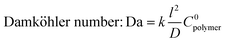Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleCreative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported Licence
Effects of polymer network flexibility on the kinetics of DEZ vapor phase infiltration into photo-polymerized polyacrylates†
Lisanne
Demelius
 ab,
Anna Maria
Coclite
ab,
Anna Maria
Coclite
 a and
Mark D.
Losego
a and
Mark D.
Losego
 *b
*b
aInstitute of Solid State Physics, Graz University of Technology, Graz, Austria
bSchool of Materials Science and Engineering, Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, GA, USA. E-mail: losego@gatech.edu
First published on 9th December 2024
Abstract
Vapor phase infiltration (VPI) enables the fabrication of novel organic–inorganic hybrid materials with distinctive properties by infiltrating polymers with inorganic species through a top-down approach. However, understanding the process kinetics is challenging due to the complex interplay of sorption, diffusion and reaction processes. This study examines how polymer network flexibility affects the kinetics of diethylzinc (DEZ) infiltration into a highly crosslinked polyacrylate copolymer system composed of two monomers: trimethylolpropane triacrylate (TMPTA) and ethoxylated trimethylolpropane triacrylate (ETPTA). The findings show that increasing the ratio of ETPTA, which enhances network flexibility, facilitates precursor diffusion, resulting in deeper infiltration and faster saturation. A reaction–diffusion transport model is employed to qualitatively interpret the experimental results and gain insights into the underlying process mechanisms, thus contributing to a better understanding of VPI kinetics.
Introduction
Due to their unique synergistic and customizable properties, organic–inorganic hybrid materials have applications across various fields,1 including catalysis,2 electronics,3 sensors,4 energy storage5,6 and biomaterials.7,8 Vapor phase infiltration (VPI), also known as atomic layer infiltration (ALI) and sequential infiltration synthesis (SIS), is an emerging technique enabling the creation of hybrid materials by infiltrating polymers with gas-phase inorganic precursors. VPI has demonstrated great potential in altering material characteristics such as solvent stability,9–11 mechanical strength,12–14 optical emission15,16 and triboelectric response.17 An interesting area of application includes the synergy of VPI processes with existing photopatterning techniques to produce hybrid 2D or 3D structures.16,18–20During VPI, polymers are exposed to gaseous metalorganic precursors that sorb and diffuse throughout the polymer matrix until they become immobilized by either a chemical reaction with the polymer or loss of volatility, often induced by reaction with a subsequently delivered co-reactant. VPI infiltration kinetics are complex because they include a convolution of precursor sorption, diffusion, and reaction with a polymer, which all depend on a wide range of operational factors (such as vapor pressure of the precursor and process temperature) and intrinsic properties (such as precursor size, density of reactive groups of the polymer, precursor-polymer reaction rates, and free volume of the polymer). Moreover, diffusivity can be time-dependent because as a precursor reacts with a polymer, the immobilized species can hinder subsequent diffusion.
The complex interplay of sorption, diffusion, and reaction makes it difficult to understand and predict how different process and material parameters affect the infiltration process kinetics and the resulting hybrid material structures. A thorough understanding of VPI kinetics and process characteristics is crucial to enable efficient and successful process design for commercialized applications.
Several experimental studies have focused on analyzing VPI process kinetics, identifying trends and extracting kinetic parameters, such as diffusion coefficients.11,21–24 The most extensively researched precursor-polymer systems include trimethylaluminum (TMA) and titanium tetrachloride (TiCl4) in polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA). Nevertheless, a handful of studies have also explored alternative precursor and polymer combinations. It has been shown that in the presence of precursor-polymer reactions, out-diffusion of the precursor is generally much slower (by a factor of 10–100) than in-diffusion.25,26 While precursor diffusion follows Fick's 2nd law in certain cases,21,25 deviations from Fickian diffusion have been observed for other precursor-polymer systems.21,22 Furthermore, the coordination energy of precursor-polymer interactions has been found to affect the measured diffusion rate.27,28 VPI process temperature influences both diffusion and reaction processes, and depending on which effect dominates, temperature increase has been observed to increase reactivity resulting in more surface growth and limited diffusion,29,30 to change the reaction mechanism,31–34 to enhance diffusion,30,31 and to promote desorption resulting in an overall lower loading of inorganics.35 Two studies have explored the impact of polymer microstructure on transport kinetics. Cianci et al.23 demonstrated a dependence of the diffusivity of TMA on the molecular weight of PMMA with faster diffusion in the lower weight polymer. Padbury and Jur36 showed that larger pendant groups in poly n-methacrylates result in faster diffusion of TMA.
In order to successfully model VPI kinetics and accurately predict both process behavior and final distribution of infiltrated inorganic species, the sorption, diffusion and reaction contributions, as well as their convolution, need to be captured mathematically. A first approach towards modelling the kinetics of VPI was undertaken by Leng and Losego31 who included a second-order reaction term to Fick's 2nd law to account for the immobilization of precursor molecules through interaction with the polymer functional groups. Building upon this model, Ren, McGuinness, et al.37 developed a reaction–diffusion transport model that also includes the decrease in precursor diffusivity due to hindering caused by immobilized precursor molecules and has been demonstrated to both qualitatively and quantitatively capture VPI behaviors in an experimental case study of TMA infiltration in PMMA. It was further used to qualitatively explain infiltration behaviors observed during VPI of TMA in a polymer with intrinsic microporosity (PIM-1)38 and VPI of TMA and TiCl4 in PMMA.39
The present work describes an in-depth study of VPI kinetics of diethylzinc (DEZ) into a highly crosslinked polyacrylate copolymer system whose mechanical flexibility can be varied by modifying the ratio of its two comonomers, trimethylolpropane triacrylate (TMPTA) and its ethoxylated and thus more flexible counterpart, ethoxylated trimethylolpropane triacrylate (ETPTA). This type of crosslinked polyacrylate system is particularly interesting for future applications due to its processability and patternability by photolithography and 2-photon polymerization. The results demonstrate how changing the composition, and thus the flexibility of the polymer network, can be used to control precursor diffusion rates. The reaction–diffusion transport model described above is then used to qualitatively explain the experimental observations and gain insights into the underlying process mechanisms.
Experimental methods
Preparation of polyacrylate thin films
Polyacrylate thin films were synthesized from the monomers trimethylolpropane triacrylate (TMPTA, Mn = 296.32, Sigma Aldrich) and ethoxylated trimethylolpropane triacrylate (ETPTA, average Mn ∼ 428, Sigma Aldrich). For the UV polymerization, 2-(dimethylamino)-2-(4-methylbenzyl)-1-(4-morpholinophenyl)butan-1-one (>95.0%, TCI) served as the photoinitiator with main absorption at 233 and 320 nm.An 8 wt%-solution of monomer was prepared in ethyl acetate (≥99.5%, Sigma Aldrich) with 6 wt% photoinitiator with respect to the monomer. For better spin-coating results, the resulting solution was diluted with 10 wt% 1-butanol (≥99.4%, Sigma Aldrich). Thin films of the acrylate monomers were achieved by spin-coating 30 μl of the solution on single-side polished 〈100〉 silicon wafers (p-type, GlobiTech Inc.) at 6000 rpm for 10 s with dynamic dispensing. Copolymer films of p(TMTPA-c-ETPTA) were prepared by mixing the two monomers in solution using different weight ratios of TMPTA and ETPTA.
UV polymerization was performed under a Dymax 2000-EC UV lamp with a 400 W metal halide flood bulb, exposing the as-spun acrylate films for 10 minutes under ambient conditions. Details on the polymerization process can be found in a previous publication.19 The resulting crosslinked polyacrylate films were between 150 and 250 nm thick, depending on the acrylate ratio (see Fig. S1f in the ESI†).
Vapor phase infiltration of DEZ
Vapor phase infiltration (VPI) of the crosslinked polyacrylate thin films was carried out in a custom-built system described elsewhere.40,41 Nitrogen (99.995% purified from air) served as the purging gas at a flowrate of 250 slpm, diethylzinc (DEZ, 95% purity from STREM Chemicals) as the metalorganic precursor, and deionized water as the oxidizing co-reactant. The polymer thin films were subjected to 1 cycle of VPI (detailed VPI recipe can be found here19) at a process temperature of 120 °C, with DEZ hold times ranging from 30 min to 50 h.Characterization methods
FTIR spectra of the polymer films on silicon were recorded in transmittance using a Thermo Scientific Nicolet iS5 spectrometer. A bare silicon wafer served as background reference, and each measurement comprised 200 scans over a wavelength range from 400 to 4000 cm−1 with a resolution of 4 cm−1. During post-processing, all spectra underwent baseline correction. A fitting routine presented by Tazreiter et al.42 was employed to estimate the volume fraction of TMPTA and ETPTA in the copolymer films from their FTIR absorption spectra, using the absorption spectra of the homopolymer thin films and their respective thickness (measured by ellipsometry) as a reference.The thickness of the polymer films before and after VPI was determined via spectroscopic ellipsometry (SE) using a J. A. Woollam Alpha-SE instrument. Spectra were acquired in a wavelength range from 380 to 900 nm at an angle of incidence of 70°. Fitting was performed with the CompleteEASE software (J. A. Woollam, Version 5.19) using a model consisting of a silicon substrate, a 1.7 nm native oxide layer, and a Cauchy layer. To achieve better fit results, thickness non-uniformity was included.
Thermal expansion and swelling of the polymer films in isopropyl alcohol (IPA, ≥99.7%, VWR Chemicals) were measured with a M-2000 V spectroscopic ellipsometer (J. A. Woollam) in a wavelength range between 370 and 1000 nm. For the thermal expansion experiments, the ellipsometer was equipped with a THMS600 heating stage (Linkam) whose temperature was controlled by a T95 system controller (Linkam). Prior to the measurement, the samples were equilibrated at 120 °C on a hot plate for 1 h. Film thickness was monitored in a temperature range from 30 °C to 120 °C with a heating/cooling rate of 9 °C min−1 and the samples were held at the maximum temperature for 5 min. Ellipsometry scans were taken continuously during heating, hold and cooling at an angle of incidence of 70°. For the swelling experiments, a 5 mL heated liquid cell attachment was used and measurements were performed in air and in IPA at an angle of 75°. Fitting was performed using the same model described above, except for the thermal expansion data, for which the room temperature Si model was replaced by a temperature dependent one. The linear coefficients of thermal expansion αz were calculated from a linear fit of the thickness expansion in the temperature range from 80 to 120 °C.
The zinc loading of polymer films after VPI was analyzed by several analytical methods. Firstly, X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy (XRF) was conducted using a Thermo Scientific Niton FXL FM-XRF instrument, featuring an Ag anode operating at 50 kV voltage and 200 μA current. Spectra were acquired in general metals mode over a 90-s measurement period. To obtain a measure of the relative zinc content with respect to the amount of polymer, the area under the Zn Kα peak at 8.637 keV, determined by integrating the spectrum from 8.35 to 8.9 keV using a linear background, was divided by the polymer film thickness measured by SE prior to VPI.
Secondly, energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX) was employed, using a Phenom XL G2 scanning electron microscope (SEM) operating at 5 kV electron energy and a chamber pressure of 0.1 Pa in imaging mode. The EDX signal was averaged over an approximately 250 × 250 μm2 region, and atomic concentrations were determined using the Phenom software. The Zn atomic concentrations are given with respect to the C and O concentrations, neglecting the Si signal originating from the substrate.
Further, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) was performed with a Thermo Scientific K-Alpha system equipped with a monochromatic Al-Kα X-ray source (1486.6 eV). For survey scans, a pass energy of 200 eV, a dwell time of 50 ms, and a step size of 1 eV were employed, while high-resolution scans utilized a pass energy of 50 eV, a dwell time of 50 ms, and a step size of 0.1 eV. The samples were analyzed without additional surface treatment, and charge compensation was achieved using an in-built flood gun. The spot size was 400 μm. Depth profiles were generated using a 2000 eV mid-current Ar ion beam with etch steps ranging from 35 to 45 s and a 5 s pause between etching and measurement. Data analysis and component fitting were conducted using the CasaXPS software (Casa Software Ltd, Teignmouth, UK). All spectra were calibrated with respect to the C–C adventitious carbon peak at 284.8 eV. For the XPS depth profiles, etch time was calibrated to etch depth using the film thickness determined by ellipsometry. The polymer–Si interface was assumed to be at the position where the Si 2p peak reached 50 at%.
Results and discussion
Preparation of p(TMPTA–ETPTA) thin films
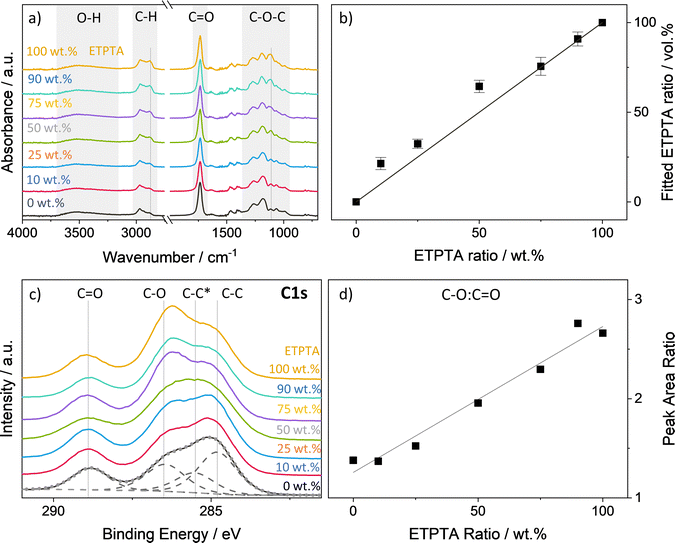
A range of p(TMPTA–ETPTA) copolymers of varying compositions have been developed to create a set of highly crosslinked polymer networks with a systematic variation in free volume and flexibility, with the goal of investigating how these changes in polymer structure affect VPI processing kinetics and inorganic loading. Scheme 1 shows the chemical structures of the two polyfunctional acrylate monomers, trimethylolpropane triacrylate (TMPTA) and ethoxylated trimethylolpropane triacrylate (ETPTA), as well as the photoinitiator 2-(dimethylamino)-2-(4-methylbenzyl)-1-(4-morpholinophenyl)butan-1-one (Omnirad 379) used to synthesize these copolymer networks. The two monomers differ in the length of their functional side chains. Compared to TMPTA, ETPTA features additional ethoxy groups, on average one in each of the three side chains. To confirm that the mixing ratio of the two monomers in solution translates to a similar copolymer ratio in the spun-cast and UV polymerized thin films, p(TMPTA–ETPTA) films of different compositions were analyzed by FTIR and XPS. Fig. 1a displays the FTIR spectra averaged over 6–12 identically prepared samples for each composition. The spectra all exhibit a carbonyl peak at approximately 1720 cm−1 and a series of peaks related to C–O bonding in the range 1010–1320 cm−1.43,44 The ethoxy groups in ETPTA show up as an additional peak in the ether region at around 1110 cm−1 that is not present for TMPTA. A difference is also observable in the C–H stretch region between 2800 and 3000 cm−1, where an increasing ETPTA content results in the emergence of a shoulder peak at 2875 cm−1. A broad absorption in the O–H region at around 3500 cm−1 is probably due to hydroxyl groups generated by some degree of photooxidation during the UV exposure.45–48 The lack of absorption peaks at 1625 cm−1 (C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C stretching), and 1405 and 810 cm−1 (
C stretching), and 1405 and 810 cm−1 (![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C–H bending) confirm the high degree of vinyl bond conversion and hence polymerization of the thin films.43,44 Using the absorption spectra of the homopolymer thin films and their respective average thickness measured by ellipsometry (see Fig. S1, ESI†), the volume fraction of TMPTA and ETPTA in the copolymer films were determined by a simple fitting routine described by Tazreiter et al.42 The results depicted in Fig. 1b show a very good correspondence of the monomer mixing ratio in wt% to the fitted comonomer volume fraction. According to the supplier, the density of the monomers TMPTA and ETPTA is almost identical (1.1 and 1.11 g ml−1 respectively), making a direct comparison of weight and volume fraction reasonable. Fig. 1c displays the XPS C 1s peaks for the different p(TMPTA–ETPTA) films. The spectra can be deconvoluted into four component peaks. The peaks at approximately 288.9 eV, 286.5 eV and 284.8 eV correspond to C
C–H bending) confirm the high degree of vinyl bond conversion and hence polymerization of the thin films.43,44 Using the absorption spectra of the homopolymer thin films and their respective average thickness measured by ellipsometry (see Fig. S1, ESI†), the volume fraction of TMPTA and ETPTA in the copolymer films were determined by a simple fitting routine described by Tazreiter et al.42 The results depicted in Fig. 1b show a very good correspondence of the monomer mixing ratio in wt% to the fitted comonomer volume fraction. According to the supplier, the density of the monomers TMPTA and ETPTA is almost identical (1.1 and 1.11 g ml−1 respectively), making a direct comparison of weight and volume fraction reasonable. Fig. 1c displays the XPS C 1s peaks for the different p(TMPTA–ETPTA) films. The spectra can be deconvoluted into four component peaks. The peaks at approximately 288.9 eV, 286.5 eV and 284.8 eV correspond to C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O, C–O and C–C bonds. A fourth component peak at 285.5 eV, often referred to as β-shifted C, is generated by the next-nearest-neighbor effect for the carbon that is bonded to the ester carbon (∼0.7 eV shift).49–51 Ideally, the ratio of the C–O and C
O, C–O and C–C bonds. A fourth component peak at 285.5 eV, often referred to as β-shifted C, is generated by the next-nearest-neighbor effect for the carbon that is bonded to the ester carbon (∼0.7 eV shift).49–51 Ideally, the ratio of the C–O and C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O components for pure pTMPTA should be 1. As the ETPTA content increases, the intensity of the C–O peak should increase relative to the C
O components for pure pTMPTA should be 1. As the ETPTA content increases, the intensity of the C–O peak should increase relative to the C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O peak since each ethoxy group adds two additional carbon atoms with a single bond to oxygen. The ETPTA used in this study has an average molecular weight of Mn ∼ 428, which corresponds to three ethoxy groups per monomer unit and therefore a theoretical C–O
O peak since each ethoxy group adds two additional carbon atoms with a single bond to oxygen. The ETPTA used in this study has an average molecular weight of Mn ∼ 428, which corresponds to three ethoxy groups per monomer unit and therefore a theoretical C–O![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) C
C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O ratio of 3. Fig. 1d indeed shows a linear relationship between the ETPTA ratio and the peak area ratio C–O
O ratio of 3. Fig. 1d indeed shows a linear relationship between the ETPTA ratio and the peak area ratio C–O![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) C
C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O with values that are comparable to the theoretical ones.
O with values that are comparable to the theoretical ones.
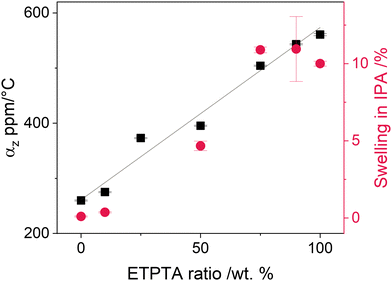
The impact of ETPTA incorporation on the thermomechanical properties of the resulting films was studied by measuring their thermal expansion behavior using spectroscopic ellipsometry (Fig. S2a, ESI†). Additionally, the swelling of the copolymer thin films upon immersion into IPA was measured to evaluate the polymer network's capability to expand upon solvent absorption. Fig. 2 displays the resulting linear thermal expansion coefficient αz in the temperature range from 80 to 120 °C and the thickness swelling in IPA as a function of ETPTA ratio. Both parameters increase linearly with increasing ETPTA fraction, indicating that the incorporation of a comonomer with longer side chains indeed results in a higher free volume and a more flexible polymer network. The measured values for αz are of a similar order of magnitude as those reported for other polymer films of a comparable thickness.52,53
Because VPI is performed at an elevated temperature (120 °C), the thermal stability of the p(TMPTA–ETPTA) films was also evaluated. Films of all compositions were placed into the heated reactor in vacuum for 24 h, which corresponds to the length of a VPI process with a 15-hour DEZ hold. Before and after the procedure, FTIR spectra were collected. Overall, the polymers demonstrate good stability at 120 °C (see Fig. S2b, ESI†), with only minor intensity losses observed in the ether region between 1200–1100 cm−1. However, copolymers containing more than 50 wt% of ETPTA do exhibit a decrease in the C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O peak intensity (1735 cm−1) with the simultaneous emergence of an additional shoulder peak at higher wavenumbers, around 1785 cm−1. This peak could indicate the formation of γ-lactones, characterized by their primary absorption at 1780 cm−1, or anhydrides, which typically absorb around 1800 cm−1. Both structures have been frequently observed during the photodegradation of aliphatic polymers.45,47,54 It should be noted that for this study, VPI processes with up to 50 h DEZ hold time were performed. This extended exposure of the polymers to 120 °C may lead to stronger degradation. However, the results presented in the following sections show no evidence of such degradation. For example, constant Zn loading were observed for hold times from 15 to 50 h, indicating that the prolonged exposures did not adversely affect the polymers.
O peak intensity (1735 cm−1) with the simultaneous emergence of an additional shoulder peak at higher wavenumbers, around 1785 cm−1. This peak could indicate the formation of γ-lactones, characterized by their primary absorption at 1780 cm−1, or anhydrides, which typically absorb around 1800 cm−1. Both structures have been frequently observed during the photodegradation of aliphatic polymers.45,47,54 It should be noted that for this study, VPI processes with up to 50 h DEZ hold time were performed. This extended exposure of the polymers to 120 °C may lead to stronger degradation. However, the results presented in the following sections show no evidence of such degradation. For example, constant Zn loading were observed for hold times from 15 to 50 h, indicating that the prolonged exposures did not adversely affect the polymers.
DEZ infiltration into p(TMPTA–ETPTA) thin films
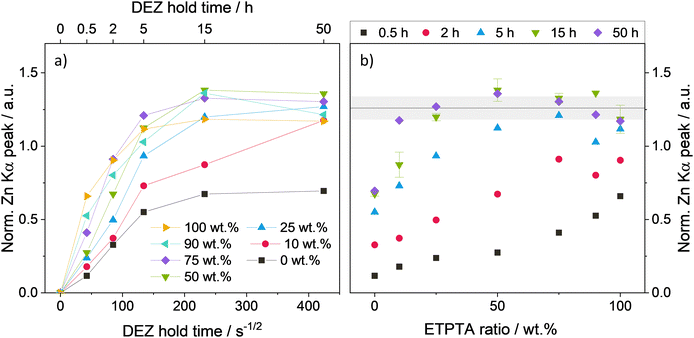
To study the effect of polymer network flexibility on the DEZ infiltration behavior, the p(TMTPA–ETPTA) films were subjected to one cycle of VPI at 120 °C with DEZ hold times ranging from 30 min to 50 h. Fig. 3 displays the XRF-derived, thickness-normalized Zn loading of the p(TMPTA–ETPTA) films as a function of DEZ hold time (Fig. 3a), and as a function of ETPTA ratio (Fig. 3b). Both plots show a general trend towards higher Zn loading with higher ETPTA ratios and longer DEZ hold times. A saturation behavior with respect to DEZ hold time is evident in Fig. 3a. For all polymers with an ETPTA ratio ≥10 wt%, the Zn loading increases with DEZ hold time until it reaches a plateau and saturates at a maximum value of approximately 1.26 ± 0.08. While samples with an ETPTA ratio >50 wt% reach saturation loading very quickly (after <15 h), the copolymer with 10 wt% ETPTA takes 50 hours of DEZ exposure to reach a comparable loading. The pTMPTA homopolymer (0 wt% ETPTA) differs from this trend, with its Zn loading saturating at a much lower value of approximately 0.7. The initial Zn uptake during the first 30 min is highest for the pETPTA homopolymer (100 wt% ETPTA, i.e., the most flexible polymer network) and decreases with decreasing ETPTA ratio, a trend that will be discussed in more detail in the next section.Fig. 3b displays the same data as Fig. 3a but visualized in a way that highlights the effect of ETPTA ratio on Zn loading. This plot shows that for a given DEZ hold time, higher Zn loading is generally achieved for higher ETPTA ratios. Increasing the DEZ hold time from 30 min to 50 h leads to an overall increase in Zn loading for all copolymer compositions until the films at the ETPTA-rich end of the series begin to hit saturation loading. After 2 h of DEZ exposure, copolymer films with ≥75 wt% ETPTA appear to be saturated. After 5 h, all films with ≥50 wt% ETPTA reach saturation loading. After 15 h, this threshold decreases to ≥25 wt% ETPTA, and after 50 h, all copolymer films with ETPTA ratios larger or equal to 10 wt% appear to have reached saturated Zn loading. It should be noted that the saturation loading after 50 hours is highest for 50 wt% ETPTA and exhibits a decreasing trend when going from 50 to 100 wt% ETPTA. A possible reason might be a lower volume density of reactive polymer sites in ETPTA compared to TMPTA, resulting in a lower saturation Zn loading for ETPTA-rich copolymers. In addition to XRF, the Zn loading has also been estimated by EDX. The corresponding plots of EDX atomic Zn concentration as a function of DEZ hold time and ETPTA ratio reproduce the trends observed by XRF and can be found in Fig. S3 (ESI†).
The XRF and EDX results presented in Fig. 3 and S3 are supplemented by XPS depth profiles conducted on a selected set of copolymer compositions (0, 10, 75 and 100 wt% ETPTA) after different DEZ hold times. It should be noted that the Ar ion beam used during depth profiling can induce chemical changes to the organic material as well as cause compositional mixing due to faster etching of oxygen compared to carbon, or organics compared to inorganics.55,56 As a result, the measured atomic concentrations may deviate from the actual composition of the undamaged zinc–polyacrylate complex, and sharp interfaces may appear as more gradual transitions. Despite these limitations, the qualitative comparison of zinc depth distributions is still meaningful and has been previously used to investigate VPI processes.12,27,39
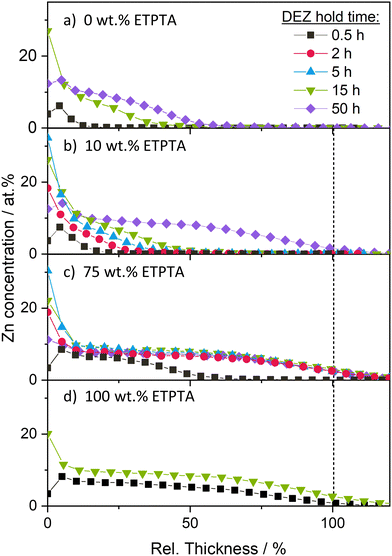
Fig. 4a displays the atomic Zn concentration, determined by the area of the Zn 2p peak, in the pTMPTA homopolymer network (0 wt% ETPTA) as a function of the relative polymer film thickness. After a 30-minute DEZ hold, the Zn concentration is nonzero at the surface but rapidly decreases to zero with increasing distance from the surface. After 15 h, the concentration profile extends significantly deeper into the bulk. Increasing the DEZ hold time further to 50 h only results in a slight increase in infiltration depth. The pTMPTA homopolymer layer remains partially infiltrated. Adding 10 wt% ETPTA (Fig. 4b) does not alter the shape of the depth profiles but appears to enhance the diffusion rate. After the same DEZ hold time, Zn penetrates further into the bulk for the copolymer with 10 wt% ETPTA compared to the pTMPTA homopolymer. The largest difference can be observed after 50 h of DEZ exposure. In contrast to the homopolymer, which exhibited Zn infiltration down to less than 50% of the polymer thickness (Fig. 4a), the Zn concentration in the copolymer with 10 wt% ETPTA is nonzero throughout the entire layer (Fig. 4b). Further increasing the ratio of ETPTA seems to continue this trend towards faster diffusion. Fig. 4c reports the Zn concentration profiles for a 75 wt% ETPTA copolymer film. After only 30 min of DEZ exposure, the Zn concentration is nonzero down to 50% of the polymer film thickness. After 2 h, full infiltration is achieved with a nearly uniform Zn concentration throughout the entire polymer layer. Further increasing DEZ hold time leaves the depth profiles unchanged. The system appears to be saturated, i.e., all accessible reactive sites of the polymer have been reacted to the precursor.
The depth profiles in Fig. 4a–c are exemplary of a diffusion-limited VPI process, which characteristically produces a sigmoidal-type profile that moves deeper into the polymer with time, as previously reported by Balogun et al.39 The temporal evolution of depth profiles for the pETPTA homopolymer (100 wt% ETPTA) in Fig. 4d, however, show a very different behavior. After 30 min DEZ exposure, the polymer layer appears uniformly infiltrated by Zn, but at a lower atomic concentration compared to the saturated polymers in Fig. 4b–c. Increasing the DEZ exposure time to 15 h results in an overall increase of the Zn concentration to a level comparable to that of the saturated polymers in Fig. 4b–c. Such a behavior is exemplary of a reaction-limited process (see again Balogun et al.39). These results indicate that increasing the ETPTA ratio does not only enhance the precursor diffusion into the polymer, resulting in a faster saturation, but also changes the rate-controlling mechanism from diffusion-limited to reaction-limited. These observations will be discussed in more detail in the next section in conjunction with a comparison to theoretical results calculated using the reaction–diffusion transport model developed by Ren, McGuinness et al.37 Finally, it should be noted that the fluctuations in Zn concentration observed at the surface of the polymers, which occasionally yield values that are significantly higher or lower than the saturation values deeper in the polymer layer, are believed to result from experimental limitations rather than representing a relevant feature of the VPI process. It is believed that, depending on the reactor leak rate, trace amounts of water vapor present during the DEZ hold step may co-react with DEZ at the surface, forming a metal oxide skin layer. Such a surface layer could influence the infiltration kinetics, e.g. by slowing down diffusion, which should be considered when extracting diffusivity values from the experimental data later. However, the consistent trends in Fig. 3 and 4 as a function of DEZ hold time and ETPTA ratio suggest that any surface layer formation does not drastically impact the VPI process.
The trends observable in the XPS depth profiles show excellent consistency with the XRF data in Fig. 3a. A complete and uniform infiltration of the polymer layer in XPS corresponds to maximum (saturated) Zn loading in XRF, while partial infiltration yields lower XRF values. The observation that the system exhibits a saturation behavior, whereby once saturation is reached, prolonging the DEZ exposure does not result in a further increase in inorganic loading, indicates that the VPI process is self-limiting, analogous to the site-limited surface saturation in an ALD process.
Within the 50-hour DEZ exposure investigated in this study, all copolymers with an ETPTA ratio larger or equal to 10 wt% appear to reach saturation, although at different speeds. Only the pTMPTA homopolymer (0 wt% ETPTA), according to the XPS depth profiles, remains partially infiltrated, an observation that is consistent with the XRF results that show significantly lower loading for the 0 wt% ETPTA–polymer compared to all other copolymer compositions after 50 h DEZ. It is also noted that the saturation Zn concentration measured by XRF (Fig. 3a) and XPS (Fig. 4) is comparable for all studied copolymer compositions. This indicates that the incorporation of the more flexible pETPTA into pTMPTA, though drastically changing the DEZ diffusivity, does not significantly affect the overall density of accessible reactive polymer sites for DEZ.
Integrating the XPS Zn signal over the entire polymer layer and dividing the result by the polymer thickness yields a value for the average atomic Zn concentration that can be directly compared to the Zn loading measured by XRF. The results (see Fig. S7a in the ESI†) exhibit a high degree of correlation and good consistency. In addition to XRF and XPS depth profiling, inorganic loading was also estimated by measuring the swelling of the polymer thickness upon VPI with spectroscopic ellipsometry, by EDX surface analysis, and by quantifying the area of the FTIR peak associated with a Zn–polymer bond (see paragraph below). In comparing the results acquired by the different characterization techniques, the XRF measurements were used as reference, since they have been previously shown to correlate well to the amount of ZnO present after calcination of infiltrated polymers.11 While polymer swelling does not appear to be suitable for measuring inorganic loading in the present polymer-precursor system, both EDX and FTIR estimates align with the trends observed by XRF and XPS (see Fig. S7b–d, ESI†). Note that although XPS and EDX results show the same trends, the reported atomic zinc concentrations are quite different. While both techniques allow for a meaningful comparison of relative zinc concentrations, the absolute atomic concentrations are prone to systematic errors, since the quantification of the EDX spectra was conducted without calibration to standards57 and the occurrence of preferential etching cannot be excluded during XPS depth profiling. A reason for the poor correlation between polymer swelling and inorganic loading might be that upon heating and interaction with the precursor, the crosslinked polymer network undergoes a certain degree relaxation that counteracts the swelling due to precursor absorption.
To determine whether DEZ chemically binds to the polymer networks, copolymer thin films were measured with FTIR spectroscopy before and after VPI. Fig. 5 shows the resulting spectra before and after VPI with a 15-hour DEZ hold. The spectra reveal the emergence of two new peaks after VPI, a very broad O–H absorption band around 3500 cm−1 and a peak at 1650–1550 cm−1. The former can be attributed to the water co-reaction that likely produces a form of zinc hydroxide, while the latter has been associated with C–O–Zn–R bonds in VPI literature.11,33,58,59 Regarding the absorption bands of the polymer after VPI, no change is observed in the C–H range from 3000–2800 cm−1, which represents the polymer backbone, but a decrease can be observed in the C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O peak at 1735 cm−1 and in the C–O–C region (∼1300–1000 cm−1). While part of this decrease could be due to thermally induced changes (see Fig. S2b, ESI†), the intensity loss is significantly stronger than the loss observed during heat exposure alone and can thus be assumed to be a result of precursor-polymer reactions. The emergence of the C–O–Zn–R peak is a clear indication of a chemical reaction of DEZ with the polymer. The simultaneous decrease in the C
O peak at 1735 cm−1 and in the C–O–C region (∼1300–1000 cm−1). While part of this decrease could be due to thermally induced changes (see Fig. S2b, ESI†), the intensity loss is significantly stronger than the loss observed during heat exposure alone and can thus be assumed to be a result of precursor-polymer reactions. The emergence of the C–O–Zn–R peak is a clear indication of a chemical reaction of DEZ with the polymer. The simultaneous decrease in the C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O and C–O–C absorption bands suggests that DEZ reacts with the ester moieties. The FTIR spectra do not show any evidence for the reaction of DEZ with the ethoxy groups in ETPTA, which are represented by peaks at 2875 and 1110 cm−1. Nevertheless, knowledge of the exact reaction mechanism is necessary to be able to definitively exclude a potential participation of the ethoxy groups. In addition, the FTIR spectra prior to VPI show the presence of a weak O–H band around 3500 cm−1, which is likely caused by photooxidation during UV polymerization (see previous publication19 for details). As DEZ is known to strongly react with hydroxyl groups,60 they can be assumed to represent additional reactive sites for the diffusing precursor. However, the intensity of the O–H band in Fig. 5 is comparable for all copolymer compositions, so the O–H groups cannot account for the observed differences in Zn loading between the different ETPTA ratios. Photooxidation can also generate other reactive groups45,47,54 (such as carbonyls or anhydrides) that might contribute to the precursor-polymer reactivity. Further in-depth experiments are necessary to fully understand which functional groups participate in the reaction.
O and C–O–C absorption bands suggests that DEZ reacts with the ester moieties. The FTIR spectra do not show any evidence for the reaction of DEZ with the ethoxy groups in ETPTA, which are represented by peaks at 2875 and 1110 cm−1. Nevertheless, knowledge of the exact reaction mechanism is necessary to be able to definitively exclude a potential participation of the ethoxy groups. In addition, the FTIR spectra prior to VPI show the presence of a weak O–H band around 3500 cm−1, which is likely caused by photooxidation during UV polymerization (see previous publication19 for details). As DEZ is known to strongly react with hydroxyl groups,60 they can be assumed to represent additional reactive sites for the diffusing precursor. However, the intensity of the O–H band in Fig. 5 is comparable for all copolymer compositions, so the O–H groups cannot account for the observed differences in Zn loading between the different ETPTA ratios. Photooxidation can also generate other reactive groups45,47,54 (such as carbonyls or anhydrides) that might contribute to the precursor-polymer reactivity. Further in-depth experiments are necessary to fully understand which functional groups participate in the reaction.
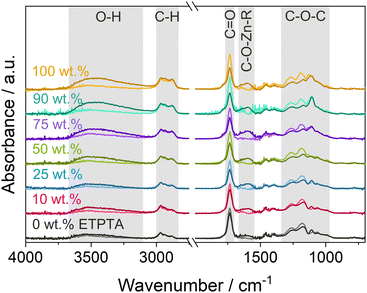 | ||
| Fig. 5 FTIR spectra of p(TMPTA–ETPTA) films of different compositions before (light color) and after (dark color) VPI with a 15-hour DEZ hold at 120 °C. | ||
The intensity of the C–O–Zn–R peak increases for higher ETPTA ratios, suggesting that a larger quantity of DEZ is reacted. This trend correlates well with the increase in Zn loading with increasing ETPTA ratio observed by XRF (Fig. 3b), XPS and EDX. Previous studies have reported no or only weak DEZ infiltration into pMMA,12,19 polybutylene terephthalate (PBT)12,61 and polyethylene naphthalate (PEN),61 which all have similar functional groups (i.e., esters) as pTMPTA and pETPTA. Only one study62 observed significant Zinc loading in PMMA after infiltration with DEZ. However, it should be noted that while the former studies12,61 exposed PMMA, PEN and PBT to only 1 cycle of alternating DEZ and water pulses, the latter used 10 cycles with fairly short (120 s) purging times, which might have led to incomplete out-diffusion of unreacted species, thus facilitating ZnO nucleation. Pilz et al.11 also reported a consumption of C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O peaks during DEZ VPI into thermally treated cis-polyisoprene. An in situ FTIR study of the reactivity of TMA to different polymers63 suggested that the position of the ester group (and hence the C
O peaks during DEZ VPI into thermally treated cis-polyisoprene. An in situ FTIR study of the reactivity of TMA to different polymers63 suggested that the position of the ester group (and hence the C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O species) in the polymer plays an important role. They showed that TMA reaction with polyethylene terephthalate (PET), which has the ester group in its main chain, was much stronger than with pMMA, where the ester group is in the side chain. Such a dependence on the position of the functional groups could at least partially explain the differences in reactivities observed between DEZ and various ester-containing polymers. Differences in precursor solubility, accessibility of reactive polymer sites and the respective process conditions could of course also play a role. Further research is needed to better understand the reaction mechanisms and pathways of DEZ with these acrylate polymers.
O species) in the polymer plays an important role. They showed that TMA reaction with polyethylene terephthalate (PET), which has the ester group in its main chain, was much stronger than with pMMA, where the ester group is in the side chain. Such a dependence on the position of the functional groups could at least partially explain the differences in reactivities observed between DEZ and various ester-containing polymers. Differences in precursor solubility, accessibility of reactive polymer sites and the respective process conditions could of course also play a role. Further research is needed to better understand the reaction mechanisms and pathways of DEZ with these acrylate polymers.
Understanding the infiltration kinetics
The infiltration kinetics during VPI can be very complex due to the convolution of sorption, diffusion and reaction processes, making it difficult to understand and predict how changing a certain process parameter affects the overall VPI process. Leng et al.31 presented a simple physicochemical kinetics model that accounts for the reduction in the freely diffusing precursor's effective concentration due to instantaneous reaction with the polymer matrix (similar to a heat sink) by adding a first order reaction term to Fick's 2nd law. The resulting solution for the precursor uptake as a function of precursor exposure time has the same functional form as that of pure diffusion but with a reduced effective diffusion coefficient Deff: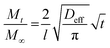 | (1) |
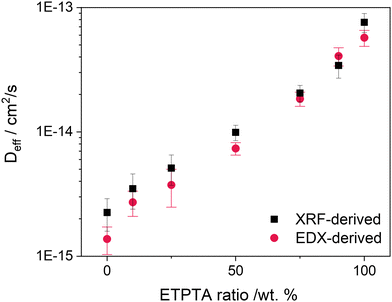 | ||
| Fig. 6 Estimates for the effective diffusion coefficient Deff for the different p(TMPTA–ETPTA) copolymer compositions at 120 °C calculated by linear fitting of the normalized temporal Zn uptake measured by XRF and EDX (Fig. S9, ESI†) according to eqn (1). | ||
These values for the effective diffusivity of DEZ in p(TMPTA–ETPTA) are in a similar range to those published by Pilz et al.11 for DEZ infiltration into thermally treated cis-polyisoprene (Deff = 0.5–3 × 10−14 cm2 s−1 for temperatures from 60 to 100 °C) using the same approach. Effective diffusivities for TMA into pMMA have been measured to be significantly higher (up to 10−12 and 10−11 cm2 s−1 for 90 °C23,24 and 125 °C31, respectively). Motta et al.64 estimated the effective diffusivity of TMA into PMMA in the temperature range from 70–110 °C, reporting values for Deff ranging from around 1.3 × 10−14 to 6 × 10−11 cm2 s−1. Extrapolation of the Arrhenius-like trend with temperature would give a value of Deff ≅ 7 × 10−10 cm2 s−1 at 120 °C. The higher diffusivities for TMA compared to DEZ are reasonable as TMA can be expected to diffuse through a polymer more easily due to its smaller size. Moreover, the choice of polymer plays an important role in determining the precursor diffusivity. In addition to the polymer chemistry, polymer microstructure has been shown to also impact diffusion behavior during VPI. Cianci et al.,23 for example, demonstrated that TMA diffusion in PMMA depends on the polymer molecular weight and proceeds faster in low-weight polymers. Another study36 showed that increasing the pendant group size in poly n-methacrylates lowers the glass transition temperature Tg, thus increasing the polymer free volume and resulting in a higher diffusivity of TMA. The present work is the first to demonstrate how increasing the side chain length and flexibility of highly crosslinked polymer networks enhances precursor diffusion.
Nevertheless, the use of eqn (1) to extract values for the effective diffusivity is subject to several limitations, some of which have already been discussed elsewhere.37 First of all, the model by Leng assumes precursor-polymer reactions to occur instantaneously, an approximation that is only reasonable if reactions occur on a much faster time scale than diffusion, i.e., if the VPI process is diffusion-limited. Based on the XPS depth profiles in Fig. 4, this condition can be considered fulfilled for all copolymers with ETPTA ratios ≤75 wt%. However, the shape of the profiles for 100 wt% ETPTA polymers suggests that reactions occur on a similar or slower time scale than diffusion. Secondly, the extracted values for Deff depend on whether the quantity Mt/M∞ refers to the amount of free precursor, the amount of reacted precursor or the total precursor uptake, i.e., the sum of the two. Since the Zn loading in this study was measured ex situ, it can be expected that a significant portion of the unreacted precursor desorbed during the 1-hour pumping step performed after the precursor exposure and before exposure to the co-reactant, and therefore mainly the amount of reacted precursor is captured. This can be expected to result in a deviation of Deff compared to the values reported in literature, which are based on the total precursor uptake, either by using in situ measurements21–24 or by keeping pumping and/or purging times short enough to render precursor desorption negligible11,31 (it is generally assumed that during co-reactant exposure, any unreacted precursor still present in the polymer is oxidized and permanently trapped). Lastly, eqn (1) assumes a constant diffusivity that is independent of the amount of reacted precursor. Since the reaction between precursor and polymer creates a new (hybrid) material, precursor diffusivities may differ from those of the unreacted system.
Keeping these limitations in mind, the effective diffusivity values reported in Fig. 6 are still useful as engineering estimates for the process rate and are particularly representative of the change in diffusivity as a function of the ETPTA ratio.
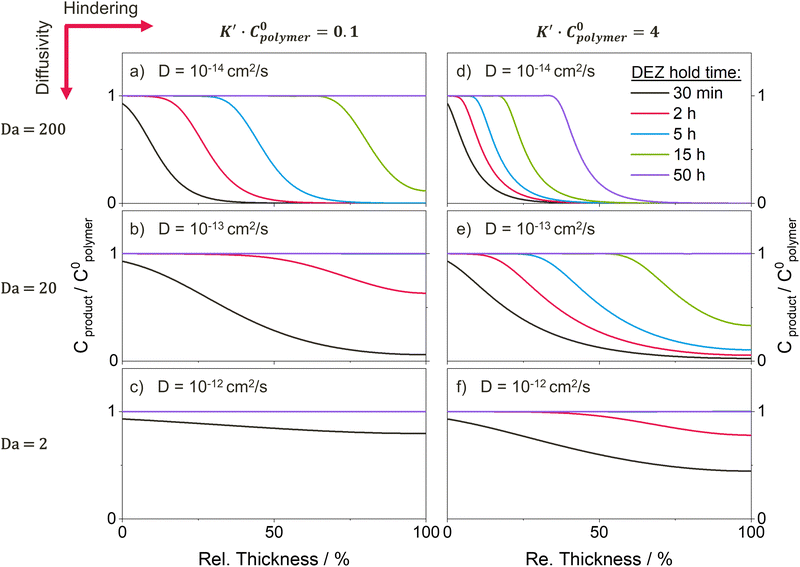
Building upon the model by Leng, Ren, McGuinness, et al.37 developed a reaction–diffusion transport model that includes a second-order chemical reaction term to account for finite reaction rates, and a non-Fickian diffusional hindering term that describes the change in diffusivity as precursor-polymer reactions occur. The model can be reduced to a set of dimensionless parameters that capture fundamental aspects of the VPI process:
where k represents a 2nd order reaction rate constant, l the polymer thickness, D the unhindered diffusion coefficient, C0polymer the reactive polymer functional group density, CS the concentration of precursor vapor sorbed at the polymer surface, and K′ a hindering factor. The Damköhler number determines whether the VPI process is diffusion- or reaction-limited. If Da ≫ 1, precursor-polymer reactions proceed much faster than diffusion, resulting in a sigmoidal inorganic depth profile that moves deeper into the bulk with time (diffusion-limited process). If Da < 1, diffusion is much faster than the reaction rate, resulting in a uniform precursor concentration throughout the polymer layer that increases with time as reactions take place (reaction-limited process). Exemplary calculated depth profiles for these two limiting cases can be found in literature39 and in the ESI,† in Fig. S9. The ratio of precursor vapor concentration at the polymer surface CS to the density of reactive polymer functional groups C0polymer dictates the availability of free diffusing precursor molecules and the maximum precursor uptake. The hindering degree K′C0polymer indicates the extent to which the diffusion of free precursor molecules is impeded by reacted, immobilized precursor molecules and depends on several parameters, such as precursor size, polymer free volume, and the density of reactive polymer functional groups. If the hindering degree is very high, immobilized precursor molecules can form a barrier layer that blocks further infiltration.
In the present study, the reaction–diffusion transport model was used to try to reproduce and understand the experimentally observed trends. For ex situ data as collected here, the model is not intended to provide a quantitative fit, but rather to serve as a tool to understand how changing specific process parameters affects the shape of temporal precursor uptake curves and spatiotemporal inorganic distributions. By comparing the modeled and experimental results, insights into the underlying reaction and diffusion phenomena can be gained. For this study, the choice of model parameters was partially based on measured physical quantities. The model was plotted for the same DEZ exposure times (30 min, 2 h, 5 h, 15 h and 50 h) studied in experiment, the polymer thickness was chosen as l = 200 nm, similar to the actual average film thickness, and the density of polymer functional groups C0polymer was estimated based on the XPS results (for details see ESI†). The remaining parameters (CS, K′, k, D) were chosen such that the modeled results capture the main features and trends of the experimental results, especially the two limiting cases of the homopolymer films. For simplicity, it is assumed that the polymer thickness l, the density of polymer functional groups C0polymer, the precursor density at the surface CS, and the reaction rate constant k are independent of the copolymer composition, and only the effect of varying the diffusivity D and the degree of hindering K′C0polymer on the precursor uptake profiles and spatiotemporal Zn distributions is explored. Since the diffusivity D and the degree of hindering K′C0polymer both depend on the polymer flexibility and free volume, they are expected to be most strongly affected by a change in ETPTA ratio. The assumption that C0polymer is mostly independent of the copolymer composition is supported by the XRF and XPS results that show approximately the same Zn loading in saturation for all ETPTA ratios. Since pTMPTA and pETPTA have a similar chemical structure and FTIR measurements (Fig. 5) do not suggest a drastic difference in reaction mechanism, assuming CS and k to be constant seems a reasonable approximation. For the comparison to the experimental data, the amount of reacted, immobilized precursor Cproduct (normalized to the total concentration of polymer reactive sites C0polymer) is plotted based on the assumption that unreacted, free precursor out-diffuses during the 1-hour pumping step and hence does not contribute to the amount of inorganic measured ex situ after completion of the process (e.g., by XRF or XPS). In cases of very low precursor diffusivity or high hindering, this assumption might not hold, and the length of the pump/desorption step might require adjustment to ensure complete desorption of unreacted precursor molecules (or the remaining unreacted precursor would need to be taken into account during modeling). It should further be noted that the reaction–diffusion transport model assumes the polymer thickness l to remain constant throughout precursor infiltration, which for some cases may not be accurate. For example, TMA infiltration into PMMA can lead to significant swelling of the polymer by up to 50%,27 and this would essentially create a “moving boundary condition” for the reaction–diffusion transport model and could further influence parameters such as the density of reactive groups C0polymer, the diffusivity D or the degree of hindering K′. However, ex situ ellipsometry measurements of the p(TMPTA–ETPTA) films after VPI reveal only minor swelling by less than 15% (see Fig. S7b, ESI†), so the impact on the model's accuracy can be assumed to be reasonably small to justify a qualitative comparison between experimental data and modelled results.
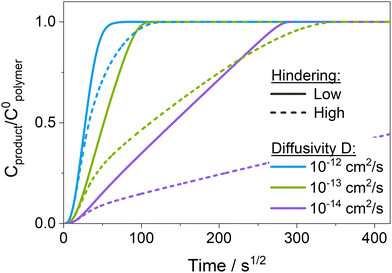
Fig. 7 presents temporal uptake profiles for the normalized concentration of reacted precursor Cproduct/C0polymer calculated from the reaction–diffusion model for different values of precursor diffusivity D and hindering. For the sake of completion and to enable a more comprehensive understanding of the complex interplay of reaction and diffusion phenomena, the temporal uptake of the normalized free, unreacted precursor concentration (Cfree/C0polymer) is plotted and discussed in Fig. S10b (ESI†) and Section 2 in the ESI.† For low hindering (solid lines in Fig. 7), Cproduct/C0polymer increases linearly as a function of the square root of time, a behavior characteristic of a Fickian diffusion process. The slope increases with increasing diffusivity D, leading to a faster saturation of the polymer layer (i.e., Cproduct/C0polymer = 1). Note that the dependence of the slope of Cproduct/C0polymer on the diffusivity shown in Fig. 7 is only present as long as the process is diffusion-limited, i.e., for Damköhler numbers Da ≫ 1 (i.e., D ≪ 2 × 10−12 cm2 s−1 for the present choice of model parameters). As diffusivity increases beyond 2 × 10−12 cm2 s−1, the Damköhler number Da drops below 1, shifting the system from a diffusion- into a reaction-limited regime. As precursor-polymer reactions start to become the rate-limiting process, the slope of Cproduct/C0polymer no longer depends on the diffusivity but is determined by the reaction rate (see Fig. S10a, ESI†). Comparing the experimental results in Fig. 3a to the calculated normalized temporal uptake curves in Fig. 7 reveals similar trends. The increase in the slope of Cproduct/C0polymer with increasing ETPTA ratio seen in Fig. 3a can be qualitatively reproduced by varying the diffusivity from 10−14 to 10−12 cm2 s−1.
When hindering is introduced (dashed lines in Fig. 7), the formation of Cproduct is slowed down compared to the unhindered system because the re-supply with free precursor molecules from the surface is hampered since diffusing species move through the reaction-altered polymer layer with a lower diffusivity. While both unhindered and hindered uptake curves initially coincide, the hindered curve eventually deviates, exhibiting a slower uptake compared to the unhindered case. Consequently, these more hindered conditions produce mass uptake curves with two or more slopes apparent in the mass uptake process. Exactly how hindering affects the shape of the temporal uptake curves of Cproduct in Fig. 7 is discussed in more detail in the ESI,† in Section 2 in conjunction with the shapes of the uptake curves for Cfree. Similar changes in slope are observed in the experimental results for the cases of 0 and 10 wt% ETPTA (Fig. 3a), indicating that, at least for the copolymers with low flexibility, hindering plays a significant role. The uptake curves of some of the copolymers with higher ETPTA ratios also seem to exhibit two separate slopes, and hence an influence of hindering. However, more precise in situ measurements would be needed to clarify this, since the apparent change in slope could also be due to measurement errors.
Fig. 8 shows the spatiotemporal distributions calculated for each of the temporal uptake curves plotted in Fig. 7. For the low diffusivity (D = 10−14 cm2 s−1, Damköhler number Da = 200) and low hindering (K′C0polymer) in Fig. 8a, the depth profiles exhibit a shape characteristic of a diffusion-limited infiltration process. As the diffusivity increases and the Damköhler number decreases (Fig. 8c and e), not only does the speed at which the sigmoidal depth profile moves into the polymer layer increase, but the shape of the profile gradually flattens, as the system is pushed towards a more reaction-limited regime. A similar trend towards faster diffusion and flattened depth profiles can also be observed in the XPS data (Fig. 4) with increasing ETPTA ratios. While the depth profiles for 0, 10 and 75 wt% ETPTA resemble a diffusion-limited process whose diffusion rate, i.e., the speed at which the depth profile moves into the polymer, increases with ETPTA ratio, the depth profiles for 100 wt% ETPTA look flat and more characteristic of a reaction-limited process. Introducing hindering (right column in Fig. 8) slows down the infiltration process and pushes it towards a more diffusion-limited regime with increasing precursor exposure time. For very high hindering, diffusivity through reacted polymer regions approaches zero, corresponding to the formation of a barrier layer that prevents the system from ever reaching saturation, an effect that has also been demonstrated experimentally.11,19,30,65 Since hindering takes some time to come into effect, depth profiles at short exposure times are less influenced by the presence of hindering. This changes the spacing between the depth profiles compared to an unhindered case (e.g., compare Fig. 8a and b). A similar effect can be seen in the XPS depth profiles for 0 and 10 wt% ETPTA, where differences between the depth profiles are small up to DEZ exposure times of 15 h, but a large discrepancy is present in the profiles after 50 h, where the 10 wt% copolymer has almost reached saturation while for the 0 wt% copolymer, the Zn concentration drops to zero at approximately 50% polymer depth. This might indicate that hindering is significantly stronger in the 0 wt% polymer compared to the 10 wt% case.
Overall, these results demonstrate that it is possible to find a set of model parameters that are able to reproduce the main features and trends observed in the experimental data by varying only the diffusivity D and the degree of hindering K′C0polymer. The modelled results suggest that in moving from copolymers with a low fraction of ETPTA to ones with a high ETPTA ratio, the diffusivity gradually increases while the effect of hindering decreases. Based on the available data, it is not possible to fully deconvolute the contributions of diffusivity and hindering, as both parameters have similar effects, i.e., they influence the diffusion rate and the time required for the system to reach saturation. Based on the results in Fig. 2 that showed a linear increase of the thermal expansion coefficient and the film swelling in a solvent with ETPTA ratio, it is postulated that by incorporating the longer-chained ETPTA, an increase in polymer network flexibility and free volume is achieved. Since both the precursor diffusivity and the hindering degree depend on the polymer free volume, it is reasonable that the experimentally observed changes in infiltration kinetics result from changes in both parameters. Considering the time scales investigated in this study, it can be noted that all p(TMPTA–ETPTA) copolymers with ETPTA ratios ≥10 wt% reach saturation within the 50 h of DEZ exposure (though at different speeds), making them well-suited for VPI use. Only for the pTMPTA homopolymer, diffusivity seems to be so low and hindering so high that it only reaches partial infiltration after 50 h. The XRF results even suggest that the Zn loading saturates at a lower value. A reason for this behavior could be that for pTMPTA, the polymer flexibility and thus its free volume are so limited that precursor reactions result in the formation of a barrier layer that inhibits further precursor diffusion. However, adding only 10 wt% of long-chain ETPTA seems to be enough to increase the polymer free volume above the critical threshold that allows complete and uniform infiltration of the layer.
Note that although the experimentally observed trends can be consistently explained by a change in precursor diffusivity and hindering caused by variations in polymer flexibility and free volume, changes in precursor-polymer solubility (affecting the surface precursor concentration CS) or reactivity (affecting the reaction rate constant k) cannot be entirely ruled out as contributing factors. However, as Jean et al.38 have shown, the parameter CS mainly affects the speed at which saturation of the polymer layer is reached but is not able to shift the rate-controlling mechanism from diffusion- to reaction-limited, a transition observed with increasing ETPTA ratio in Fig. 4. Such a transition could be initiated by an increase in reaction rate (caused by a change in reaction mechanism), but since the FTIR spectra presented in Fig. 5 do not indicate a difference in reaction mechanism between the copolymer compositions, it is considered unlikely that the reaction rate constant varies strongly with the ETPTA ratio. Based on this reasoning, it is hypothesized that the observed trends in Fig. 3 and 4 are mainly effects of changes in precursor diffusivity and hindering originating from the variation in polymer flexibility and free volume.
Conclusions
This study explored the kinetics of vapor phase infiltration (VPI) of DEZ into a highly crosslinked polyacrylate system whose polymer network flexibility can be tuned by varying the ratio of the two comonomers trimethylolpropane triacrylate (TMPTA) and its ethoxylated counterpart, ethoxylated trimethylolpropane triacrylate (ETPTA). Thin films of polyacrylate networks with defined TMTPA:ETPTA ratios (150–250 nm thick) were successfully prepared by spin-coating, followed by UV polymerization. Both the linear coefficient of thermal expansion and the film swelling in a good solvent increased linearly with the ETPTA ratio, confirming enhanced flexibility in the polymer network.The infiltration behavior of these polyacrylate films was studied in detail by varying DEZ hold times from 30 min to 50 h and analyzing the Zn loading and chemistry of the resulting hybrid organic–inorganic materials. Increasing the ETPTA ratio, and thus enhancing polymer flexibility and free volume, increased VPI precursor diffusion rates into the polymer. While pTMPTA did not reach full saturation within the maximum DEZ hold time of 50 h examined within this study, adding 10 wt% of ETPTA proved enough to fully infiltrate the polyacrylate film within 50 h DEZ exposure. Further increasing the ETPTA ratio reduced the time required to achieve saturation down to approximately 30 min for pure pETPTA but did not significantly affect the saturation loading. Increasing the ETPTA ratio above 75 wt% also shifted the infiltration process from diffusion-limited to reaction-limited.
FTIR measurements confirmed the formation of Zn-polymer bonds upon infiltration with simultaneous consumption of C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O and C–O–C bonds of the polyacrylates, suggesting that DEZ reacts with the ester groups of p(TMPTA–ETPTA).
O and C–O–C bonds of the polyacrylates, suggesting that DEZ reacts with the ester groups of p(TMPTA–ETPTA).
Comparison of the experimental results with the reaction–diffusion transport model by Ren, McGuinness et al.34 showed that the observed trends with ETPTA ratio can be semi-qualitatively reproduced by varying only two model parameters: the precursor diffusion coefficient D and the hindering degree, both of which depend on the polymer free volume. This further validates the hypothesis that polymer network flexibility can be a key factor in designing VPI infiltration kinetics into crosslinked polyacrylate networks.
Author contributions
L. Demelius: conceptualization, methodology, investigation, formal analysis, writing – original draft, writing – review & editing, funding acquisition. A. M. Coclite: supervision, writing – review & editing, funding acquisition. M. D. Losego: resources, supervision, writing – review & editing, funding acquisition.Data availability
Data for this article, including raw experimental data and modelled data are available at Zenodo at https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.14204083.Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest to declare.Acknowledgements
This project has received funding from the European Union's Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreement no. 899349. L. D. acknowledges personal funding from the Austrian Marshall Plan Foundation for funding her research stay at Georgia Institute of Technology. A portion of this work was performed at the Georgia Tech Institute for Electronics and Nanotechnology, a member of the National Nanotechnology Coordinated Infrastructure (NNCI), which is supported by the National Science Foundation (ECCS-2025462). Additional financial support was also supplied by the U.S. National Science Foundation under DMREF-1921873. Some measurements were also completed in Georgia Tech's Materials Innovation and Learning Laboratory (The MILL), an open-access research space for materials science and engineering.References
- C. Sanchez, B. Julián, P. Belleville and M. Popall, Applications of hybrid organic–inorganic nanocomposites, J. Mater. Chem., 2005, 15, 3559 RSC.
- S. Chongdar, S. Bhattacharjee, P. Bhanja and A. Bhaumik, Porous organic–inorganic hybrid materials for catalysis, energy and environmental applications, Chem. Commun., 2022, 58, 3429–3460 RSC.
- Y. Zhao and K. Zhu, Organic–inorganic hybrid lead halide perovskites for optoelectronic and electronic applications, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2016, 45, 655–689 RSC.
- S. Wang, Y. Kang, L. Wang, H. Zhang, Y. Wang and Y. Wang, Organic/inorganic hybrid sensors: a review, Sens. Actuators, B, 2013, 182, 467–481 CrossRef CAS.
- P. Gómez-Romero, O. Ayyad, J. Suárez-Guevara and D. Muñoz-Rojas, Hybrid organic–inorganic materials: from child's play to energy applications, J. Solid State Electrochem., 2010, 14, 1939–1945 CrossRef.
- Z. Liang, R. Zhao, T. Qiu, R. Zou and Q. Xu, Metal-organic framework-derived materials for electrochemical energy applications, EnergyChem, 2019, 1, 100001 CrossRef.
- W. Park, H. Shin, B. Choi, W.-K. Rhim, K. Na and D. Keun Han, Advanced hybrid nanomaterials for biomedical applications, Prog. Mater. Sci., 2020, 114, 100686 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Marcelja, L. Demelius, T. A. Ali, M. Aghito, F. Muralter, G. H. Rodriguez, M. Kräuter, K. Unger, L. Wolfsberger and A. M. Coclite, Applications of soft biomaterials based on organic and hybrid thin films deposited from the vapor phase, J. Phys. Mater., 2023, 6, 042001 CrossRef CAS.
- V. P. Nguyen, J. Yoo, J. Y. Lee, J. J. Chung, J. H. Hwang, Y. Jung and S. M. Lee, Enhanced mechanical stability and biodegradability of Ti-infiltrated polylactide, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2020, 12, 43501–43512 CrossRef CAS.
- N. A. Vogel, P. S. Williams, A. H. Brozena, D. Sen, S. Atanasov, G. N. Parsons and S. A. Khan, Delayed Dissolution and Small Molecule Release from Atomic Layer Deposition Coated Electrospun Nanofibers, Adv. Mater. Interfaces, 2015, 2, 1500229 CrossRef.
- J. Pilz, A. M. Coclite and M. D. Losego, Vapor phase infiltration of zinc oxide into thin films of cis-polyisoprene rubber, Mater. Adv., 2020, 1, 1695–1704 RSC.
- M. Qiu, W. Du, X. Luo, S. Zhu, Y. Luo and J. Zhao, Vapor-Phase Molecular Doping in Covalent Organosiloxane Network Thin Films Via a Lewis Acid–Base Interaction for Enhanced Mechanical Properties, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2022, 14(20), 22719–22727 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S.-M. Lee, E. Pippel, O. Moutanabbir, I. Gunkel, T. Thurn-Albrecht and M. Knez, Improved Mechanical Stability of Dried Collagen Membrane after Metal Infiltration, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2010, 2, 2436–2441 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. P. Padbury and J. S. Jur, Systematic study of trimethyl aluminum infiltration in polyethylene terephthalate and its effect on the mechanical properties of polyethylene terephthalate fibers, J. Vac. Sci. Technol., A, 2015, 33, 01A112 CrossRef.
- L. E. Ocola, D. J. Gosztola, A. Yanguas-Gil, H.-S. Suh and A. Connolly, in Proceedings Quantum Sensing and Nano Electronics and Photonics XIII, ed. M. Razeghi, San Francisco, California, United States, 2016, vol. 9755, p. 97552C Search PubMed.
- A. Singhal, R. Divan, A. Dalmiya, L. Stan, A. Ghiacy, P. T. Lynch and I. Paprotny, Sequential infiltration of two-photon polymerized 3D photonic crystals for mid-IR spectroscopic applications, J. Vac. Sci. Technol., A, 2024, 42, 012404 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Yu, Z. Li, Y. Wang, S. Gong and X. Wang, Sequential Infiltration Synthesis of Doped Polymer Films with Tunable Electrical Properties for Efficient Triboelectric Nanogenerator Development, Adv. Mater., 2015, 27, 4938–4944 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Subramanian, N. Tiwale, K. Kisslinger and C. Nam, Reduced Stochastic Resistive Switching in Organic–Inorganic Hybrid Memristors by Vapor-Phase Infiltration, Adv. Electron. Mater., 2022, 8, 2200172 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Demelius, L. Zhang, A. M. Coclite and M. D. Losego, ZnO vapor phase infiltration into photo-patternable polyacrylate networks for the microfabrication of hybrid organic–inorganic structures, Mater. Adv., 2024, 5, 8464–8474 RSC.
- Z. Li, J. He, A. Subramanian, N. Tiwale, K. J. Dusoe, C.-Y. Nam, Y. Li and S.-W. Lee, Unraveling the ultrahigh modulus of resilience of Core–Shell SU-8 nanocomposite nanopillars fabricated by vapor-phase infiltration, Mater. Des., 2023, 227, 111770 CrossRef.
- A. Sinha, D. W. Hess and C. L. Henderson, Transport behavior of atomic layer deposition precursors through polymer masking layers: influence on area selective atomic layer deposition, J. Vac. Sci. Technol., B: Microelectron. Process. Phenom., 2007, 25, 1721–1728 CrossRef CAS.
- Q. Peng, Y.-C. Tseng, Y. Long, A. U. Mane, S. DiDona, S. B. Darling and J. W. Elam, Effect of Nanostructured Domains in Self-Assembled Block Copolymer Films on Sequential Infiltration Synthesis, Langmuir, 2017, 33, 13214–13223 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- E. Cianci, D. Nazzari, G. Seguini and M. Perego, Trimethylaluminum Diffusion in PMMA Thin Films during Sequential Infiltration Synthesis: In Situ Dynamic Spectroscopic Ellipsometric Investigation, Adv. Mater. Interfaces, 2018, 5, 1801016 CrossRef.
- F. E. Caligiore, D. Nazzari, E. Cianci, K. Sparnacci, M. Laus, M. Perego and G. Seguini, Effect of the Density of Reactive Sites in P(S-r-MMA) Film during Al2O3 Growth by Sequential Infiltration Synthesis, Adv. Mater. Interfaces, 2019, 6, 1900503 CrossRef.
- M. Biswas, J. A. Libera, S. B. Darling and J. W. Elam, Kinetics for the Sequential Infiltration Synthesis of Alumina in Poly(methyl methacrylate): An Infrared Spectroscopic Study, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2015, 119, 14585–14592 CrossRef CAS.
- R. Z. Waldman, D. Choudhury, D. J. Mandia, J. W. Elam, P. F. Nealey, A. B. F. Martinson and S. B. Darling, Sequential Infiltration Synthesis of Al2O3 in Polyethersulfone Membranes, JOM, 2019, 71, 212–223 CrossRef CAS.
- N. Sasao, S. Sugimura and K. Asakawa, Metal diffusion model in polymer matrices in vapor phase infiltration, Jpn. J. Appl. Phys., 2021, 60, SCCC04 CrossRef CAS.
- R. Z. Waldman, N. Jeon, D. J. Mandia, O. Heinonen, S. B. Darling and A. B. F. Martinson, Sequential Infiltration Synthesis of Electronic Materials: Group 13 Oxides via Metal Alkyl Precursors, Chem. Mater., 2019, 31, 5274–5285 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Sun, R. P. Padbury, H. I. Akyildiz, M. P. Goertz, J. A. Palmer and J. S. Jur, Influence of Subsurface Hybrid Material Growth on the Mechanical Properties of Atomic Layer Deposited Thin Films on Polymers, Chem. Vap. Deposition, 2013, 19, 134–141 CrossRef CAS.
- R. P. Padbury and J. S. Jur, Temperature-Dependent Infiltration of Polymers during Sequential Exposures to Trimethylaluminum, Langmuir, 2014, 30, 9228–9238 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Z. Leng and M. D. Losego, A physiochemical processing kinetics model for the vapor phase infiltration of polymers: measuring the energetics of precursor-polymer sorption, diffusion, and reaction, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2018, 20, 21506–21514 RSC.
- M. Biswas, J. A. Libera, S. B. Darling and J. W. Elam, New insight into the mechanism of sequential infiltration synthesis from infrared spectroscopy, Chem. Mater., 2014, 26, 6135–6141 CrossRef CAS.
- G. T. Hill, D. T. Lee, P. S. Williams, C. D. Needham, E. C. Dandley, C. J. Oldham and G. N. Parsons, Insight on the Sequential Vapor Infiltration Mechanisms of Trimethylaluminum with Poly(methyl methacrylate), Poly(vinylpyrrolidone), and Poly(acrylic acid), J. Phys. Chem. C, 2019, 123, 16146–16152 CrossRef CAS.
- E. C. Dandley, C. D. Needham, P. S. Williams, A. H. Brozena, C. J. Oldham and G. N. Parsons, Temperature-dependent reaction between trimethylaluminum and poly(methyl methacrylate) during sequential vapor infiltration: experimental and ab initio analysis, J. Mater. Chem. C, 2014, 2, 9416–9424 RSC.
- S. Obuchovsky, H. Frankenstein, J. Vinokur, A. K. Hailey, Y. L. Loo and G. L. Frey, Mechanism of Metal Oxide Deposition from Atomic Layer Deposition inside Nonreactive Polymer Matrices: Effects of Polymer Crystallinity and Temperature, Chem. Mater., 2016, 28, 2668–2676 CrossRef CAS.
- R. P. Padbury and J. S. Jur, Effect of polymer microstructure on the nucleation behavior of alumina via atomic layer deposition, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2014, 118, 18805–18813 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Ren, E. K. McGuinness, C. Huang, V. R. Joseph, R. P. Lively and M. D. Losego, Reaction–diffusion transport model to predict precursor uptake and spatial distribution in vapor-phase infiltration processes, Chem. Mater., 2021, 33, 5210–5222 CrossRef CAS.
- B. C. Jean, Y. Ren, E. K. McGuinness, R. P. Lively and M. D. Losego, Effects of trimethylaluminum vapor pressure and exposure time on inorganic loading in vapor phase infiltrated PIM-1 polymer membranes, Mater. Chem. Phys., 2022, 290, 126577 CrossRef CAS.
- S. A. Balogun, Y. Ren, R. P. Lively and M. D. Losego, Interpreting inorganic compositional depth profiles to understand the rate-limiting step in vapor phase infiltration processes, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2023, 25, 14064–14073 RSC.
- E. K. McGuinness, F. Zhang, Y. Ma, R. P. Lively and M. D. Losego, Vapor Phase Infiltration of Metal Oxides into Nanoporous Polymers for Organic Solvent Separation Membranes, Chem. Mater., 2019, 31, 5509–5518 CrossRef CAS.
- B. D. Piercy and M. D. Losego, Tree-based control software for multilevel sequencing in thin film deposition applications, J. Vac. Sci. Technol., B: Nanotechnol. Microelectron.: Mater., Process., Meas., Phenom., 2015, 33, 043201 Search PubMed.
- M. Tazreiter, P. Christian, R. Schennach, T. Grießer and A. M. Coclite, Simple method for the quantitative analysis of thin copolymer films on substrates by infrared spectroscopy using direct calibration, Anal. Methods, 2017, 9, 5266–5273 RSC.
- H. Kaczmarek and I. Vukovic-Kwiatkowska, Preparation and characterization of interpenetrating networks based on polyacrylates and poly(lactic acid), eXPRESS Polym. Lett., 2012, 6, 78–94 CrossRef CAS.
- B. C. Smith, Infrared Spectroscopy of Polymers X: Polyacrylates, Spectroscopy, 2023, 10–14 Search PubMed.
- O. Chiantore, L. Trossarelli and M. Lazzari, Photooxidative degradation of acrylic and methacrylic polymers, Polymer, 2000, 41, 1657–1668 CrossRef CAS.
- G. G. Goourey, P. Wong-Wah-Chung, F. Delor-Jestin, B. Légeret, L. Balan and Y. Israëli, Photostability of acrylate photopolymers used as components in recording materials, Polym. Degrad. Stab., 2015, 119, 208–216 CrossRef CAS.
- J. M. Chalmers, in Encyclopedia of Analytical Chemistry, ed. R. A. Meyers, Wiley, 1st edn, 2000 Search PubMed.
- A. H. Soeriyadi, V. Trouillet, F. Bennet, M. Bruns, M. R. Whittaker, C. Boyer, P. J. Barker, T. P. Davis and C. Barner-Kowollik, A detailed surface analytical study of degradation processes in (meth)acrylic polymers, J. Polym. Sci., Part A: Polym. Chem., 2012, 50, 1801–1811 CrossRef CAS.
- G. P. López, D. G. Castner and B. D. Ratner, XPS O 1s binding energies for polymers containing hydroxyl, ether, ketone and ester groups, Surf. Interface Anal., 1991, 17, 267–272 CrossRef.
- H. Kaczmarek and H. Chaberska, AFM and XPS study of UV-irradiated poly(methyl methacrylate) films on glass and aluminum support, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2009, 255, 6729–6735 CrossRef CAS.
- C. De Marco, S. M. Eaton, R. Suriano, S. Turri, M. Levi, R. Ramponi, G. Cerullo and R. Osellame, Surface Properties of Femtosecond Laser Ablated PMMA, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2010, 2, 2377–2384 CrossRef CAS.
- O. Kahle, U. Wielsch, H. Metzner, J. Bauer, C. Uhlig and C. Zawatzki, Glass transition temperature and thermal expansion behaviour of polymer films investigated by variable temperature spectroscopic ellipsometry, Thin Solid Films, 1998, 313–314, 803–807 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Singh, P. J. Ludovice and C. L. Henderson, Influence of molecular weight and film thickness on the glass transition temperature and coefficient of thermal expansion of supported ultrathin polymer films, Thin Solid Films, 2004, 449, 231–241 CrossRef CAS.
- N. Grassie and J. D. Fortune, Thermal degradation of copolymers of methyl methacrylate and butyl acrylate, 3. Residual polymer, Makromol. Chem., 1973, 168, 13–18 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. J. Hofstetter and Y. Vaynzof, Quantifying the Damage Induced by X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy Depth Profiling of Organic Conjugated Polymers, ACS Appl. Polym. Mater., 2019, 1, 1372–1381 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Miyayama, N. Sanada, S. R. Bryan, J. S. Hammond and M. Suzuki, Removal of Ar+ beam-induced damaged layers from polyimide surfaces with argon gas cluster ion beams, Surf. Interface Anal., 2010, 42, 1453–1457 CrossRef CAS.
- D. E. Newbury and N. W. M. Ritchie, Is Scanning Electron Microscopy/Energy Dispersive X-ray Spectrometry (SEM/EDS) Quantitative?, Scanning, 2013, 35, 141–168 CrossRef CAS.
- E. K. McGuinness, C. Z. Leng and M. D. Losego, Increased Chemical Stability of Vapor-Phase Infiltrated AlOx–Poly(methyl methacrylate) Hybrid Materials, ACS Appl. Polym. Mater., 2020, 2, 1335–1344 CrossRef CAS.
- W. Xie, S. Khan, O. J. Rojas and G. N. Parsons, Control of Micro- and Mesopores in Carbon Nanofibers and Hollow Carbon Nanofibers Derived from Cellulose Diacetate via Vapor Phase Infiltration of Diethyl Zinc, ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng., 2018, 6, 13844–13853 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Mameli, B. Karasulu, M. A. Verheijen, B. Barcones, B. Macco, A. J. M. Mackus, W. M. M. E. Kessels and F. Roozeboom, Area-Selective Atomic Layer Deposition of ZnO by Area Activation Using Electron Beam-Induced Deposition, Chem. Mater., 2019, 31, 1250–1257 CrossRef CAS.
- B. Gong, Q. Peng, J. S. Jur, C. K. Devine, K. Lee and G. N. Parsons, Sequential vapor infiltration of metal oxides into sacrificial polyester fibers: shape replication and controlled porosity of microporous/mesoporous oxide monoliths, Chem. Mater., 2011, 23, 3476–3485 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Ko, A. Kirakosyan, H.-U. Kim, H. Seok, J. Choi and N. Jeon, A New Nanoparticle Heterostructure Strategy with Highly Tunable Morphology via Sequential Infiltration Synthesis, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2022, 593, 153387 CrossRef CAS.
- B. Gong and G. N. Parsons, Quantitative in situ infrared analysis of reactions between trimethylaluminum and polymers during Al2O3 atomic layer deposition, J. Mater. Chem., 2012, 22, 15672–15682 RSC.
- A. Motta, G. Seguini, C. Wiemer and M. Perego, Sequential Infiltration Synthesis of Al2O3 in PMMA Thin Films: Temperature Investigation by Operando Spectroscopic Ellipsometry, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2024, 16(27), 35825–35833 CrossRef CAS.
- J. T. Bamford, R. A. Smith, C. Z. Leng, W. R. Gutekunst and M. D. Losego, Measuring the Glass Transition Temperature of Vapor-Phase-Infiltrated AlOx-PS-r-PHEMA Organic–Inorganic Hybrid Thin-Film Materials, Macromolecules, 2021, 54, 6790–6798 CrossRef CAS.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available. See DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/d4cp02864c |
| This journal is © the Owner Societies 2025 |