 2898–2910 CrossRef CAS.
- I. K. Kgosiemang, R. Lefojane, P. Direko, Z. Madlanga, S. Mashele and M. Sekhoacha, Inorg. Nano-Met. Chem., 2020, 50, 1070–1080 CrossRef CAS.
- S. A. Memon, D. Hassan, J. A. Buledi, A. R. Solangi, S. Q. Memon and I. M. Palabiyik, Microchem. J., 2020, 159, 105480 CrossRef CAS.
- S. O. Ogunyemi, X. Xu, L. Xu, Y. Abdallah, M. Rizwan, L. Lv, T. Ahmed, H. M. Ali, F. Khan, C. Yan, J. Chen and B. Li, Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf., 2023, 257, 114935 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Ahmed, J. Hussain, F. Ullah and S. Asif, Engineering Engrxiv ArchiveIt, 2020, DOI:10.31224/osf.io/75fa6.
- S. K. Jesudoss, J. Judith Vijaya, P. Iyyappa Rajan, K. Kaviyarasu, M. Sivachidambaram, L. John Kennedy, H. A. Al-Lohedan, R. Jothiramalingam and M. A. Munusamy, Photochem. Photobiol. Sci., 2017, 16, 766–778 CrossRef CAS.
- R. A. Raimundo, J. N. Silva, T. R. Silva, A. J. M. Araújo, J. F. G. A. Oliveira, L. C. de Lima, M. A. Morales, M. M. Soares and D. A. Macedo, Mater. Lett., 2023, 341, 134196 CrossRef CAS.
- G. Pal, P. Rai and A. Pandey, Green Synthesis of Nanoparticles: A Greener Approach for a Cleaner Future, Elsevier Inc., 2018 Search PubMed.
- B. A. Omran, H. N. Nassar, S. A. Younis, R. A. El-Salamony, N. A. Fatthallah, A. Hamdy, E. H. El-Shatoury and N. S. El-Gendy, J. Appl. Microbiol., 2020, 128, 438–457 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Yang, W. Guan, B. Bai, Q. Xu and Y. Xiang, J. Alloys Compd., 2010, 504, 10–13 CrossRef.
- S. C. Kumari, V. Dhand and P. N. Padma, Nanomater. Appl. Biofuels Bioenergy Prod. Syst., 2021, 259–281 Search PubMed.
- H. W. Shim, C. S. Lee and D. W. Kim, J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol., 2010, 10, 1129–1134 CrossRef CAS.
- U. Kumar, A. Shete, A. S. Harle, O. Kasyutich, W. Schwarzacher, A. Pundle and P. Poddar, Chem. Mater., 2008, 20, 1484–1491 CrossRef CAS.
- H.-W. Shim, Y.-H. Jin, S.-D. Seo, S.-H. Lee and D.-W. Kim, ACS Nano, 2010, 5, 443–449 CrossRef.
- H.-W. Shim, A.-H. Lim, J.-C. Kim, E. Jang, S.-D. Seo, G.-H. Lee, T. D. Kim and D.-W. Kim, Sci. Rep., 2013, 3, 2325 CrossRef.
- G. M. Al-Senani and S. I. Al-Saeedi, Materials, 2022, 15, 3129, DOI:10.3390/ma15093129.
- M. Nidhin, K. J. Sreeram and B. U. Nair, Chem. Eng. J., 2012, 185–186, 352–357 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Z. Mohammadi, B. Lashkari and A. Khosravan, Surf. Interfaces, 2021, 23, 100970 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Goudarzi and M. Salavati-Niasari, J. Alloys Compd., 2019, 784, 676–685 CAS.
- Ş. Aslan Korkmaz, Inorg. Nano-Met. Chem., 2022, 1–7 Search PubMed.
- J. Mohanta, B. Dey and S. Dey, J. Chem. Eng. Data, 2020, 65, 2819–2829 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Absalan, R. Alabada, M. R. Razavi, M. Gholizadeh, O. V. Avramenko, I. N. Bychkova and O. V. Kovalchukova, Tonkie Khim. Tekhnol., 2023, 18, 559–571 CAS.
- K. L. Boorn, Y. -Y. Khor, E. Sweetman, F. Tan, T. A. Heard and K. A. Hammer, J. Appl. Microbiol., 2010, 108, 1534–1543 CrossRef CAS.
- G. Wu, Q. Yang, M. Long, L. Guo, B. Li, Y. Meng, A. Zhang, H. Wang, S. Liu and L. Zou, J. Antibiot., 2015, 68, 661–665 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Bhattarai, B. K. Sharma, N. Subedi, S. Ranabhat and M. P. Baral, Clin. Infect. Dis., 2021, 73, S415–S421 CrossRef.
- R. Manikandan, G. Vanitha, A. Prakasam, M. D. Navinkumar, K. Sathiyamoorthi and B. Dhinakaran, Pakistan Heart, 2023, 56, 1162–1174 Search PubMed.
- I. G. Munteanu and C. Apetrei, Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2021, 22, 3380, DOI:10.3390/ijms22073380.
- T. Shahzadi, M. Zaib, T. Riaz, S. Shehzadi, M. A. Abbasi and M. Shahid, Arabian J. Sci. Eng., 2019, 44, 6435–6444 CAS.
- C. Mattiuzzi, G. Lippi and J. Epidemiol, Global Health, 2019, 9, 217–222 Search PubMed.
- S. Chen, Z. Cao, K. Prettner, M. Kuhn, J. Yang, L. Jiao, Z. Wang, W. Li, P. Geldsetzer, T. Bärnighausen, D. E. Bloom and C. Wang, JAMA Oncol., 2023, 9, 465–472 CrossRef.
- H. Huang, J. Wang, J. Zhang, J. Cai, J. Pi and J.-F. Xu, Pharmaceutics, 2021, 13, 1599, DOI:10.3390/pharmaceutics13101599.
- B. H. Abbasi, S. Anjum and C. Hano, RSC Adv., 2017, 7, 15931–15943 CAS.
- D. Das and B. J. Saikia, Chem. Phys. Impact, 2023, 6, 100137 Search PubMed.
- A. Waris, M. Din, A. Ali, S. Afridi, A. Baset, A. U. Khan and M. Ali, Inorg. Chem. Commun., 2021, 16, 14–30 CAS.
- Z. Hadavand, A. Babaei and D. Ghanbari, J. Nanostruct., 2023, 13, 512–522 CAS.
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2024 |